
by Pat Williams | Jan 22, 2021
For all my years in the classroom, I never let students say the “d-word” when discussing soil science. In some instances, we had a “d-word” swear collection jar of a quarter when you used the term and even today, I hesitate from spelling the word out in text due to feedback from all those I have corrected. In case you still need a clue on the “d-word”, it ends in irt.
As a horticulturist for 46 years, I have read, heard, and been told many secrets to growing good plants. I still hold firm that without proper knowledge of how soil works, most of what we do is by chance. Soil is a living entity comprised of parent material (sand, silt, and clay), air, water, organic matter (OM), and microorganisms. It is this last item which makes our soils come to life. If you have pets, then you know they need shelter, warmth, air, water, and food. From this point forward think of soil microorganisms as the pets in your soil. If you take care of them, they will take care of your plants.

Sandy soil without any organic matter at the Wakulla County Extension office.
There is a huge difference in habitat from a sandy soil to a healthy soil with a good percentage of OM (5% – 10%). In one gram of healthy soil (the weight of one standard paper clip), you can have bacteria (100,000,000 to 1,000,000,000), actinomycetes (10,000,000 to 100,000,000), fungi (100,000 to 1,000,000), protozoa (10,000 to 100,000), algae (10,000 to 100,000), and nematodes (10 to 100) (1). A teaspoon of healthy soil can contain over four billion organisms (2). These microorganisms are part of the soil food web and they form a relationship between soil and your plants. They help convert nutrients to useable forms and assist with other plant functions.
The question becomes how to take care of your soil pets. For years we have performed practices that compromise these populations. Growing up we put all of our grass clippings in the weekly trash. We know now how valuable those clippings are and to leave them be. Two practices still common today though are tilling and raking leaves.

Master Gardener Volunteer vegetable bed with organic matter added.
Tilling has a limited purpose. If I place a layer of organic matter on top of the ground, then tilling incorporates the OM which feeds my pets. Excess tilling of soil introduces large amounts of oxygen which accelerates the breakdown of OM thus reducing our pet populations over time. Another adverse result from tilling is disturbing the soil structure (how the parent materials are arranged) which can reduce pore spaces thus limiting water percolation and root growth. There is a reason agriculture has adapted no-till practices.
Raking leaves (supposedly the sign of a well-kept yard) is removing large amounts of OM. Do you ever wonder why trees in a forest thrive? All of their leaves fall to the ground and are recycled by the microorganisms. Each of those leaves contains macronutrients (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, sulfur, and magnesium) and micronutrients (boron, copper, chlorine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, and zinc) which are necessary for plant growth. You would be hard pressed to find all those nutrients in one fertilizer bag. So recycle (compost) your leaves versus having them removed from the property.
We are in our off season and tasks such as improving soil health should be considered now for soils to be ready in spring. Remember a little organic matter at a time and never work wet soils. As your OM levels build over the years, remember to change your watering and fertilizing schedules as the soil will be better adapted at holding water and nutrients. Soil tests are still recommended before fertilizing.
If you would like more tips on improving your soil, contact me or your local county horticulture extension agents. For a more in depth look at caring for your soils, read The Importance of Soil Health in Residential Landscapes by Sally Scalera MS, Dr. A.J. Reisinger and Dr. Mark Lusk (https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss664).
- Chapter 2: Soils, Water, and Plant Nutrients. Texas Master Gardener Training Manual.
- The Importance of Soil Health in Residential Landscapes. 2019.

by Ray Bodrey | Oct 7, 2020
Who doesn’t enjoy a fresh, crisp bowl of salad? Lettuce happens to be a vegetable that is easily grown in Florida for fall & winter gardens. In Florida, four types of lettuce are commonly grown: crisphead, butterhead, leaf, & today’s topic, romaine.

Photo courtesy of Tyler Jones, UF/IFAS.
An interesting, little known fact about romaine lettuce is that it was cultivated extensively by the Roman Empire. By the fourteenth century, the Catholic Hierarchy had moved from Rome to Avignon, France bringing their prized lettuce along with them. During this period, the plant was known as “Avignon” lettuce. In England, romaine is called “cos” lettuce named after the Greek islands from which the lettuce was originally distributed. Of course, in the U.S., the name we give, Romaine, refers to the time when it was grown extensively in the Roman Empire.
Romaine is grown both commercially and in backyard gardens across the state. Like all lettuce, this is a cool season vegetable. September through March is a generally the extent of the growing season. Romaine can be grown from seeds or by transplants. If you are going the seeding route, just remember these seeds are very small and should be sown shallow and in a tight pattern, with 12”-18” row spacing and a light sprinkle of soil over the top. Newly planted seeds may require burlap or straw to help retain soil moisture for successful germination. Once plants reach a few inches in height, rows can be thinned to where plants are 8” apart.
Romaine needs adequate soil moisture throughout the season. Mulching around plants to retain moisture and adding a complete fertilizer such as 8-8-8 will help ensure a good yield. Lettuce is vulnerable to the usual suspects of garden pests. However, gardening in cooler months helps combat that threat.
Romaine lettuce is fun and rewarding to harvest, as well. You can pick a few leaves off a plant or harvest the entire head.
For more information, contact your local UF/IFAS County Extension office.
Supporting information for this article can be found in the UF/IFAS EDIS publication, “Romaine – Lactuca sativa L.” by James M. Stephens, Emeritus Extension Vegetable Crops Specialist, UF/IFAS: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/mv125
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Sep 28, 2020
2020 has not been the most pleasant year in many ways. However, one positive experience I’ve had in my raised bed vegetable garden has been the use of a cover crop, Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum)! Use of cover crops, a catch-all term for many species of plants used to “cover” field soil during fallow periods, became popular in agriculture over the last century as a method to protect and build soil in response to the massive wind erosion and cropland degradation event of the 1930s, the Dust Bowl. While wind erosion isn’t a big issue in raised bed gardens, cover crops, like Buckwheat, offer many other services to gardeners:

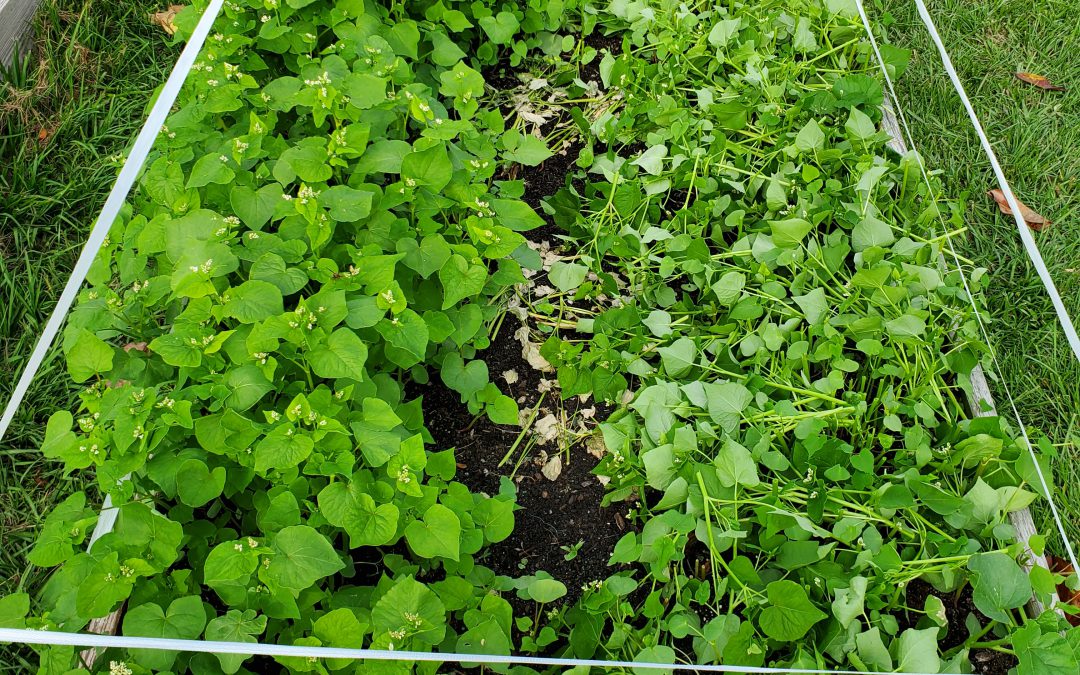
Buckwheat in flower behind summer squash. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
- Covers, like Buckwheat, provide valuable weed control by shading out the competition. Even after termination (the cutting down or otherwise killing of the cover crop plants and letting them decompose back into the soil as a mulch), Buckwheat continues to keep weeds away, like pinestraw in your landscape.
- Cover crops also build soil. This summer, I noticed that my raised beds didn’t “sink” as much as normal. In fact, I actually gained a little nutrient-rich organic matter! By having the Buckwheat shade the soil and then compost back into it, I mostly avoided the phenomena that causes soils high in organic matter, particularly ones exposed to the sun, to disappear over time due to breakdown by microorganisms.
- Many cover crops are awesome attractors of pollinators and beneficial insects. At any given time while my Buckwheat cover was flowering, I could spot several wasp species, various bees, flies, moths, true bugs, and even a butterfly or two hovering around the tiny white flowers sipping nectar.
- Covers are a lot prettier than bare soil and weeds! Where I would normally just have either exposed black compost or a healthy weed population to gaze upon, Buckwheat provided a quick bright green color blast that then became covered with non-stop white flowers. I’ll take that over bare soil any day.

Buckwheat cover before termination (left) and after (right) interplanted with Eggplant. Photo courtesy Daniel Leonard, UF/IFAS Calhoun County Extension.
Now that I’ve convinced you of Buckwheat’s raised bed cover crop merits, let’s talk technical and learn how and when to grow it. Buckwheat seed is easily found and can be bought in nearly any quantity. I bought a one-pound bag online from Johnny’s Selected Seeds for my raised beds, but you can also purchase larger sizes up to 50 lb bags if you have a large area to cover. Buckwheat seed germinates quickly as soon as nights are warmer than 50 degrees F and can be cropped continuously until frost strikes in the fall. A general seeding rate of 2 or 3 lbs/1000 square feet (enough to cover about thirty 4’x8’ raised beds, it goes a long way!) will generate a thick cover. Simply extrapolate this out to 50-80 lbs/acre for larger garden sites. I scattered seeds over the top of my beds at the above rate and covered lightly with garden soil and obtained good results. Unlike other cover crops (I’m looking at you Crimson Clover) Buckwheat is very tolerant of imperfect planting depths. If you plant a little deep, it will generally still come up. A bonus, no additional fertilizer is required to grow a Buckwheat cover in the garden, the leftover nutrients from the previous vegetable crop will normally be sufficient!

Buckwheat “mulch” after termination. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard, UF/IFAS Calhoun County Extension.
Past the usual cover crop benefits, the thing that makes Buckwheat stand out among its peers as a garden cover is its extremely rapid growth and short life span. From seed sowing to termination, a Buckwheat cover is only in the garden for 4-8 weeks, depending on what you want to use it for. After four weeks, you’ll have a quick, thick cover and subsequent mulch once terminated. After eight weeks or so, you’ll realize the plant’s full flowering and beneficial/pollinator insect attracting potential. This lends great flexibility as to when it can be planted. Have your winter greens quit on you but you’re not quite ready to set out tomatoes? Plant a quick Buckwheat cover! Yellow squash wilting in the heat of summer but it’s not quite time yet for the fall garden? Plant a Buckwheat cover and tend it the rest of the summer! Followed spacing guidelines and only planted three Eggplant transplants in a 4’x8’ raised bed and have lots of open space for weeds to grow until the Eggplant fills in? Plant a Buckwheat cover and terminate before it begins to compete with the Eggplant!
If a soil building, weed suppressing, beneficial insect attracting, gorgeous cover crop for those fallow garden spots sounds like something you might like, plant a little Buckwheat! For more information on Buckwheat, cover crops, or any other gardening topic, contact your local UF/IFAS County Extension Office. Happy Gardening!

by Mark Tancig | Jul 9, 2020
North Florida vegetable gardeners have made it to summer and now the plants and gardeners are starting to give in to the heat and humidity. The squash has likely succumbed to squash vine borers, many of the tomato varieties are having trouble setting fruit, stink bugs are all over, and gardeners easily wilt by noon. This is a good time to use our oppressive heat to your advantage in the vegetable garden by solarizing the soil.
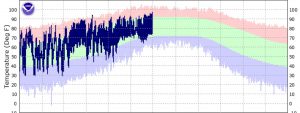
We have reached the peak of heat. Use it to your advantage in the garden. Source: National Weather Service.
Soil solarization is a method of pest control that creates a greenhouse to heat up the soil in an effort to drive away pests. Pests that can be reduced with soil solarization include weeds, various soil-borne fungal pathogens, and nematodes. Weed seeds can actually be killed by the increased temperatures, sometimes as high as 140 degrees Fahrenheit, while fungi and nematodes are merely driven deeper into the soil layer as they try to escape the heat. Although they are not killed, this can help vegetable gardeners as it may take these organisms 3-4 months to repopulate in high enough numbers to cause damage. Soil solarization can be considered another tool in your integrated pest management (IPM) toolbox, along with other cultural, physical, and chemical means of pest control.

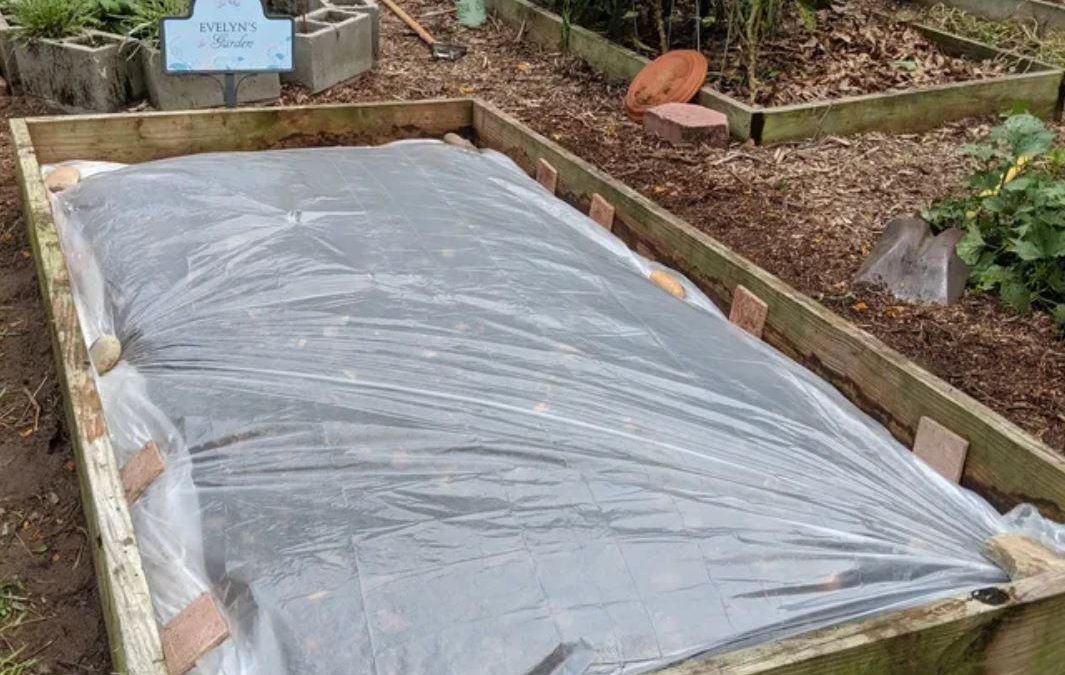
A raised bed being solarized over the summer. Source: Evelyn Gonzalez, UF/IFAS Master Gardener Volunteer.
To properly execute soil solarization, the site should be in full sun and the existing vegetation removed, either by hand or with a tiller or other implement. Tilling can help loosen the soil surface and allow heat to penetrate deeper in the soil horizon. Before being covered with plastic, the area should receive rainfall or be irrigated, as the water will help conduct heat to greater depths. The next step is to cover the area with plastic. Note that this can also be done over raised beds! Clear plastic is best for maximum solar radiation penetration. Black plastic will heat up mostly on the surface and opaque plastic sheeting may not let enough light in to get temperatures high enough. The plastic should be slightly larger than the area covered, as the edges will need to be buried to create an air-tight seal. It’s recommended to leave the plastic in place for at least six to eight weeks, just in time to begin fall gardening preparations.
It’s important to monitor the site while it’s “cooking” to look for any holes that might appear. Small holes can be repaired with duct tape, while large holes or rips in the plastic may require starting over. Overlapping strips of plastic is not recommended since too much heat will be lost.
You may be wondering what happens to all of the good soil microbes. Well, unfortunately, they are also either killed or suppressed. Fortunately, researchers have found that they are able to repopulate quicker than the pest organisms, especially in soils with a good amount of organic matter.
Much more information on soil solarization can be found in these two documents:
Introduction to Soil Solarization – https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/IN/IN85600.pdf
Solarization for Pest Management in Florida – http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/IN/IN82400.pdf
Also, please contact your local county extension office for more gardening tips.
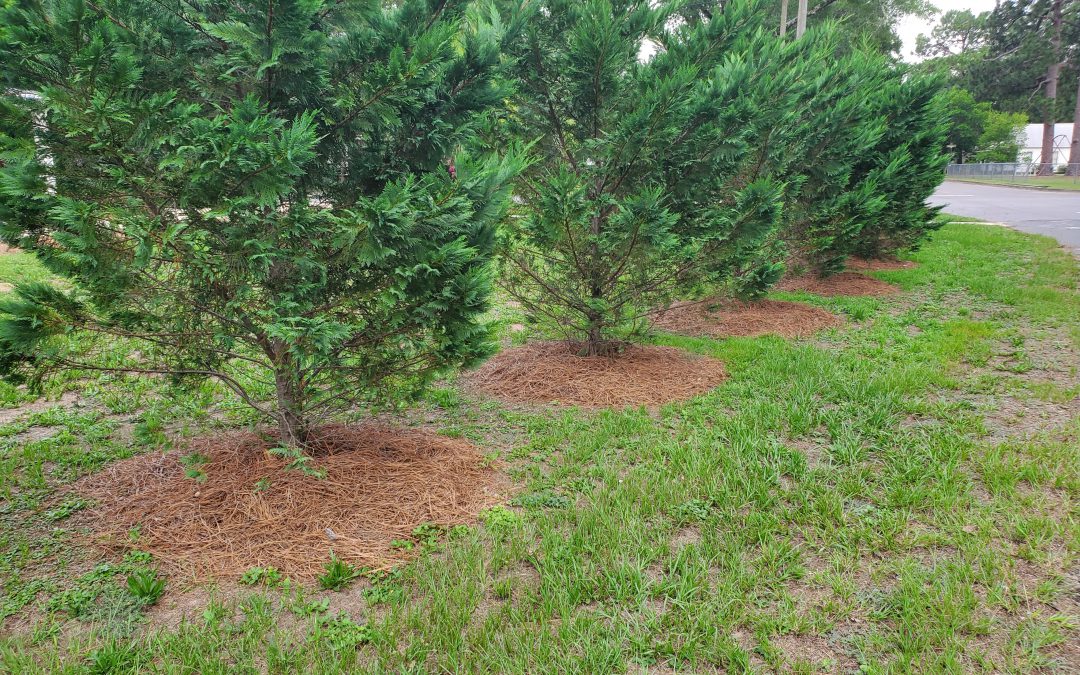

by Evan Anderson | Jul 1, 2020
A lot can go wrong in a garden or landscape, but proper preparation can help to avoid many of these problems from popping up in the first place. For some of these problems, a good preventative measure is mulch.

Pine straw is a common material used as mulch.
Mulch is any material that’s spread over the surface of the soil. One of the most common materials used in our area is pine straw, which is simply the needles of pine trees harvested from forested lands. Pine bark, another byproduct of the forestry industry, can be found easily as well. Both of these mulches will tend to have an acidifying effect on soils over time.
Other popular mulches include shredded or chipped wood. Melaleuca trees were originally planted in South Florida in an attempt to convert wetlands into farmable areas; to help remove this invasive species, the trees are now cut and ground into mulch. Eucalyptus mulch is also popular, as well as cypress, though it can be difficult to determine where cypress mulch originated from. Improperly harvested cypress can damage Florida’s natural wetlands. Hardwood mulch from other species may also be found.
Utility companies may sometimes give away mulch produced as they trim trees and bushes along their power lines, but this should be used only with the understanding that it may contain weed seeds or traces of herbicides or other chemicals. Homeowners may sometimes produce their own mulch in the form of raked leaves or grass clippings, but the same concerns about weed seeds and chemicals apply here as well.

Mulch can be used to help avoid hitting plants with a mower or trimmer.
Gravel or pebbles may often be used, especially in wet areas, or close to houses where flammable materials may be ill advised. Lastly, garden mulches may include materials such as paper or plastic spread in sheets over the ground.
Choosing the proper mulch can depend on the reason for its use. There are a number of effects mulch can have on a garden or landscaping bed. Mulch can help to retain moisture in the soil, keep weed growth down, reduce erosion, and act as a temperature buffer for the soil and plant roots below. It may also add visual appeal and help to keep lawn mowers and trimmers from needing to get too close to plants which may be damaged by them.
Whatever the reasons for adding mulch, there are a few things to avoid. Do not mound mulch around the base of plants. Moisture held against the trunk or stem of a plant can lead to fungal problems. Try to maintain a layer two to four inches deep. Any less and weeds will grow through the material; more mulch will not allow water to filter properly to the ground. Finally, if mulch becomes clumped and matted over time, do not let these block air or moisture to areas below. Rake or stir the mulch to evenly spread it.
You can find more information on mulching at our EDIS site https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/topic_mulch or in the Florida Friendly Landscaping site at https://ffl.ifas.ufl.edu/handbook/Mulch_vSept09.pdf.
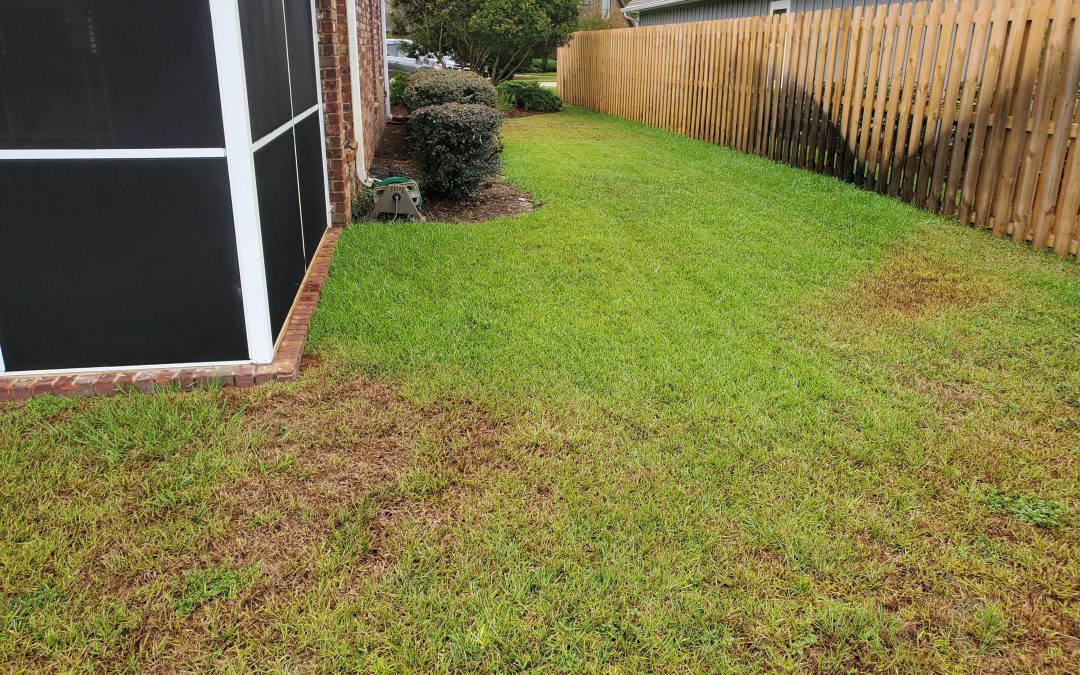

by Evan Anderson | May 13, 2020
As temperatures lean more toward summertime highs, conditions can sometimes leave a landscape looking sad. Water issues can be a major source of headaches for homeowners when they cause plants to decline. The cause is not always readily apparent.

Footprints remain in droughty grass. Photo courtesy of Taylor Vandiver.
Water is something not even the meanest cactus in the driest desert can do without. Too little, and plants start to develop symptoms of drought stress. These symptoms include more than just wilting; stunted growth, curling or rolling leaves, fruit or leaves dropping, and yellowing or browning especially at leaf edges are all clues that a plant is thirsty. In lawns, underwatered grass may not spring back when stepped upon, leaving visible footprints in the turf. Long periods of drought stress can cause grass to thin. Plants exhibiting symptoms such as these may require extra water. A layer of mulch around landscaping can also help to retain moisture if soil dries out too quickly. Newly installed plants are particularly susceptible to drying out, and hot weather dries out all plants more quickly.
Plants can also be overwatered, however. Even with the well-drained, sandy soils that are present in much of the Florida Panhandle, it is possible to put too much water on a lawn or landscape. This can lead to problems that may be similar to those caused by underwatering – stunted growth, curled leaves, wilting, limbs or leaves dying, and increases in fungal disease can all occur. Lawns may become patchy and weeds, especially those that enjoy damp conditions such as sedges or dollarweed may establish themselves.

Improperly calibrated sprinklers. Photo courtesy of Evan Anderson.
Stress of any sort can also leave plants more susceptible to pest and disease issues. A healthy plant is better able to compete with weeds and fight off infestation or infection. If you notice problems with fungal disease, increased insect populations, or weed issues, it could be made worse by over- or underwatering!
To help avoid watering issues, make sure plants with similar water requirements are planted near one another. If you have irrigation for your lawn or landscape, it is important to calibrate it regularly. Make sure the system has a rainfall shutoff device and check systems for damaged or malfunctioning emitters. And remember, if you are having trouble with your lawn or landscape, contact your local Extension office for help!
You can find further information on watering in our EDIS publications located at https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/topic_landscape_irrigation_and_fertilization, and at our Gardening Solutions website at https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/care/irrigation/.


















