Northwest Florida experienced record-setting floods this spring, and many landscapes, roads, and buildings suffered serious damage due to the sheer force of water moving downhill. That being said, we are just entering our summer “rainy season,” so it may be wise to spend extra time thinking about how you want to landscape based on our typically heavy annual rainfall. For example, if you have an area in your yard where water always runs after a storm (even a mild one) and washes out your property, you may want to consider a rain garden for that spot.
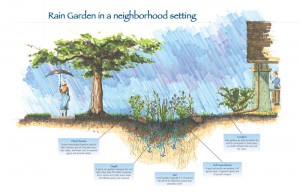
Rain gardens work similarly to swales and stormwater retention ponds in that they are designed to temporarily hold rainwater and allow it to soak into the ground. However, they are quite different aesthetically, because they are planted with water-tolerant trees, shrubs, groundcovers and flowers to provide an attractive alternative to the eroding gully that once inhabited the area! Rain gardens are not “created wetlands,” but landscaped beds that can handle both wet and drier soil. Many of the plants best suited for rain gardens are also attractive to wildlife, adding another element of beauty to the landscape.
A perfect spot for a rain garden might be downhill from a rain gutter, areas notorious for excess water and erosion. To build a rain garden, the rainwater leaving a particular part of the property (or rooftop), is directed into a gently sloping, 4”-8” deep depression in the ground, the back and sides of which are supported by a berm of earth. The rain garden serves as a catch basin for the water and is usually shaped like a semi-circle. The width of the rain garden depends on the slope and particular site conditions in each yard. Within the area, native plants are placed into loose, sandy soil and mulched. Care should be taken to prevent the garden from having a very deep end where water pools, rather allowing water to spread evenly throughout the basin.
Besides reducing a problematic area of the lawn, a rain garden can play an important role in improving water quality. With increasing populations come more pavement, roads, and rooftops, which do almost nothing to absorb or treat stormwater, contributing to the problem. Vegetation and soil do a much better job at handling that water. Excess sediment, which can fill in streams and bays, and chemicals from fertilizers and pesticides are just some of the pollutants treated within a rain garden via the natural growth processes of the plants. Many commercial properties are considering rain gardens, also known as “bioretention” as more attractive alternatives to stormwater retention ponds.

The North Carolina Arboretum used a planted bioretention area to manage stormwater in their parking lot. Photo courtesy Carrie Stevenson
A handful of well-known perennial plants that work great in rain gardens include: Louisiana iris, cinnamon fern, buttonbush, Virginia willow, black-eyed Susan, swamp lily, tulip poplar, oakleaf hydrangea, wax myrtle, Florida azalea, river birch, holly, and Southern magnolia. For a complete list of rain garden plants appropriate for our area, visit the “Rain Garden” section of Tallahassee’s “Think about Personal Pollution” website, tappwater.org or contact your local Extension Office.
- The Praying Mantis - June 20, 2025
- Bluebirds in Florida - May 8, 2025
- The Brahminy Blind Snake - April 10, 2025