
by Carrie Stevenson | Jul 31, 2020

A living shoreline project was implemented on this bay in Santa Rosa County to try and prevent further erosion. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
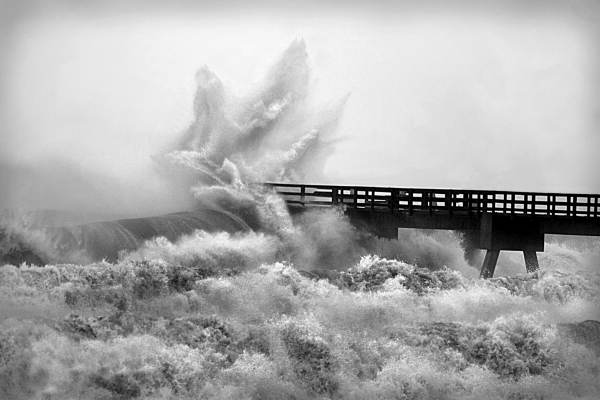
We have reached that time of year when the Atlantic starts cranking out storms, and they will continue to roll out as the dog days of summer progress. Over the last decade, many experts have speculated on how climate change and sea level rise might impact hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico. Two big issues are coastal erosion and flooding from storm surge and rainfall.
Those who live on the water or frequently visit area shorelines have probably noticed coastal erosion. While a natural part of a coastal ecosystem–and often exacerbated by heavy boat traffic–rising seas can also cause erosion. Sea level rise moves water slowly inland and washes away the roots of grasses and trees that once held the shoreline in place. Buildings and roads close to the water are impacted as well, with “sunny day flooding” on the roads and under pilings in many south Florida cities where water has moved in to stay. Large scale beach renourishment projects, living shorelines, and even road relocations (like the one at Ft. Pickens on Pensacola Beach) are all ways that local officials and property owners can respond to rising seas. However, these efforts always come with a big price tag. When that “line in the sand” is drawn beyond government and household budgets, there will come a point when we can no longer support protection of highly vulnerable coastal infrastructure. The closer a building is physically located to the water (whether built there intentionally or reached by rising seas), the greater the likelihood a hurricane will cause flooding damage from dangerous storm surge. Storm surge and heavy flooding cause 75% of the deaths in any given hurricane.
During a recent webinar, the appropriately named Dr. Chris Landsea of the National Hurricane Center answered several frequently asked questions on the impacts of global warming on hurricanes. Some of the predictions are surprising based on assumptions that have been put out in the media. He made a disclaimer that these are his predictions based on years of expertise and data analysis, and not an official proclamation by the National Hurricane Center. Following are a few of the points he made during his talk.

Dr. Chris Landsea of the National Hurricane Center recently met with floodplain managers around the Gulf Coast to discuss hurricanes.
Question: Will hurricanes get stronger based on increased temperatures?
Answer: The world average temperature has gone up 1.5 degrees Fahrenheit in the past 100 years. Based on data and computer modeling from the NOAA Geophysics Lab, typical hurricane wind intensity will increase slightly, by 3%. In this example, a storm with 100 mph average winds would be 103 mph by the end of the 21st century.
Question: Will we experience more tropical storms as the climate changes?
Answer: Dr. Landsea does not expect more tropical storms as the temperature increases. In fact, frequency may drop very slightly. While there may be more heat energy for hurricanes to feed on, the surrounding conditions will make it tougher for a storm to form. Those conditions may be atmospheric or include a vertical wind shear that tears up the storm.
Question: How will global warming affect rainfall during hurricanes?
Answer: Models and recent experience show that rainfall will increase by 10-20% during tropical storms. Global warming increases the amount of moisture in the atmosphere, and a hurricane can recycle this water into a constant loop of rainfall. Hurricane Harvey in Texas was one example of this situation, during which nearly 8 feet of rainfall fell, flooding neighborhoods. One of the aphorisms of climate change is “wet places get wetter, and dry places get drier.”
Dr. Landsea’s full presentation can be found online here, if you are interested in learning more. Keep in mind that these predictions can change based on land use, atmospheric carbon levels, and human practice change. For more on the work UF IFAS is doing on climate, visit this Florida Sea Grant Climate page.

by Rick O'Connor | Sep 23, 2015

This area along Florida’s east coast is experiencing coastal flooding.
Photo: University of Florida
As we come towards the end of National Estuaries Week we will now look at some issues our estuaries are facing. Sea level rise is one that generates a variety of responses from the public. For some it is of concern, something we need to be planning for and need to spend more research dollars on to improve our models to understand it. For others, it is a problem for the back burner; yea, it is happening but the changes are over a long period of time and the serious impacts will not occur for a while – and we have more pressing issues to deal with. The old “it’s not a problem until it’s a problem” form of planning. Others still understand it but do not believe the models and do not believe the impacts will be very serious – thus warrants little or no planning. And there are those who do not believe climate change and sea level rise is actually occurring. They see no tangible evidence of any changes. Each year feels like the last – it just is not happening.
A couple of years ago I was part of a team that conducted a series of focus group meetings with residents and businesses who live and work on our barrier islands. The focus of the discussion was to determine what the coastal residents were most concerned about in terms of climate change, sea level rise, and coastal resiliency. The majority of the participants did not deny climate change but were not concerned about planning for it at this time; they had other issues were more pressing… like coastal flooding and the national flood insurance plan – which plans to increase rates for properties in flood prone areas. Ironically, this issue is tied to climate change and sea level rise. They were more concerned about it than they realized. And we did have a few who asked the question – “is there any science that supports the notion of climate change?” Let’s start there… is there any science to support this?
Yes… this link to NASA (http://climate.nasa.gov/evidence/) is a page developed to help the public better understand what the science says about this. Yes, there is evidence that the carbon is increasing in our atmosphere, that global temperatures are rising, as are sea levels. Many are experiencing some of the changes that were discussed in the 1980’s. Some areas are seeing more rain, others more drought. Gardeners in parts of the country are noticing that things they use to do in April, they now do in March. More tropical plants and animals are migrating north – there are at least three records of red and black mangroves growing the Florida panhandle and a snook was caught a couple of years ago at Dauphin Island, Alabama. These subtle changes have been noticed by some. Others, such as those in southeast Florida, have witnessed more direct evidence, such as portions of A1A going underwater during extreme high tides. But there is science to support this.

Islands in the south Pacific who are dealing with the impacts of sea level rise during storm events.
Photo: Greenpeace
What is causing sea level rise?
Well, according to a document published by Florida Sea Grant there are three general causes.
- Temperature – as the atmosphere and oceans warm the water expands thus causing the sea level to rise. This thermal expansion has accounted for about 25% of the sea level rise we have witnessed; between 1993 and 2010 it accounted for 40% of it.
- Ice melt – 60% of the current rise in sea level has been due to the melting of land based ice; such as glaciers.
- Land fall – for a variety of reasons, some coastal land masses have actually dropped; thus forcing the sea level to rise.
What do the current models predict for future sea level rise?
Most of the models are predicting an increase between 1.5 and 4.5 feet, depending on where you are, by 2100.
So what?
Again some coastal communities are experiencing impacts now. South Florida Water Management District is currently replacing all of their gravity flow drains due to the fact that sea level has risen enough that they only work at low tide. Monroe County (Florida Keys) is now replacing their vehicles at a faster rate due to constant driving through salty flood waters. Many Florida coastlines are now experiencing saltwater intrusion of their freshwater supply. This is partially due to the over consumption of that resource but it is also due to sea level rising introducing salt water to these systems. There has been increased flooding in many parts of the country, including the Florida Panhandle.
So what does this mean for our local estuaries?
As we have said, sea level rise has occurred before – will this be a problem for our estuarine habitats? Generally ecosystems adjust to environmental change over time but they cannot respond if these changes occur too fast. Scientists have determined that an increase of 0.13” of sea level/year will flood our coastal marshes and we may lose them; currently the rate is about 0.11”/year. It is believed that our barrier islands will “roll” landward but science is not sure how fast this will happen. There may be changes in species composition within our estuaries – which could be good or bad – and there is certainly room for the expansion of invasive species.
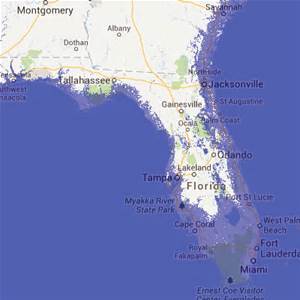
A graphic indicating the potential flooding of Florida.
Graphic: Green Policy 360
How has government responded?
Federal and county governments have responded – the state… not so much. According to Thomas Ruppert (Florida Sea Grant) the local governments have done the best job planning for these future changes. Many areas in the state now require some form of sea level rise planning in all new development projects. At the very least coastal communities should look at future development plans and think long term as to where flooding may become a bigger issue.
“The times they are a changing…”







