
by Mary Salinas | May 6, 2021

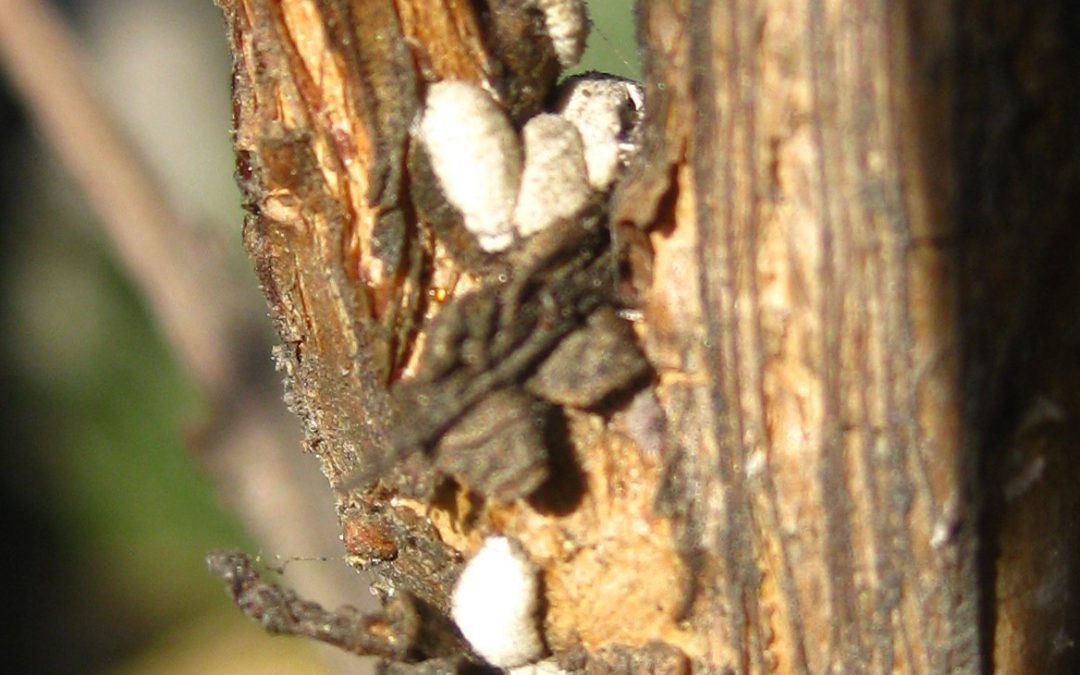
Crapemyrtle bark scale are often found in branch crotches and wounds to the bark. Photo credit: Gary Knox, UF/IFAS.
There is a new pest in the western panhandle of Florida. Crapemyrtle bark scale (CMBS) is a scale that is found on the trunks, branches, and twigs of crapemyrtle. It is the only known scale insect found on the bark of crapemyrtle. There are other scales that occur on the leaves.
When scouting for this pest, look for very small (2 mm or 0.08 inch) white or light gray spots on the bark of crapemyrtle. The adult females do not ever move once they have found a place to feed and reproduce. Under her protective covering, she lays eggs that hatch into ‘crawlers’ that then crawl away to find their own spot to settle down. When squished, they exude a pink goo (the eggs or newly hatched crawlers). Males are winged and travel to find their mates. See this comprehensive information on their interesting biology.
While the scale does not outright kill the trees, it lessens their landscape value and can reduce flowering. And like other scale, CMBS secretes lots of honeydew; black sooty mold then feeds and grows on the honeydew. The black sooty mold does not harm the plants directly, but it is unsightly and can interfere with photosynthesis if present on the leaves.

Crapemyrtle bark scale are white to gray and ooze pink when squished. Photo credit: Gary Knox, UF/IFAS. ,
Unfortunately, CMBS has also been found on a very popular native bush, American beautyberry, Callicarpa americana, and it is yet unknown whether CMBS will expand its host range to other plant species in our country. In Asia, this pest has been found on some economically important crops like pomegranate and persimmon.
CMBS is a tough insect to control. And it is best left to the professionals. Dr. Adam Dale, an entomologist at the University of Florida, recommends using pyriproxyfen (in the product Distance) or buprofezin (in the product Talus). These are insect growth regulators that have shown to provide great control of CMBS and other similar scale insects on trees and other woody plants. Although these products are not systemic, they are translaminar, which helps increase their control and reduce any non-target effects on beneficial insects like bees. Two applications 7–14 days apart are suggested. However, these products can only be applied by licensed pest control applicators.

Severe infestation of crapemyrtle bark scale and sooty black mold. Photo credit: Gary Knox, UF/IFAS.
Systemic insecticide drenches are effective but pose a dangerous hazard to bees and other pollinators as the poison also gets into the flower nectar. The product labels prohibit application of these type of products to flowering plants for that very reason.
Routine close inspection of your crapemyrtle trees is critical for CMBS control. Early treatment will help prevent heavy infestations as seen in some of the photographs. When pruning your crapemyrtles, thoroughly clean your tools between plants to prevent any accidental spread.
Prevent this scale from coming into your landscape in the first place. Inspect all new plants you are considering adding to your landscape for any sign of CMBS or other insect or disease presence.
If you have any questions on making the correct identification of CMBS, or any other insect, contact your county extension office.
Lastly, consider reporting the presence of this new scale to enable researchers to track its spread.
For more information:
Stop CMBS Website
UF/IFAS Featured Creatures: crapemyrtle bark scale

by Matt Lollar | Apr 1, 2021
If you’ve been raking leaves recently, you’ve probably noticed little green worms hanging from the trees. They seem to be in abundance this year and can be found crawling on driveways, just hanging around, and maybe even feeding on oak tree leaves.
These green worms that are all over the yard are oak leafrollers (Archips semiferanus) or oak leaftiers (Croesia semipurpurana). Some people may refer to them as inchworms, however a number of different caterpillars can go by that name. Leafrollers and leaftiers range in length from 1/4″ to 1″. The adult form of these insects is a 1/2″ long moth. The oak leafroller moth is mottled tan and brown and the oak leaftier moth is yellow with brown markings.

An oak leafroller caterpillar crawling on a leaf. Photo Credit: Blair Fannin, Texas A&M University
In May, the adults of both species lay their eggs in the twigs and leaf buds of a number of tree species. The eggs don’t hatch until March of the following year. When the caterpillars emerge, they feed on the newly forming leaves and flowers of oak, hackberry, pecan and walnut trees. If they are disturbed, they will stop feeding and hang from a strand of silk. Oak leafroller caterpillars pupate in tree branches, while oak leaftier caterpillars drop to the ground and pupate in leaf litter. Adult moths emerge in one to two weeks.

A leafroller moth with wings spread. Photo Credit: U.S. National Museum
The oak leafrollers and oak leaftiers don’t really do enough damage to be considered pests, but they are a bit of a nuisance. Thankfully, birds and parasitic wasps will eat and kill the majority of the population. For in-depth information on most of the interesting insects in your yard, please visit the UF/IFAS Featured Creatures Website.

by Molly Jameson | Mar 18, 2021
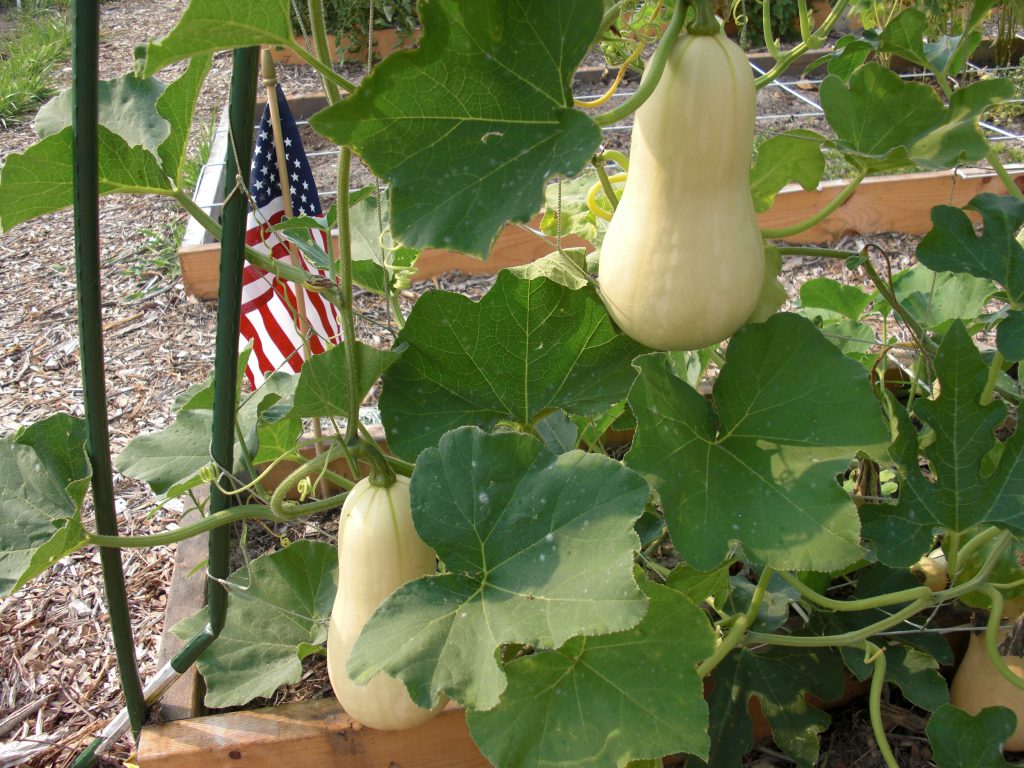

Butternut squash is more resistant to squash vine borers and it has a vining growth habit, perfect for growing on a trellis. Photo by Janis Piotrowski.
Last spring, I fought the good fight against a very pesky garden pest. As the pandemic ramped up, I started working remotely from home, which I figured would at least afford me the ability to scout my patch of summer squash a bit more diligently.
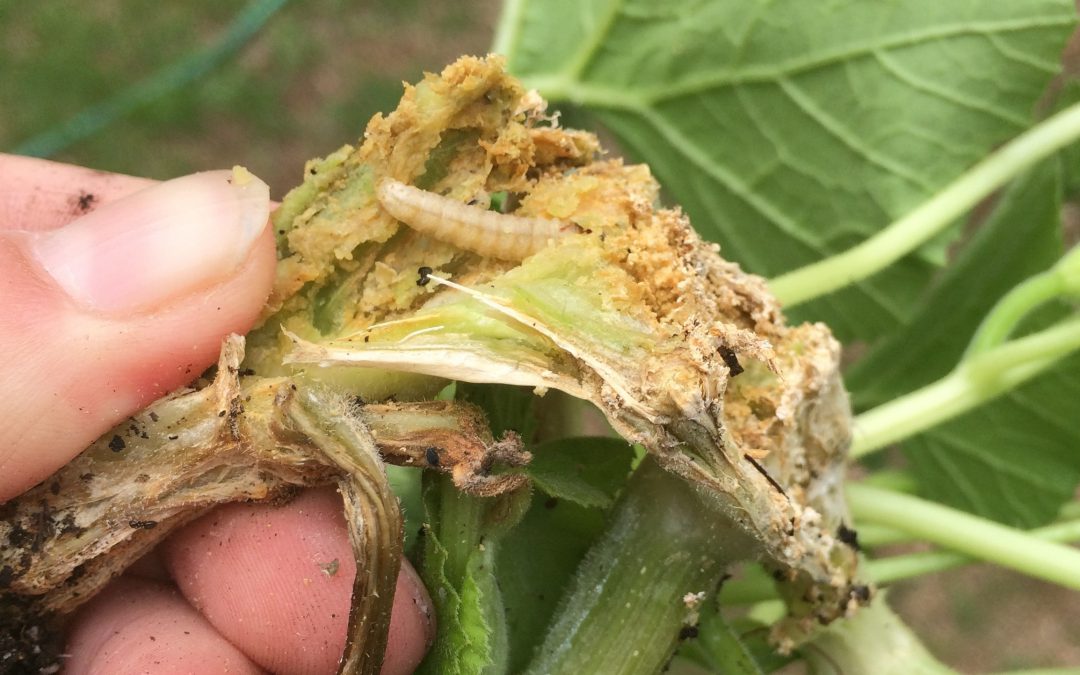
I was able to successfully remove a few tiny eggs that had been deposited individually on the base of the squash’s elongating bright green stems. And, since I planted early in the season, I was able to harvest a few beautiful looking – and very delicious tasting – summer squash for the dinner table. But alas, most of my hard work succumbed to my biggest garden foe: Melittia cucurbitae. Aka, the squash vine borer.

Squash vine borer larvae can most easily navigate the stems of summer squash varieties. Photo by Molly Jameson.
This year, I am trying a new approach. Instead of marching through my garden morning and night swatting wildly at borer moths – or repeatedly coating Baccillus thuringiensis biological insecticide spray over the squash stems every week – I am switching it up. This year, it is all about Cucurbita moschata. Aka, butternut squash.
How can this cucurbit avoid the mighty squash vine borer, you ask? Well typically, after hatching, squash vine borer larvae will quickly chew into the succulent stem of a summer squash variety. These large, hollow stems then act as an open highway for the borers, and they easily work their way up. The stems of butternut squash, on the other hand, are less palatable for the larvae. Their vining habit produces stems that are harder to navigate, thicker, and tougher than summer squash stems. Although not completely resistant, they are certainly not the borers’ preferred host plant.
And thankfully, butternut squash is quite delicious. It can be roasted to accompany just about anything, including spaghetti, lasagna, salads, chilis, and stews. It can also be blended into soups or purees to be paired with herbs and spices, such as turmeric, sage, garlic, and thyme. Or, it can be used as a filling in pies or frittatas, brushed with brown butter to sweeten up the plate as a delicious side dish, or be paired with goat cheese and crackers to be served as an appetizer.
Sometimes, simply omitting your toughest garden foe’s favorite host plant is the best path to both garden and dinner plate success.

by Mark Tancig | Feb 11, 2021
Gardeners worldwide and throughout time have bemoaned weeds. In Florida, we get to enjoy weeds all year long! Our February Gardening in the Panhandle (GIP) Live episode focused on weeds and weed control. Many homeowners are interested in ways to control weeds and UF/IFAS Extension and your local extension agents are here to help. The following is a summary of the topics we discussed and links for more research-based information on weeds.
What is a Weed?
Many folks come to the extension office holding a plant and ask, “Is this a weed”? Well, whether it is a weed or not is up to the individual, as the only definition for a weed is “a plant out of place”. Bermudagrass and Oxalis are good examples of plants that some try to grow while others try to kill. One person’s weed is another’s wildflower! However, to be clear, plants classified as invasive by UF/IFAS and governmental entities are officially weeds. There are resources to help identify several common plants that are generally considered weeds by most homeowners and landscapers.
Weed ID Links

Common, and aggravating, weeds.
How to Prevent Weeds?
There are some general gardening practices that can help prevent weeds so there is less of a need to control them. A lawn that is healthy is less likely to be invaded by weeds and the use of mulch can greatly reduce weed growth in planting beds. Other practices, like the placement of weed fabrics/cloths are less effective and/or less practical in many garden situations.
Weed Prevention Links
How to Control Weeds?
Once you know and/or decide that what you have is a weed and that it needs to be dealt with, then you have to consider your control options. Prevention, as mentioned above, is key but sometimes you may need to use other methods of control, such as physical, mechanical, and/or chemical means. With chemical weed control, it is important to always read and follow the product label.
Weed Control Links
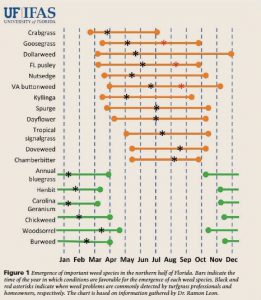
General dates of common annual weed emergence. Credit: Dr. Ramon Leon, UF/IFAS.
Specific Weed Recommendations
When managing pests, proper identification is key to effective control. Because some weeds are annuals, and present either during the cool or warm season, and others are perennials, proper weed identification can provide a more detailed control strategy. Use the weed ID links above and the document links below for more precise, and effective, weed management.
Species-Specific Control Links
If you need additional assistance with weed control, please contact your local county extension office. Please tune in for future GIP LIVE episodes for more research-based information on gardening topics.

by Larry Williams | Feb 11, 2021

Be careful when bringing firewood indoors. Photo credit: Larry Williams
Your firewood pile could be “bugged.” Many insects like to overwinter in wood. A wood pile is an ideal place for some insects to survive the winter. They don’t know that you intend to bring their winter home indoors during cold weather.
During colder weather, you can unknowingly bring in pests such as spiders, beetles and roaches when you bring in firewood. It’s best to bring in firewood only when you are ready to use it. Otherwise, those pests could become active and start crawling around inside your house. Many insects are potential problems indoors and there are usually control options once insects move into your home. However, preventing the insects from getting inside is the best approach.
If you store wood indoors for short periods of time, it is a good idea to clean the storage area after you have used the wood. Using a first-in, first-out guideline as much as possible will reduce chances of insect problems.
It’s best to keep your wood pile off the ground and away from the house. This will make it less inviting to insects and help the wood dry. It’s not difficult to keep the wood off the ground. The wood can be stacked on a base of wooden pallets, bricks or blocks, which will allow air movement under the wood. The wood can also be covered with a waterproof tarp or stored in a shed. Regardless of how it is stored, avoid spraying firewood with insecticides. When burned, insecticide treated wood may give off harmful fumes.
Some critters that live in firewood can be harmful to humans. To avoid a painful sting or bite from insects, spiders or scorpions (no Florida scorpion is considered poisonous, but they can inflict a painful sting), it is a good practice to wear gloves when picking up logs from a wood pile.
Firewood can be a good source of heat during our cold weather. If you’re careful with how you handle your firewood, hopefully it will warm you, not “bug” you.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Feb 2, 2021
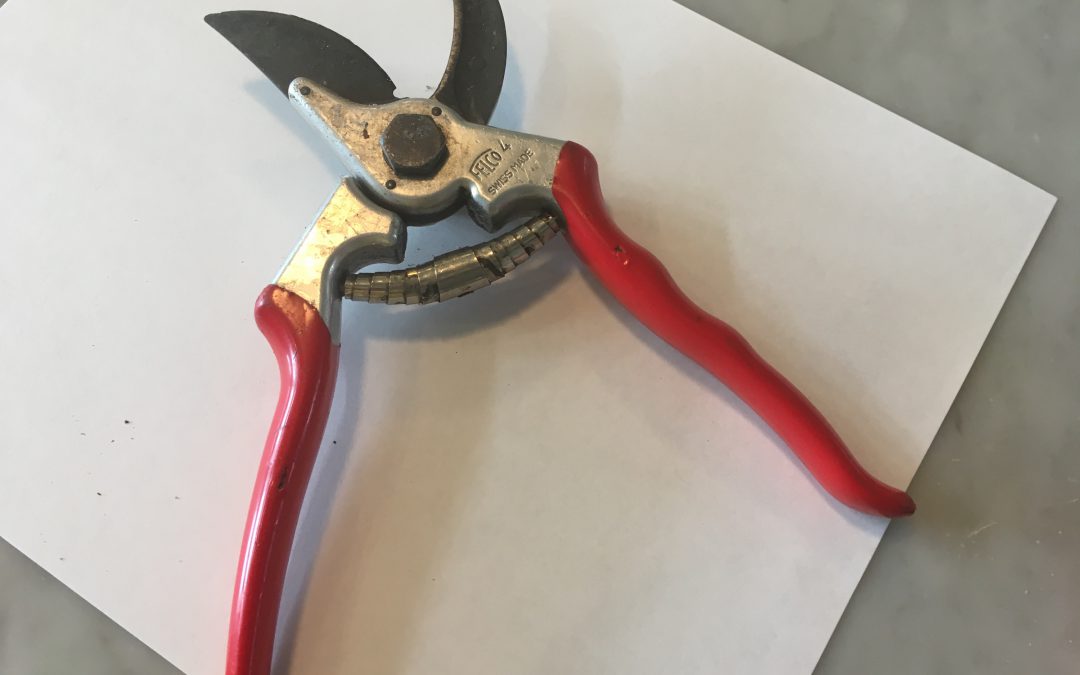
There is an old saying that rings true in pretty much any situation – “You get what you pay for.” Gardening tools, especially pruners, are no exception. We’ve all been there, fumbling around with a pair of rusty, dull, cheap garden pruners that just barely get the job done. Unfortunately, they can also do considerable harm to the plants you’re trying to improve, as anything short of a nice, sharp, clean cut introduces the potential for insect/disease infestation and will produce a wound that takes much longer to heal, if it ever heals properly at all. You wouldn’t want your doctor to start hacking away at you with a dirty, second-rate scalpel. Don’t subject your plants to the same treatment! While I’m not advocating blowing hundreds or thousands of dollars outfitting your garden tool shed with top of the line everything, investing in a pair of quality bypass hand pruners will pay dividends many years into the future and make your gardening experience much more enjoyable!

The classic Felco #4 bypass hand pruners. Photo courtesy of Walton County Master Gardener Andrea Schnapp.
Found in three designs, from old-fashioned anvil pruners that smush and smash their way to a cut, to ratcheting pruners that make short work of larger branches but tend to be cumbersome and complicated, to bypass pruners that produce clean cuts in a scissor-like manner, hand pruners accomplish many tasks in the landscape. From cutting small limbs, to harvesting vegetables, to deadheading annual flowers and everything in between, there isn’t a more frequently used, versatile tool. Therefore, it makes sense to buy a quality pair that will perform excellently, still be snipping long after your pruning days are over (if you take care of them), and that are comfortable enough you will enjoy using them. When shopping for your pair of “forever” pruners, there are a few things to look for.
- Only use bypass style pruners. Your plants will appreciate it.
- Look for heavy duty pruners with frames made from quality aluminum or stainless steel; they won’t rust and won’t easily bend or break.
- Buy pruners with replaceable parts. This is especially key because springs eventually rust and gum up and blades break and will eventually lose their ability to hold an edge over time (though you can and should resharpen them).
There are two commonly found brands that fit all three above criteria, albeit at different price points. For a high quality “budget” blade, various models from Corona do an excellent job for the money ($20-30) and won’t hurt your feelings too badly if you happen to lose a pair. Should you decide to splurge a little, Felco makes sharp, indestructible pruners, in multiple models around $50 to fit all size hands. Felco has become the horticulture industry standard and you’d be hard pressed to find a nursery owner or landscaper that didn’t own a pair (or two).

Corona ComfortGel bypass hand pruner. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
Regardless of which brand you buy (and there are many more than the two above listed) a pair of well-made pruners, if taken care of, should last a lifetime and make your gardening experience much more enjoyable for you and your plants! If you have any questions about gardening tools or equipment or any other horticulture or agronomic topic, feel free to contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Office. Happy Gardening!


















