
by Molly Jameson | Oct 28, 2021

As you garden this fall, check out the North Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide, compiled by UF/IFAS Leon County Extension.
Getting into vegetable gardening, but don’t know where to start?
Even experienced gardeners know there’s always more to learn. To help both beginners and advanced gardeners find answers to their questions, the UF/IFAS Leon County Extension Office put together the North Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide. It incorporates multiple resources, including articles, planting calendars, photos, and UF/IFAS EDIS publications.
The North Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide covers the many aspects of vegetable gardening, including how to get started, site selection, insects and biodiversity in the garden, soil testing, composting, cover crops in the garden, irrigation, and more.
You can click here to view the digital version of the guidebook. We also have physical copies of the guide available at the UF/IFAS Leon County Extension Office (615 Paul Russell Rd., Tallahassee, FL 32301).
Happy fall gardening!

by Evan Anderson | Oct 21, 2021
While most people are familiar with the European honey bee, the domesticated insect that pollinates our crops and provides us with honey, there are plenty of other species of bees and their relatives out there. Most of them are harmless, spending their time quietly pollinating plants, including our crops. Their presence in the landscape, however, may cause some alarm, as it can be difficult for the untrained eye to distinguish between aggressive species and those that are innocuous.

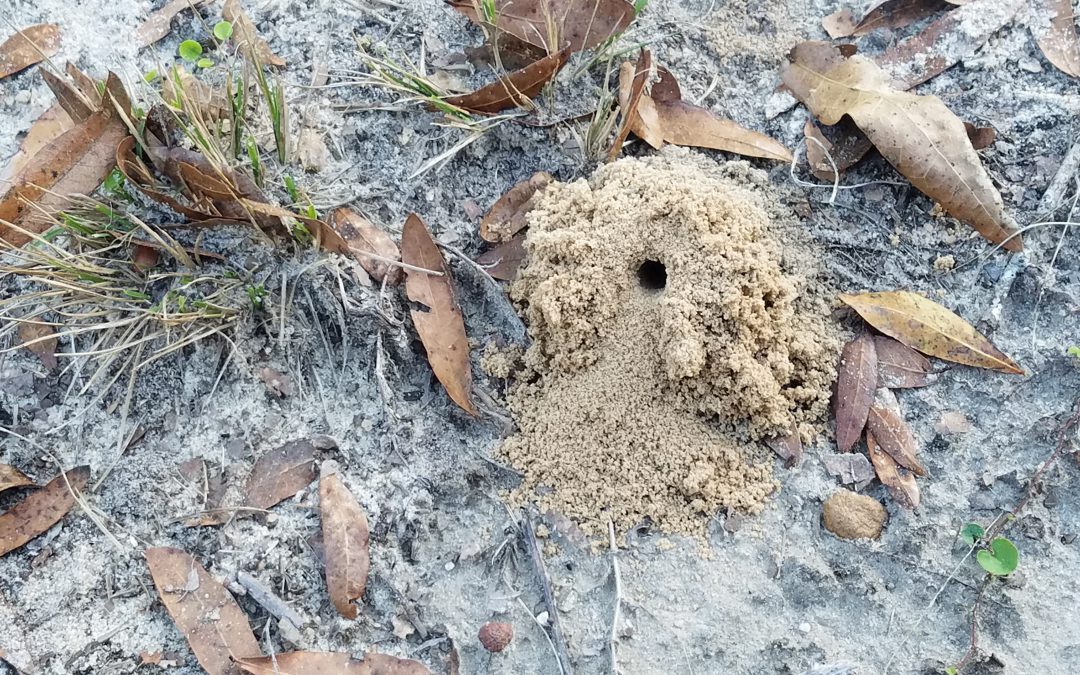
The entrance to a miner bee burrow.
Homeowners may occasionally note small mounds of soil in sandy areas of their lawns. Sometimes sporting a small hole in the center, these are the nesting sites of solitary, ground-nesting bees or hornets. Miner bees or digger bees build underground chambers, usually in well-drained, otherwise bare areas of sandy soil. Multiple bees may choose to dig their nests in the same location, though each bee makes its own tunnel and they do not live communally. Each bee lays her eggs in the nest she has excavated. She gathers pollen to feed the young when they hatch, stocks the larder, and leaves. When the young emerge from the nest, they fly away and do not remain; they will dig their own nests when they are ready to reproduce. While there is no need to control these insects (they serve as fantastic pollinators), the mounds of soil they make may be aesthetically displeasing to some people. Keeping a healthy lawn with no bare patches can deter miner bees from nesting in an area. Irrigation sprinklers can also help to keep the ground moist; these bees prefer dry soil, so it may keep them away. Care must be taken not to over-water a lawn, however!

A cicada killer wasp. Photo credit: Division of Plant Industry
Another species of note is the cicada killer hornet. Also known as the giant ground hornet, these insects grow to a size of about an inch and a half in length. Instead of pollen, they capture cicadas to feed their young. Like the miner bee, though, they are not harmful. Females do possess a stinger which they use to hunt their prey. Males may try to warn people or animals away from their burrows by acting aggressive, but they have no stingers. Some may see the large size of the cicada killer and wonder if the so-called “murder hornet” has made its way from Washington state to Florida, but as of this writing it has not. Unless you are a cicada, you have nothing to fear.
One ground-dwelling hornet that does warrant some concern is the yellowjacket. These are communal hornets, living in hives that are often build underground. Yellowjackets are known for their bad attitudes, attacking anyone who disturbs the entrance to their nest. They can be beneficial, being predators of many other insects including plant pests. A colony located too close to human dwellings or areas of activity is most often a nuisance, however. Any attempts to control yellowjacket nests should be done at night when they are less active. Protective clothing is recommended even then. Large or difficult to reach nests may require the attention of a certified pest control company.
For more information on these topics, see our EDIS publications:
Miner Bees: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/in912
Cicada Killers: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/in573
Yellowjackets: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/IN238

by Ray Bodrey | Oct 14, 2021
Tree dieback is a complex syndrome and slow developing. Dieback is essentially a process in which trees lose leaves and limbs. This usually occurs as a result of severe stress to the tree’s bark or root system, but could be a result of a declining life cycle.
It’s important to note that there is a significant balance between a tree’s root system and the number of leaves and limbs it can support. For example, if a tree loses part of its root system, possibly due to disease or lawn equipment damage, the tree will forfeit a portion of its leaves. Dieback doesn’t happen overnight, though. It’s a slow process, with larger trees taking much longer time for signs of stress to emerge. However, a large tree root system is very sensitive to damage, whereas a small tree will adapt quickly and is much more resilient to damage. So, what can be done to prevent dieback in trees?
First and foremost, trees, like all living things, have a natural life cycle. Regardless of how you care for your trees, dieback will occur. The most important management measure in extending the life of a tree is to protect the root system and bark.
With each passing year, a tree grows new bark in the rejuvenation process. The bark replacement process inevitably becomes more difficult as the tree gets older and in turn the tree is more and more susceptible to dieback. If the bark becomes damaged, especially later in the tree’s life cycle, then fungi and insects have a much greater chance to cause serious harm. Treating bark damage with a wound dressing to prevent decay is the recommended procedure.

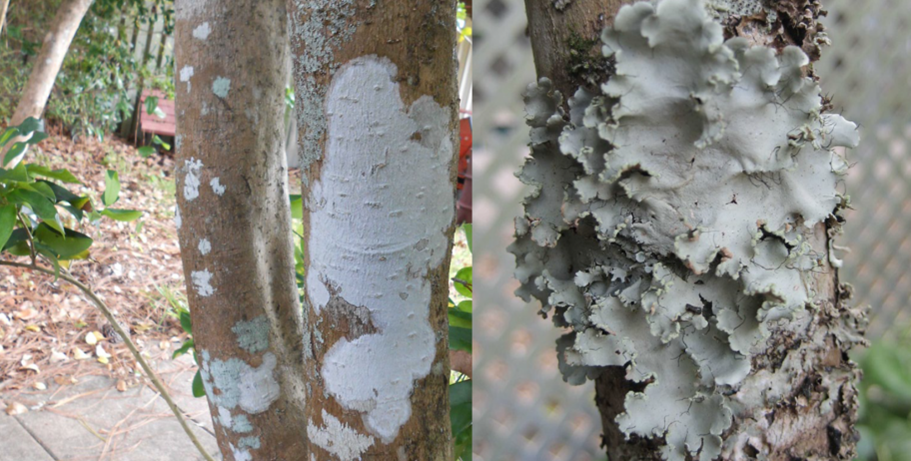
Lichens come in many forms and are commonly blamed for the decline and death of trees and shrubs, however they do not cause harm. Credit. Sydney Park Brown and Joseph Sewards, UF/IFAS.
A common misconception is that epiphytes, such as lichens and Spanish moss, are tree diseases. Epiphytes are known as “air plants” and thrive in the Panhandle. They survive on moisture and nutrients in the atmosphere and are harmless to trees. However, a tree that becomes inundated with epiphytes may be an indicator of excessive soil moisture, which may lead to root rot.
Lawn weed killers can have detrimental effects to trees, even if the application seems to be from a safe distance. When using a weed killer near a tree’s root system, confirm on the label that the product is designed to kill green growth only. It can’t be overstated that excessively fertilizing an old tree will greatly accelerate the decline of the tree. Some may think this will stimulate a tree and extend its life, but instead it will do the opposite. Young trees can tolerate fertilizer applications, as they need crown growth. Older trees will simply become top heavy, and structural damage will likely occur.
Don’t forget, trees need space too. A mature tree forced to occupy a small space will simply not adapt. Be sure to have adequate spacing when planting younger trees and shrubs in the vicinity of older trees. Also, keep your trees pruned away from touching structures and utilities.
Tree dieback is a complex issue to manage. By following these measures, you can help extend the life of your trees and continue to have a picturesque landscape.
For more information on tree dieback, contact your local county extension office.
Please visit Florida Friendly Landscaping, http://fyn.ifas.ufl.edu/, for more information on maintaining your landscape.
For more general information on lichens, please see UF/IFAS EDIS document “Spanish Moss, Ball Moss and Lichens-Harmless Epiphytes” by Joe Sewards and Dr. Sydney Park Brown: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/EP/EP48500.pdf
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Oct 8, 2021
Over the last decade or so, the Panhandle has been overrun, and I don’t just mean by the summer beach traffic. Rather, by an aggressive, exotic perennial grass that quickly displaces all native species, is not useful as a forage to wildlife or livestock, can spread by roots or seeds, and has no natural enemies. If you own property in the Panhandle or spend any amount of time on its roads, chances are you have become acquainted with this worst of invasive species, Cogongrass (Imperata cylindrica).
A native of Southeast Asia, cogongrass was introduced into the US in 1912 around Mobile, AL as a hitchhiker in orange crate packing. Then the 1920s, 30s, and 40s, it was intentionally introduced from the Philippines into other Gulf Coast states, including Florida, as a potential pasture forage for livestock. Since then, cogongrass has become one of the most economically and ecologically important invasive species in the US and worldwide, infesting nearly 500 million acres and is now found on every continent.

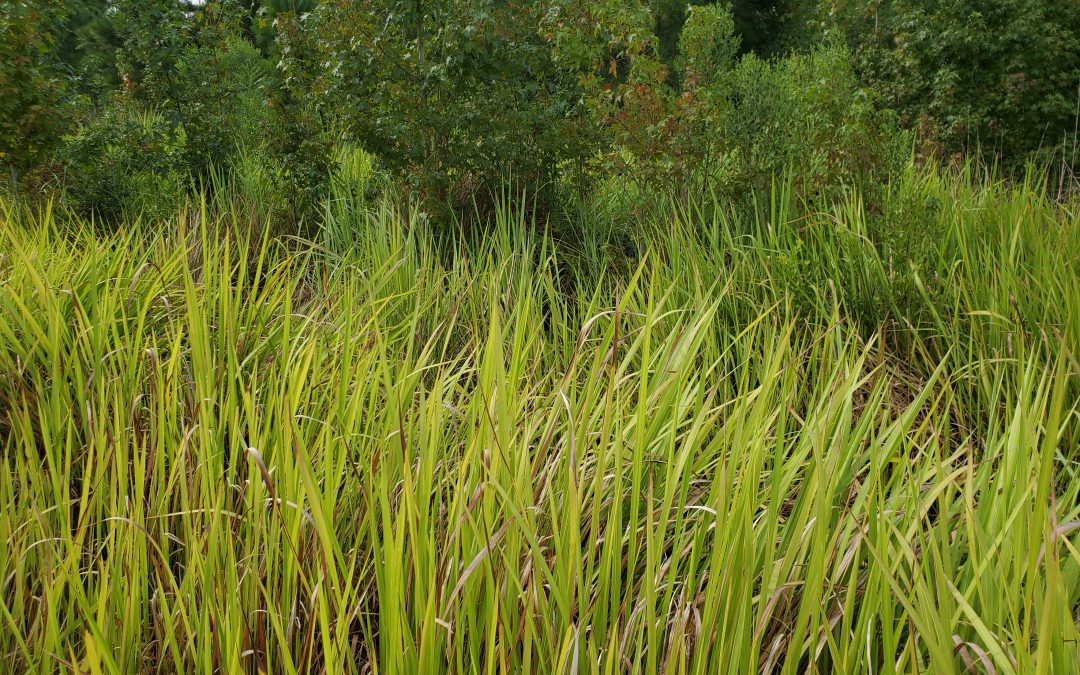
Cogongrass in Calhoun County, FL. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
Cogongrass is easily identified in late spring, when the grass throws easily spotted fluffy, white-colored seedheads above the mats of grass beneath. Additionally, patches of cogongrass are almost always noticeably circular in nature, radiating out indefinitely from the initial infestation. A closer inspection of the grass will reveal light green leaves up to 4’ in length, with an off-center, silvery colored midrib (the primary leaf vein that runs from the base of the leaf to the tip) and serrated leaf edges. Underground, cogongrass exhibits a dense underground root system that can reach as deep as 4’. This feature is the primary reason cogongrass outcompetes other plants, withstands any drought, fire, or soil condition thrown at it, aids in its resistance to herbicide activity, and generally makes it very difficult to manage.
The first step in managing cogongrass is prevention. If your property or the property you manage doesn’t have cogongrass, do everything you can to keep it that way. While the species can spread distances through seed dispersal, it is much more frequently moved around by fragmented rhizomes hitching a ride on equipment. If you or a contractor you’ve hired are working in or around an area with cogongrass present, avoid disturbing it with equipment and be diligent in monitoring the site for outbreaks following the job’s completion.
If you find cogongrass on your property, effectively eradicating it requires patience, persistence, and several years’ worth of herbicide applications. Currently, of the hundreds of herbicides available for purchase, only two chemistries have been proven to be very effective in destroying cogongrass, impazapyr (Arsenal, Stalker, etc.) and glyphosate (Roundup, Cornerstone, etc.).
- Imazapyr is an extremely effective non-selective, residual herbicide that controls a wide variety of weed species, including cogongrass. Just one or two applications of imazapyr can provide 18-24 months of effective cogongrass control, with follow up treatments required as needed after that. However, Imazapyr has a major downside that limits its use in many settings. Because it is a non-selective herbicide with significant soil residual activity, it cannot be used around the root zones of desirable plants. Oaks, other hardwood trees, and most landscape plants are especially sensitive to imazapyr. This herbicide is best limited to use in fields, waste/fallow areas, natural areas, and monoculture pine plantations – it is not appropriate in most residential and commercial landscapes.
- The other option, glyphosate is a non-selective herbicide with no soil residual activity. It is often a better option where severe injury or death of desirable hardwood trees and ornamental plants cannot be tolerated. However, due to its lack of residual soil activity, glyphosate applications on cogongrass patches will need to be repeated on an annual or biannual basis for up to five years for eradication of the infestation.
*Regardless of which herbicide you choose, controlling cogongrass is a multi-year affair requiring diligence and patience.
For more information on cogongrass and for specific herbicide recommendations and application rates/timing for your site, please contact your local UF/IFAS County Extension Office.

by Pat Williams | Sep 9, 2021
As homeowners, we do value our trees and no one wants to lose a shade tree especially on the house’s south side in Florida. On a recent site visit, a hickory tree had multiple concerns. Upon closer inspection, the tree had a bacterial infection about 30” off the ground with a smelly, black-brown ooze seeping forth. The leaf canopy was riddled with beetle holes and leaf margins were chewed by caterpillars. When leaves were viewed under the microscope, thrips (insects) and spider mites were found running around. The biggest homeowner cosmetic concern arose from hickory anthracnose (fungus) and upon closer inspection found the leaves to have hickory midge fly galls. The obvious question is should the tree come down? I’ll have you read the whole article before giving you the answer.
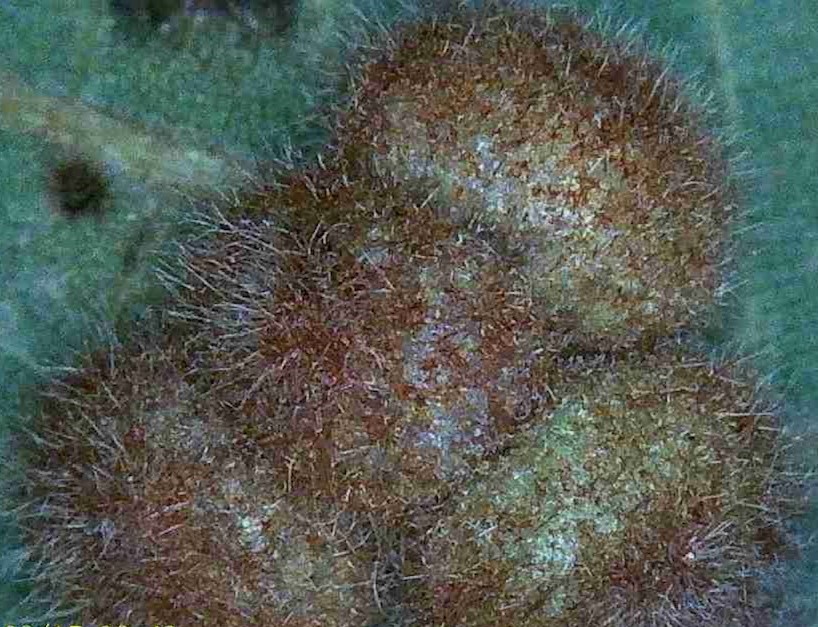

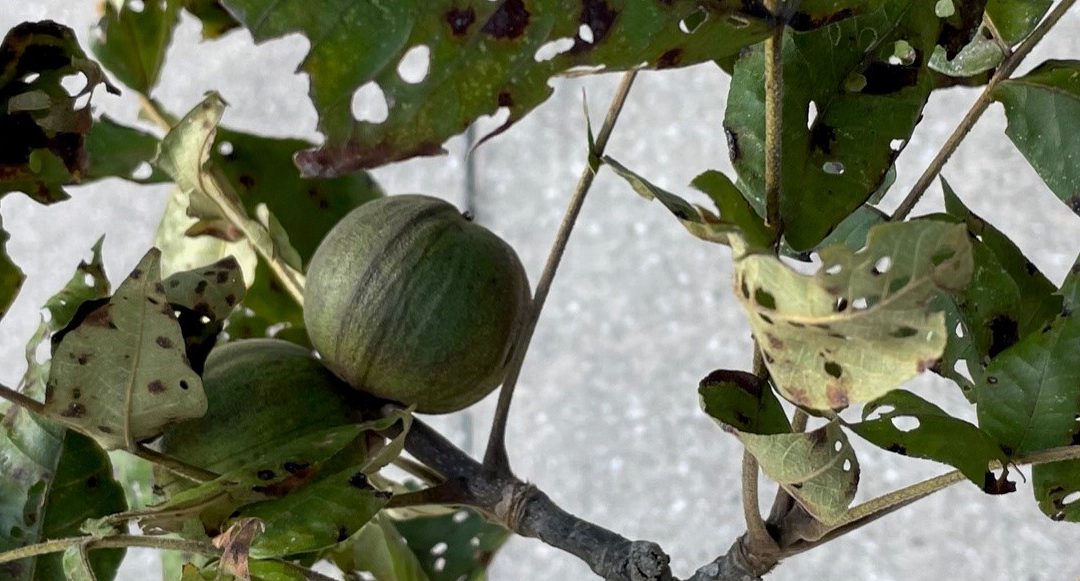
Each hickory gall is approximately 3/16″ wide.
Hickory anthracnose or leaf spot as seen in the banner photo is caused by a fungal infection during the wet summer months in Florida. The homeowner can usually recognize the disease by the large reddish brown spots on the upper leaf surface (sending a sample to the NFREC Plant Pathology Lab will confirm the diagnosis) and brownish spots with no formal shape on the bottom. Be sure to rake and remove all leaves to prevent your disease from overwintering close to the tree thus reducing infection next year.
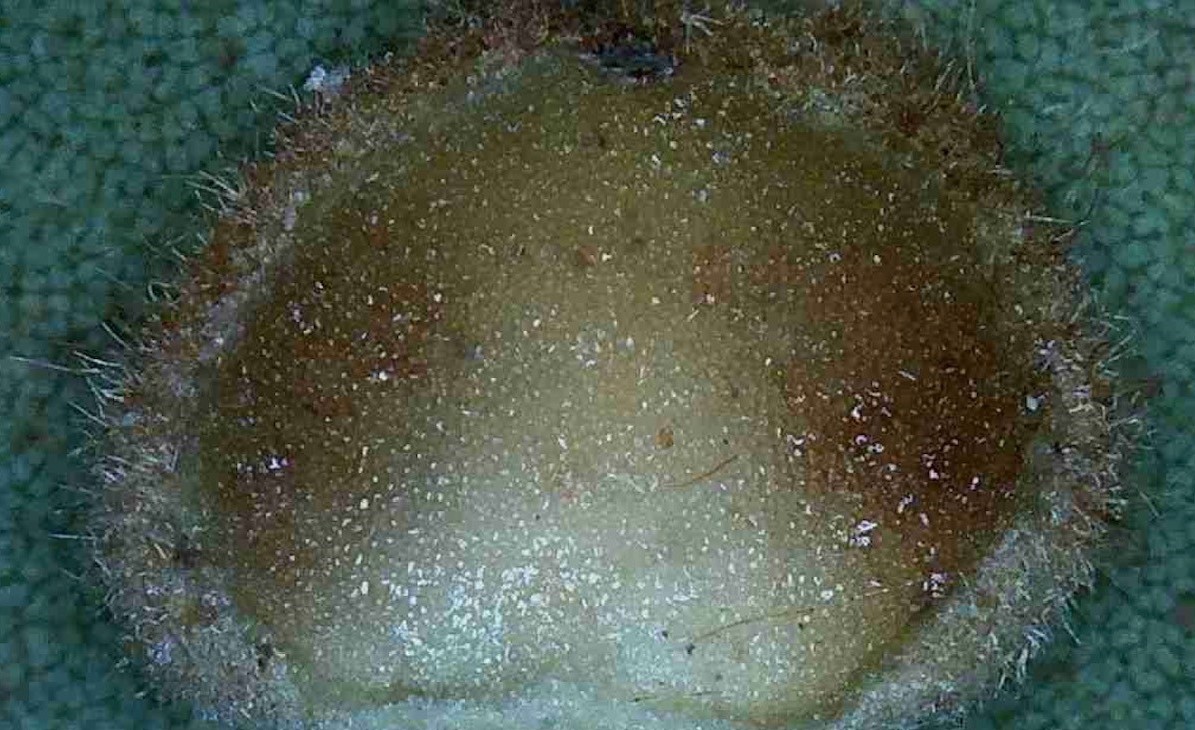
A hickory gall has been cut in half to show the leaf tissue.
The fungus can be lessened by good cultural practices and appropriate fungicidal applications. Please remember it is best left to professionals when spraying a large tree. This alone is not cause to remove your tree.
Hickory gall is caused by the hickory midge fly, an insect that lays eggs in the leaf tissue. The plant responds by building up tissue around each egg almost like the oyster when forming a pearl.
As the gall tissue grows, eggs hatch and larva start to feed on this tissue. The larva will continue to
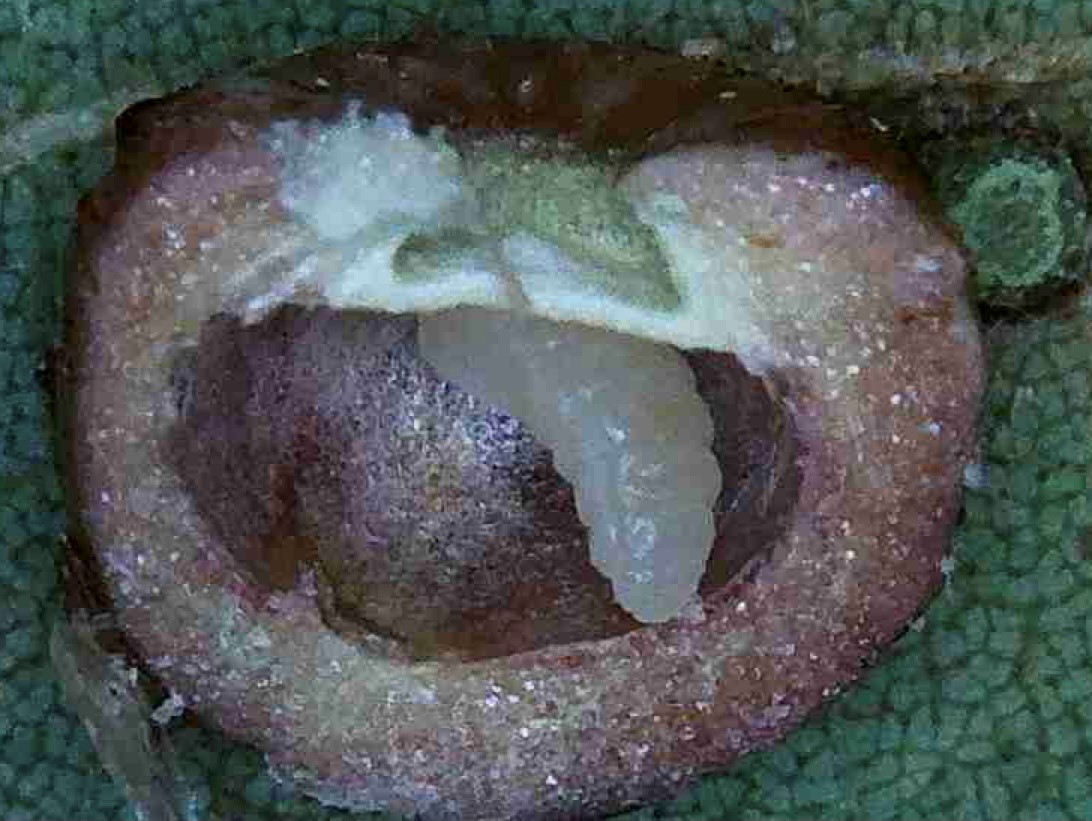
The larva has eaten all soft material inside the gall and is ready to pupate.
feed until it is ready to pupate within the gall. After forming a pupa, the midge fly will eventually emerge as an adult and females will continue to lay eggs on other leaves. The galls are more of a cosmetic damage and because your hickory leaves will fall from the tree as winter comes, the galls will normally not cause enough damage to worry about each year. Once again good cultural practices and disposal of each year’s leaves will reduce the gall numbers next year.
In a large tree with many leaves, foliar feeding by beetles and caterpillars do cause damage though the leaves will still produce enough food (photosynthesis) to keep the tree alive. Most of us never climb our trees to look at leaves to see the small insects/mites and there are more than enough leaves to maintain tree health.
The biggest concern during my site visit was their tree’s bacterial infection. A knife blade was pushed into the wound area and went in less than 1/4″. The homeowner was instructed to look at bactericide applications. In the end, this hickory tree with so many problems is still shading the home and helping cool the house. It is still giving refuge to wildlife and beneficial insects. When in doubt give our trees the benefit and keep them in place. Remember your local Extension agent is set up to make site visits and saving a tree is time well spent.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Aug 26, 2021
Nearly everyone likes turfgrass lawns. They’re pretty and green. They filter water, chemicals, and nutrients before they enter our groundwater systems. They provide a recreation spot for people and pets. But lawns also come with maintenance tasks, one of which is weed control. Fortunately, keeping our common Centipedegrass lawns relatively weed free is as simple as smart management and utilizing herbicides effectively. Though the number of herbicides available for purchase can be overwhelming, you only need three to keep weeds at bay – a selective grass herbicide, a strong broadleaf herbicide, and a sedge herbicide!

Dollarweed, one of the toughest broadleaf weeds for homeowners to control. Picture courtesy of Julie McConnell, UF/IFAS.
First up on the essential herbicide list is the selective grass herbicide Sethoxydim. While most folks’ weed focus is centered on broadleaf weeds, grassy weeds like Crabgrass, Bahiagrass, Goosegrass, and others can be just as problematic and make for a very unsightly lawn. Enter Sethoxydim. Cheap and easy to find, Sethoxydim is offered as the active ingredient in many branded products like Fertilome Over the Top Grass Killer, Hi-Yield Grass Killer, and many more. These products control weedy grass species without seriously harming Centipedegrass or broadleaf ornamental trees and shrubs (Centipedegrass may temporarily be yellowed after sethoxydim application but will recover). Not only will it kill out the unwanted grass growing in your Centipede, but it will also remove these weeds from your flower beds!
Second, having a strong broadleaf herbicide on hand is necessary. I say “strong” because many of the homeowner grade products available at garden centers simply don’t have the “juice” to control tough broadleaf weeds like Dollarweed, Doveweed, Virginia Buttonweed, and others. For this job, I prefer to use a commercial grade 3-way product like Celsius WG by Bayer. Celsius WG is a 3-way combination herbicide with a healthy dose of Dicamba as its primary ingredient. Though Dicamba is a notoriously volatile chemical known to cause damage to unintended plants through drift in hot weather, combining it with the two other products in Celsius WG makes it safe to use in lawns, even in the heat of summer. While strong broadleaf herbicides like Celsius WG are expensive on the front end, don’t let that deter you. These products wind up being very cost effective in the long run due to minute mixing rates (one bottle goes a very long way in most residential lawns) and effectiveness – you simply will not need to waste time and money spraying lawn weeds over and over to obtain control like is necessary with lesser products – one or two applications will solve the toughest broadleaf weed problems.
Finally, any good lawn weed control program will include a quality sedge control herbicide. Sedges (often called “nutgrass”) look like grasses but are a completely different category of plants and as such, require specialized herbicide chemistries to achieve control. Sedge weeds prefer wetter areas of lawns, though they can occur in pretty much any lawn site and are very unsightly. For this weed category, there are several options available to homeowners. The one that consistently provides the best control in lawns is Halosulfuron-methyl, the active ingredient in the aptly named product Sedgehammer. Conveniently coming in individually pre-mixed packets for small lawns or a larger bottle when more acreage is to be treated, Sedgehammer couldn’t be easier to mix and use. While Sedgehammer and similar products are extremely effective in controlling various sedge weeds, they tend to work very slowly, and patience is required. Weeds immediately stop growing following a Sedgehammer application, but it can take up to three weeks to notice the sedges dying.
While having and using the above three herbicides can control almost any weed homeowners may encounter in their lawns, it is important to remember that herbicides are not substitutes for proper lawn management. When good cultural practices in lawns are followed, such as mowing at the correct height, only watering when necessary, following UF/IFAS fertilizer recommendations, etc., chemical weed control may not even be necessary in many cases! Also, once the decision to purchase and use chemical herbicides has been made, it is critical that one always read the label before using any herbicide product. This ensures safe and effective use of the product; the label is literally the law!
For assistance in choosing the correct herbicide for your lawn and other lawn care concerns, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Office! Happy Gardening!















