
by Mary Salinas | Sep 16, 2014
Many of us have a tendency to want to spoil those we care for – our significant other, our pets, our children, even our lawns. Some homeowners who long to have a lush, green, healthy lawn tend to spoil their lawns with lots of water. Their lawns should not suffer through a dry, thirsty day! However, spoiling a lawn with too much water can literally be killing it with kindness. (Keep in mind that we are discussing established turf, not newly installed lawns; new lawns do need special care.)
 Turfgrass that is overwatered can suffer several fates. Roots can stay shallow near the surface and not dig deep into the soil as they should. A deep root system allows the turf to be more resistant to stress from drought, disease and abiotic factors such as wear from traffic. Excessive water leads to excessive lush growth – that may sound like a good thing, but it’s not. Excessive lush growth leads to thatch build-up and it creates a perfect environment for pests and diseases. An abundance of water also assists those nasty weed seeds to germinate and compete with your turfgrass.
Turfgrass that is overwatered can suffer several fates. Roots can stay shallow near the surface and not dig deep into the soil as they should. A deep root system allows the turf to be more resistant to stress from drought, disease and abiotic factors such as wear from traffic. Excessive water leads to excessive lush growth – that may sound like a good thing, but it’s not. Excessive lush growth leads to thatch build-up and it creates a perfect environment for pests and diseases. An abundance of water also assists those nasty weed seeds to germinate and compete with your turfgrass.
So how do you know how much irrigation is best for the health of your lawn? That depends on the temperature, time of year, the type of turf and your soil type. Irrigate just enough to get water to the root zone without leaching beond that zone. Usually, that amount is 1/2″ to 3/4″ of water each time you irrigate. How often, then, do you turn on those sprinklers?
Let your lawn get thirsty before you water. University of Florida research shows that lawns that dry out and start to show a little drought stress before getting more water actually perform better in the long run. So wait until the leaf blades start to fold, the blades start to look a bit off-color, or you can start to see footprints where you’ve walked.
For lots of great information and publications on caring for your lawn, consult the Your Florida lawn website.
by Alex Bolques | May 13, 2014

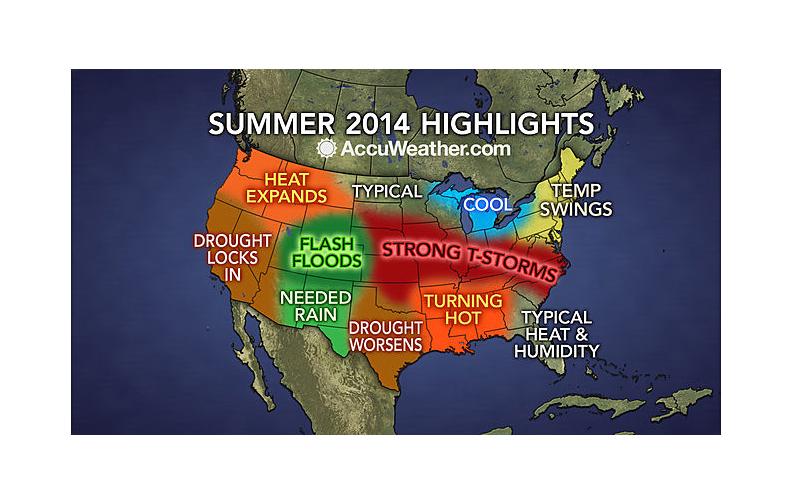
Expect typical heat and humidity east of the Apalachicola River with hotter temperatures west.
http://www.accuweather.com/en/weather-video/video-summer-2014-forecast-highlights-drought-severe-weather-increase/3520160310001
As we begin to approach our North Florida hot summer months, Gary Wade with the University of Georgia College of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences Cooperative Extension reminds us that, “temperatures in the high 90s and several weeks without rain can lead to serious, sometimes fatal, conditions for landscape (and garden) plants“. Most likely, we will also experience extreme temperatures in June and July. Under these conditions, heat stress is a great concern for both plants and people in the landscape or garden. Remaining hydrated is key to preventing heat stress.
For plants, mulching is an effective means to conserve moisture in the soil. It also cools the plant root zone, and helps to control weeds. Removing weeds that are growing around desirable plants will also help reduce soil moisture losses.
Consider watering your garden or landscape early in the morning. This method takes advantage of cooler morning temperatures, which can extend soil moisture conditions thus making soil moisture available during the hottest times of the day. Early morning watering will also discourage disease problems on plants susceptible to fungal growth such as lawns, roses, and cucurbits.
The best time to work in the garden or landscape is during the morning hours. To beat the heat, stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Heat stress disorders develop when the body cannot shed excess heat. Heat stress, heat exhaustion, and heat stroke are illnesses that can overcome you when your body is unable to cool itself. For more information and resources on how to “Beat the Heat”, visit the UF IFAS Solutions page.
Ref: Wade, G. 2013. Heat, Drought Take Toll on Landscape Plants. University of Georgia College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences Cooperative Extension.
by Julie McConnell | May 3, 2014
The last week of April 2014 brought with it 10-22 inches of rain across the panhandle in a matter of days. Some areas had immediate flooding and standing water, while others may be in areas at risk of rising rivers and streams. As the water recedes, many people are wondering how all the water will affect their landscapes.
Only time will tell what the long term impact will be, but here are a few things to watch for and what you can do to try to moderate damage.
- Let soils dry out before driving vehicles or other equipment on grassy areas. Even if the water is not visible, if the soil is still saturated, driving lawn equipment or cars may cause ruts.
- Do not leave automatic irrigation systems running on established shrubs, trees, and lawns. If your system is set to run in the early morning hours, you may not think about it being on, check your systems and hold off on adding water until soils dry out and the plants need it.
- Watch for fungus symptoms and treat if needed. Wet plants and cool weather are ideal for some Brown Patch on lawns, be aware and monitor landscapes closely. If disease is suspected, contact your local county extension office for recommendation.
- When mowing, leave a longer leaf blade to compensate for root stress.
- Look at the base of trees and shrubs to make sure silt and sand have not buried the crown or root flare. Also look for erosion of root zone, these areas may need correction. “Salvaging Flood-Damaged Shrubs and Ornamentals.”
- Adjust fertilization as needed; if you recently applied fertilizer it has likely runoff or leached from the site. However, if you suspect fungal disease do not fertilize until disease is managed.
- Stress in turfgrass, for details read “Watch Turf for Flooding Stress”
- You may see new weeds (seeds or segments may have washed or blown into your yard)
- Tree and shrub decline or death read “We Had Plenty of Rain, Why are My Trees Dying?”
- Although this storm was not a hurricane, “Assessing Damage and Restoring Trees After a Hurricane” has helpful information for areas with wind damage
- Nutritional deficiency symptoms in palms may show up 4-5 months from now. “Nutrient Deficiencies of Landscape and Field-grown Palms in Florida.”
- Decreased availability and increased price of sod (flooded fields prevent harvest and increase inputs for disease, weed, and nutrition management)
- Scheduling changes or maintenance adjustments by landscape contractors. Turfgrass and ornamentals will likely need different maintenance applications than in years past to correct issues related to flooding and excess rain.

by Carrie Stevenson | Jan 14, 2014

The branching structure of crape myrtles makes an impact to landscapes even in winter time. Photo credit: Beth Bolles
Most people associate yard work with the spring and summer, but if you’re considering a major redesign of a home landscape, now is a great time to start. Without the vegetation on deciduous trees, it’s easy to see the “bones” of your yard—the tree trunks and branches, sidewalks, and fences—which frame it.
One of the best ways to start with landscape design is a piece of paper and pencil. If you’ve got a paper copy of your survey, even better—you can sketch in trees, sidewalks, and fences with an aerial view and see where the open spots lie. Take some time to walk around your yard, considering how you use the space. Do you have children or pets that need room to run? A shady area for relaxing? Full sun for a garden? All of these uses can co-exist in a single yard, but the key to good landscape design is allowing for them to flow together in a logical, attractive way.
If you’ve never put together a comprehensive landscape design before, there are several very helpful tools online provided by horticulture experts with UF IFAS Extension. The “pattern guide” is ideal for starting and completing small projects, such as side yards, shade areas, etc. and even suggests appropriate plants based on light conditions and region of the state. Using this guide is a great way to start from scratch and build up to a diverse, healthy landscape. On the other hand, if you are essentially satisfied with your yard but just need a few accent plants or another tree somewhere, a great online resource is http://deactivated_site/. Here, you can enter a set of specific criteria based on the type of plants you’re looking for, and the site will create a customized list of suggestions to use in your landscape.
The online Florida-friendly landscaping pattern book has great ideas for redesigning your landscape.
After deciding on additional needs for hardscape and plantings, the next step is to make room for them by removing sod or unwanted landscape plants. Now is also the time to look at irrigation needs—if you have an existing system, make sure it still works with your new landscape design. If it doesn’t, it’s much better to redirect water, piping, or add new sprinkler heads while you’re digging into the soil than after you’ve finished installing new vegetation. If you aren’t using an irrigation contractor, you’ll need a solid understanding of how the system is set up before making changes. Inexpensive kits can also be purchased to add drip or micro-irrigation to an already-installed system.
Once irrigation and hardscape are complete, you can begin with plant installation. It makes the most sense to plant trees first, add mulch around the root zone, then put in shrubs and groundcovers based on your plan. Many do-it-yourselfers will take their time on this step, adding new plants as time and budget allow. This method works well and can be a fascinating way to watch your yard transform.
We have many great resources for more in-depth discussion of landscape design and irrigation work, including your local UF IFAS Extension office. Don’t hesitate to call us with questions or send photos of your new and improved yards!
by Sheila Dunning | Nov 11, 2013

It doesn’t take expert gardeners or landscapers to create a Florida-friendly yard. All it takes is a willingness to learn and a desire to build a beautiful yard that helps protect Florida’s environment. Florida-friendly landscaping is now part of state law. Florida Statute 373.185 prohibits government entities and homeowners associations from enacting or enforcing any governing document to prevent homeowners from implementing Florida-friendly landscaping (FFL) principles. A guideline to ease the development of a manual can be found at this link on the Florida Yards and Neighborhoods website. “Florida-Friendly Landscape Guidance Models for Ordinances, Covenants, and Restrictions.”  Florida Statutes 482.1562 states that all commercial fertilizer applicators must have a license from the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS) by January 1, 2014. To get this license, each Green Industry employee must be trained in Best Management Practices, which teaches professionals how to implement FFL principles. Additionally, to address water conservation Florida Statute 373.62 says the following: “Any person who operates an automatic landscape irrigation system shall properly install, maintain, and operate technology that inhibits or interrupts operation of the system during periods of sufficient moisture, regardless of when the system was installed”. Irrigation contractors are required by law to ensure that there is an operational rain shut off device on site before they can perform any services. If it doesn’t exist or isn’t working, the contractor can be fined for not reporting the property owner or by completing the repair work without installing or repairing the rain shut off device.
Florida Statutes 482.1562 states that all commercial fertilizer applicators must have a license from the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS) by January 1, 2014. To get this license, each Green Industry employee must be trained in Best Management Practices, which teaches professionals how to implement FFL principles. Additionally, to address water conservation Florida Statute 373.62 says the following: “Any person who operates an automatic landscape irrigation system shall properly install, maintain, and operate technology that inhibits or interrupts operation of the system during periods of sufficient moisture, regardless of when the system was installed”. Irrigation contractors are required by law to ensure that there is an operational rain shut off device on site before they can perform any services. If it doesn’t exist or isn’t working, the contractor can be fined for not reporting the property owner or by completing the repair work without installing or repairing the rain shut off device.
 Fertilizing Appropriately and Watering Efficiently are just two of the nine Florida-friendly landscaping principles. Right Plant, Right Place; Mulch, Attracting Wildlife, Managing Yard Pests Responsibly, Recycling, Reducing Stormwater Runoff and Protecting the Waterfront.are the other principles. Utilizing landscape techniques that reduce the inputs that can negatively impact natural resources is the foundation of Florida-friendly landscaping. By implementing the practices, the user saves money, reduces their workload and protects the environment. Many of the Florida-friendly landscaping principles are common sense applications. For more information visit the Florida Yards website.
Fertilizing Appropriately and Watering Efficiently are just two of the nine Florida-friendly landscaping principles. Right Plant, Right Place; Mulch, Attracting Wildlife, Managing Yard Pests Responsibly, Recycling, Reducing Stormwater Runoff and Protecting the Waterfront.are the other principles. Utilizing landscape techniques that reduce the inputs that can negatively impact natural resources is the foundation of Florida-friendly landscaping. By implementing the practices, the user saves money, reduces their workload and protects the environment. Many of the Florida-friendly landscaping principles are common sense applications. For more information visit the Florida Yards website.

by | Sep 16, 2013
While the recently passed Labor Day is often is touted as the traditional “end of summer,” according to the calendar, fall officially will begin with the fall equinox on Sept. 22nd at 4:44 EDT. In north Florida, however, we know good and well that our summer season extends a good bit longer.
Still, even if it just feels right, there is something going on now. When you walk out in the morning, the air feels just a bit more comfortable. The days are getting shorter, and that is beginning to have an effect. Perhaps it’s just wishful thinking, but if you squint just right, you can ALMOST see the end of our long and brutally hot summer.
The word “fall” commonly conjures up images of harvest, falling leaves, the end of the growing season and the beginning of dormancy leading into winter. For gardeners in North Florida, however, the traditional fall period is not a time of winding things down in the garden or even landscape but of revival and renewed effort. It’s a time when we finally can get back into outside and enjoy ourselves as the debilitating heat of summer starts to lose its grip on the weather.
For the next couple of months we will experience a gradual shift to milder weather. There will be cool spells followed by decidedly hot, summer-like weather, but as we move into late October, cooler weather will begin to dominate the scene. Not until mid-to late November do we generally experience the nippy cold weather and changing leaves that tell us, yes, indeed, fall has finally arrived.
One thing you that you might notice that may surprise you may be an increase of vigor in your warm-season bedding plants in September. Even heat-tolerant flowers do not always look their best in August.
Since shorter days mean fewer hours of intense heat, even though the daytime highs may stay about the same, plants begin to experience less stress. This encourages a “second wind”, if you will, in the flower garden that may last well into October or early November. Given this, consider cutting back some of your summer bedding plants and flowers that have grown tall and leggy over the just passed long growing season. This should be done in by the second or third week in September at the latest – and generally involves cutting plants back about one-third to one-half their height.
While you’re at it, it might be a good idea to impose some order on those overgrown flower beds. In addition to cutting back, groom plantings to remove dead flowers and unattractive foliage.
If plants are leaning or have fallen over onto nearby neighbors, prop them up or stake them so they will stand upright. Just about every year at this time I find the remains of some unfortunate plant that was overwhelmed when larger, more vigorous, nearby plants leaned over it.
In addition, if you haven’t done so already, gently trim your everblooming rose bushes, including such popular groups as Hybrid Teas, Grandifloras, Floribundas, Miniatures, Teas, Polyanthas, Bourbons, Chinas and English roses, to name just a few. This should be a very light trimming, little more than deadheading, since the main pruning of everblooming types is done in mid February. On the other hand, keep in mind that many old-fashioned climbers, ramblers, Lady Banks roses and some bush roses that bloom heavily only in spring to early summer will bloom next year on the growth they made this summer. Those roses should not be cut back at all now.
Even though you can get back into the garden to work, it is still too early to plant hardy trees, shrubs, ground covers and vines in the landscape. Temperatures in the 80s and 90s likely will be common in September, and that is still too stressful for new plantings. Wait at least until the cooler weather of October, since the ideal planting season for hardy trees, shrubs and ground covers really is from November through February. And for those that like to plant pecan trees, these are often done in bare root when the trunk of the tree is about the size of a pencil. These MUST be done when completely dormant or you will not have a successful outcome.

While Fall is for Planting, be sure that you don’t start too early!
Keep in mind that even though they will begin to show up in area nurseries this month, it is also is too early to plant cool-season bedding plants. Even if you have an area where your summer flowers have finished and have been removed, it is still too hot to plant most cool-season bedding plants. Instead mulch the area now and wait until the reliably cooler weather of October or November before you plant your bedding plants.
Spring-flowering bulbs, such as tulips and daffodils, become available this month, but there is absolutely no hurry to plant them. Purchase them if you like while the selection is good, but wait to plant your spring flowering bulbs from mid-October through early December.
Keep in mind that insects and diseases stay active through the fall, so continue to control any pest problems with timely applications of the proper material. In addition, don’t forget, now as always, water well during dry periods, and you should have an excellent crop of flowers in October through November.
I guess if you think about it, it’s best to say that Labor Day really marks that time in north Florida when we can anticipate the soon-to-arrive milder weather and look forward to enjoying the delights of gardening over the next few months. When the fall equinox arrives later this month, don’t get carried away. For us, summer will still be lingering for a little while longer.

 Turfgrass that is overwatered can suffer several fates. Roots can stay shallow near the surface and not dig deep into the soil as they should. A deep root system allows the turf to be more resistant to stress from drought, disease and abiotic factors such as wear from traffic. Excessive water leads to excessive lush growth – that may sound like a good thing, but it’s not. Excessive lush growth leads to thatch build-up and it creates a perfect environment for pests and diseases. An abundance of water also assists those nasty weed seeds to germinate and compete with your turfgrass.
Turfgrass that is overwatered can suffer several fates. Roots can stay shallow near the surface and not dig deep into the soil as they should. A deep root system allows the turf to be more resistant to stress from drought, disease and abiotic factors such as wear from traffic. Excessive water leads to excessive lush growth – that may sound like a good thing, but it’s not. Excessive lush growth leads to thatch build-up and it creates a perfect environment for pests and diseases. An abundance of water also assists those nasty weed seeds to germinate and compete with your turfgrass.







