
by Sheila Dunning | Mar 20, 2017
 Now is the time to prevent your azaleas from being attacked by lace bugs. The azalea lace bug, Stephanitis pyrioides, overwinters as eggs on the underside of infested leaves. Eggs hatch in late March and early April. The insect then passes through five nymphal instars before becoming an adult. It takes approximately one month for the insect to complete development from egg to adult and there are at least four generations per year. Valuable plants that are susceptible to lace bug damage should be inspected in the early spring for the presence of overwintering lace bug adults, eggs and newly hatched nymphs. Inspect these plants every two weeks during the growing season for developing lace bug infestations.
Now is the time to prevent your azaleas from being attacked by lace bugs. The azalea lace bug, Stephanitis pyrioides, overwinters as eggs on the underside of infested leaves. Eggs hatch in late March and early April. The insect then passes through five nymphal instars before becoming an adult. It takes approximately one month for the insect to complete development from egg to adult and there are at least four generations per year. Valuable plants that are susceptible to lace bug damage should be inspected in the early spring for the presence of overwintering lace bug adults, eggs and newly hatched nymphs. Inspect these plants every two weeks during the growing season for developing lace bug infestations.
Both adults and nymphs have piercing-sucking mouthparts and remove sap as they feed from the underside of the leaf. Lace bug damage to the foliage detracts greatly from the plants’ beauty, reduces the plants’ ability to produce food, decreases plant vigor and causes the plant to be more susceptible to damage by other insects, diseases or unfavorable weather conditions. The azalea can become almost silver or bleached in appearance from the feeding lace bug damage.
 However, lace bugs often go undetected until the infested plants show severe damage sometime into the summer. By then several generations of lace bugs have been weakening the plant. Inspecting early in the spring and simply washing them off the underside of the leaves can help to avoid damage later and the need for pesticides.
However, lace bugs often go undetected until the infested plants show severe damage sometime into the summer. By then several generations of lace bugs have been weakening the plant. Inspecting early in the spring and simply washing them off the underside of the leaves can help to avoid damage later and the need for pesticides.
Adult lace bugs are flattened and rectangular in shape measuring 1/8 to 1/4 inch long. The area behind the head and the wing covers form a broadened, lace-like body covering. The wings are light amber to transparent in color. Lace bugs leave behind spiny black spots of frass (excrement).
Lace bug nymphs are flat and oval in shape with spines projecting from their bodies in all directions. A lace bug nymph goes through five growth stages (instars) before becoming an adult. At each stage the nymph sheds its skin (molts) and these old skins often remain attached to the lower surface of infested leaves.
Azalea lace bug eggs are football-shaped and are transparent to cream-colored. Lace bug eggs are found on the lower leaf surface, usually alongside or inserted into a leaf vein. Adult females secrete a varnish-like substance over the eggs that hardens into a scab-like protective covering.
For more information go to: http://entomology.ifas.ufl.edu/creatures/orn/shrubs/azalea_lace_bug.htm

by Ray Bodrey | Mar 20, 2017

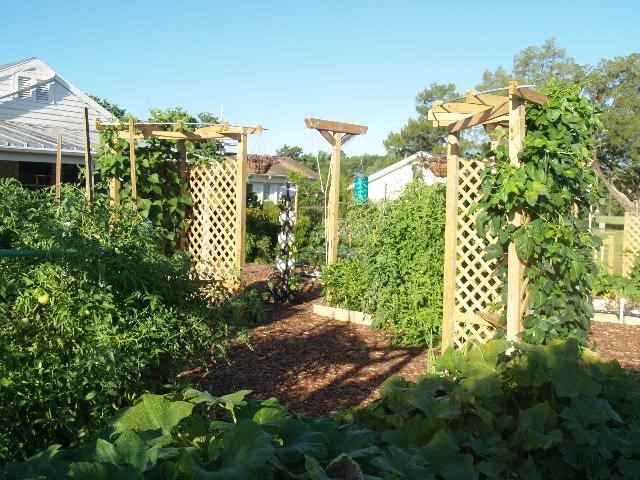
Figure 1: Edible Landscaping.
Credit: Dr. Gail Hansen, Environmental Horticulture-UF/IFAS
Edible landscaping has become a trend for many gardening enthusiasts. A combination of edible plants along with traditional ornamentals can create an artful presentation. There are some challenges when designing such a landscape, but in those challenges opportunities’ may be found. One of the most difficult challenges is making sure your garden or landscape is healthy and vibrant year-round since many edibles are short-lived annuals. These include plants such as eggplant, pepper, lettuce, artichoke and some annual herbs. There is a solution to this concern. First, know your edible plant’s propagation and maturity months. This way you can offset plantings to ensure color in your landscape. Another key measure is to mix some evergreen ornamentals in with short season edibles and long season edibles. Examples of long season edibles include berry shrubs, fruit trees and biennial or perennial herbs.
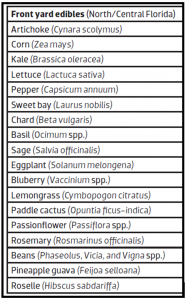
Table 1: North/Central Florida Front Yard Edibles.
Credit: Dr. Gail Hansen, Environmental Horticulture-UF/IFAS.
When designing your edible landscape, think about style and theme to help guide you through the process. A formal design has more straight edges and geometric shapes, whereas the more natural approach has meandering edges and irregular shapes. A color scheme in harmony is very important. Remember, an edible landscape should not just be a production food garden but a visual treat. The goal is not to grow a high yield garden, but only to produce supplemental edibles to make the endeavor worthwhile.
Dr. Gail Hansen, Associate Professor of Environmental Horticulture at the University of Florida, has developed twelve ideas when creating an edible landscape:
- Combine reliable, low-maintenance ornamental with edible plants. Use evergreen ornamentals to maintain enough green structure, so that potential cool season bare spots are not visual.
- Use support structures for an artistic effect and to assist in growth of some plants. Trellises, arbors and even tomato cages are some examples that can be used.
- Use containers in areas to keep the landscape more organized. Planters will also help in maintenance, as plants will be easier to reach and the soil will be easier to manage.
- Create some hard edges in your landscape. Raised beds, garden walls and borders will give defining lines to the landscape and promote a clean appearance.
- A pathway through the landscape will both provide an access to plants and give an inviting appeal. Brick pavers, gravel and mulch are good examples of pathway material.
- Remember color is key. Create a visually pleasing combination of plant color, form, texture and sizes.
- Always start by keeping it simple. So, start small and simple. Then, you can begin filling in the landscape.
- Look for one unique feature to create an added interest to you landscape and provide growth to plants. This could be a shade house for ferns and other hanging baskets or a hay bale, where lettuce, tomatoes or peppers could grow upon.
- Select appealing and easy to grow plants that you want to eat!
- Let plants reach maturity before taking them out of the landscape. For example, rainbow chard will grow larger, if allowed to continue to grow after seed has been produced.
- Use the Florida-Friendly Landscaping principle, “Right Plant, Right Place”, when adding edibles to your landscape. Match the growing needs with the most suitable location.
- Consider your location and layout for irrigation. All plants need some degree of water. An above ground drip irrigation system is usually the most flexible and adjustable irrigation method in regards to overall plant watering needs in a landscape.
Following Dr. Hansen’s ideas will help you create the edible landscape of your dreams. For more information on edible landscaping, please contact your local county extension office for more details.
Supporting information for this article can be found in the UF/IFAS EDIS Publications, “Landscape Design with Edibles” by Dr. Gail Hansen: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/EP/EP47500.pdf
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Les Harrison | Mar 11, 2017
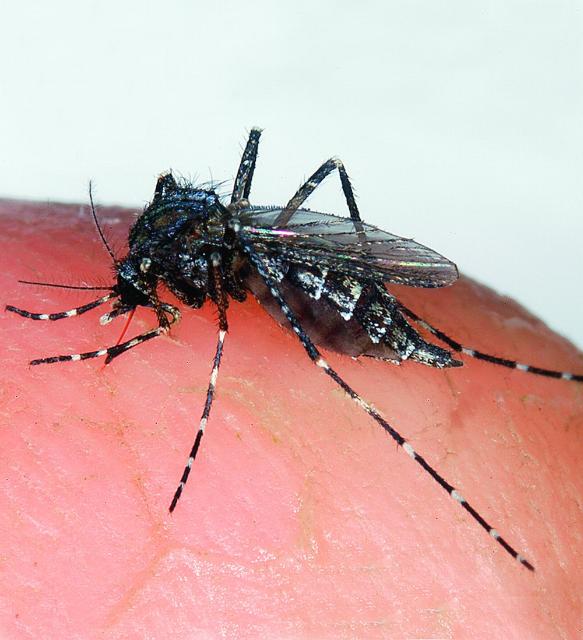
 It is an often made wish of summer that the cold weather of winter will kill all the mosquitoes, gnats and no-see-ums. This climactic fete would spare people, pets and livestock the irritation of encountering these low flying pest and their predatory behavior.
It is an often made wish of summer that the cold weather of winter will kill all the mosquitoes, gnats and no-see-ums. This climactic fete would spare people, pets and livestock the irritation of encountering these low flying pest and their predatory behavior.
Unfortunately, the thermometer would have to drop to levels approaching the surface temperature of the planet Neptune to eliminate these winged annoyances.
There are individual steps which will help minimize the potential for exposure to exotic diseases.
Check surroundings for standing water, especially in secluded spots or small quantities. The home landscape and patio garden can produce hundreds, if not thousands, of hungry mosquitos during the summer if standing water is left for long.
Trays and dishes under flower pots commonly collect water which is usually left to evaporate or be absorbed by the plant over time. To mama mosquito this shallow and protected source is an ideal location to deposit eggs for the next generation of voracious airborne insects.
Plants with natural depressions or “cups” can accumulate enough irrigation and rain water to establish an effective mosquito nursery. Even though it may evaporate, these tiny pools will last long enough to hatch many mosquito larvae into potential disease vectors.
Back porch bromeliads can easily deliver this undesirable outcome. So too can mature live oak trees which commonly have hollow spaces between large branches.
Even a wheelbarrow left to the elements can serve as a portable pond to maternity minded mosquitos. Dumping the water on a frequent basis is the easiest method, but there are also larvae-cides which are effective in difficult to dump reservoirs.
Protective clothing when outdoors is useful to reduce exposed skin which mosquitos view as an excellent dining site. Heavier fabrics and loose-fitting designs provide the best protection while maintaining maximum comfort for the wearer.
Minimizing exposure at dusk and dawn, when native mosquitos are most active, will reduce the probability of serving as an unsuspecting blood meal for a swarm or lone hunter. Unfortunately, some of the exotic mosquitos are prowling 24 hours a day and are pleased to attack at any opportunity.
As the weather warms, be ready for mosquito season. This past winter only whetted their appetite.

by Blake Thaxton | Mar 9, 2017

UF/IFAS File Photo
Lawns in northwest Florida are really starting to get going early this year. It is early March but feels much later in the year and many feel behind on their lawn maintenance and various other landscape chores. Maybe it is time to think about hiring a lawn maintenance company to do the job for you. Keep in mind a few tips while trying to decide which company you will hire.
- Lawn Maintenance and Landscape companies are NOT required to have a “professional license” in order to operate their business. This means anyone can start a lawn maintenance company whether they have experience or not. All it takes is a quick visit to the tax collectors office to get a tax receipt. This fact should make you want to go the extra mile to be sure you receive excellent service.

Photo Credits: UF/IFAS File Photo
- Make sure the company chosen has the proper amount of liability insurance.
- There are licenses required for specific services, such as applying fertilizers or pesticides. Check with the company to be sure that the pesticide or fertilizer applicator will be properly licensed to do the job required. Here is a list of licenses to be aware of while choosing a lawn service:
- Receive several quotes from different companies to compare pricing structures and rates. Ask for a very detailed quote. Communicate your needs accurately. Some companies will be better suited for a simple “mow and blow” job while others specialize in a full service job.
- Interview the company and be sure they follow University of Florida recommended mowing heights, fertilization rates, etc.* Quiz them on the subject to be sure they are familiar with properly maintaining landscapes.
There are a lot of really good Landscape and Lawn Maintenance professionals working in Northwest Florida. If you take some time while searching you will find a really good company who can help with beautifying your lawn and landscape.
*Call your local extension office to get the recommended mowing heights, fertilization rates, etc.

by Mary Salinas | Mar 9, 2017

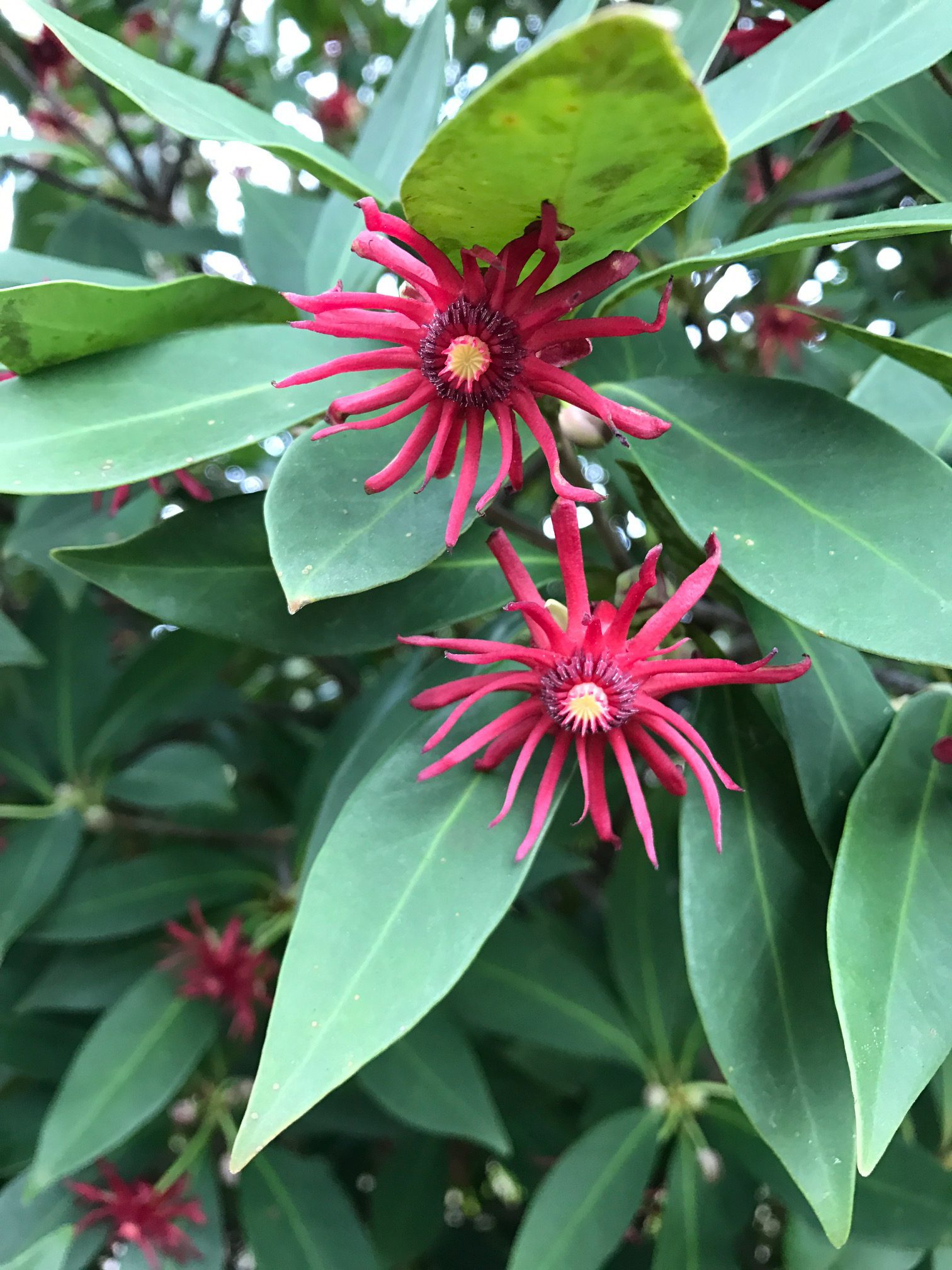
Dark red flowers of Florida red anise arrive in the springtime. Photo credit: Mary Derrick, UF/IFAS Extension.
Springtime brings small but very pretty red blooms on an outstanding native shrub/small tree, Florida red anise (Illicium floridanum). It occurs naturally in the wild in the central and western panhandle of Florida and west along the gulf coast into Louisiana. Its natural environment is in the understory along streams and in rich, wooded areas.
This is a great shrub for a part shade to shady and moist area in your landscape. The dense foliage, dark green leaves and the fact that it is evergreen all year makes it a great choice for an informal hedge. Plan for it to grow to a maximum height of 12 to 15 feet.

Dense growth habit of Florida red anise. Photo credit: Mary Derrick, UF/IFAS Extension.
The leaves have a licorice-like aroma when crushed but this is NOT the species that gives us the edible culinary anise. Maybe it is that aroma that makes this a relatively pest-free plant!
Yellow anise (Illicium parviflorum) is a very similar native shrub but has small yellow flowers and adapts better to a drier environment. The native range of the yellow anise is north central Florida.

 Now is the time to prevent your azaleas from being attacked by lace bugs. The azalea lace bug, Stephanitis pyrioides, overwinters as eggs on the underside of infested leaves. Eggs hatch in late March and early April. The insect then passes through five nymphal instars before becoming an adult. It takes approximately one month for the insect to complete development from egg to adult and there are at least four generations per year. Valuable plants that are susceptible to lace bug damage should be inspected in the early spring for the presence of overwintering lace bug adults, eggs and newly hatched nymphs. Inspect these plants every two weeks during the growing season for developing lace bug infestations.
Now is the time to prevent your azaleas from being attacked by lace bugs. The azalea lace bug, Stephanitis pyrioides, overwinters as eggs on the underside of infested leaves. Eggs hatch in late March and early April. The insect then passes through five nymphal instars before becoming an adult. It takes approximately one month for the insect to complete development from egg to adult and there are at least four generations per year. Valuable plants that are susceptible to lace bug damage should be inspected in the early spring for the presence of overwintering lace bug adults, eggs and newly hatched nymphs. Inspect these plants every two weeks during the growing season for developing lace bug infestations.
 However, lace bugs often go undetected until the infested plants show severe damage sometime into the summer. By then several generations of lace bugs have been weakening the plant. Inspecting early in the spring and simply washing them off the underside of the leaves can help to avoid damage later and the need for pesticides.
However, lace bugs often go undetected until the infested plants show severe damage sometime into the summer. By then several generations of lace bugs have been weakening the plant. Inspecting early in the spring and simply washing them off the underside of the leaves can help to avoid damage later and the need for pesticides.










