
by Mark Tancig | Sep 18, 2017
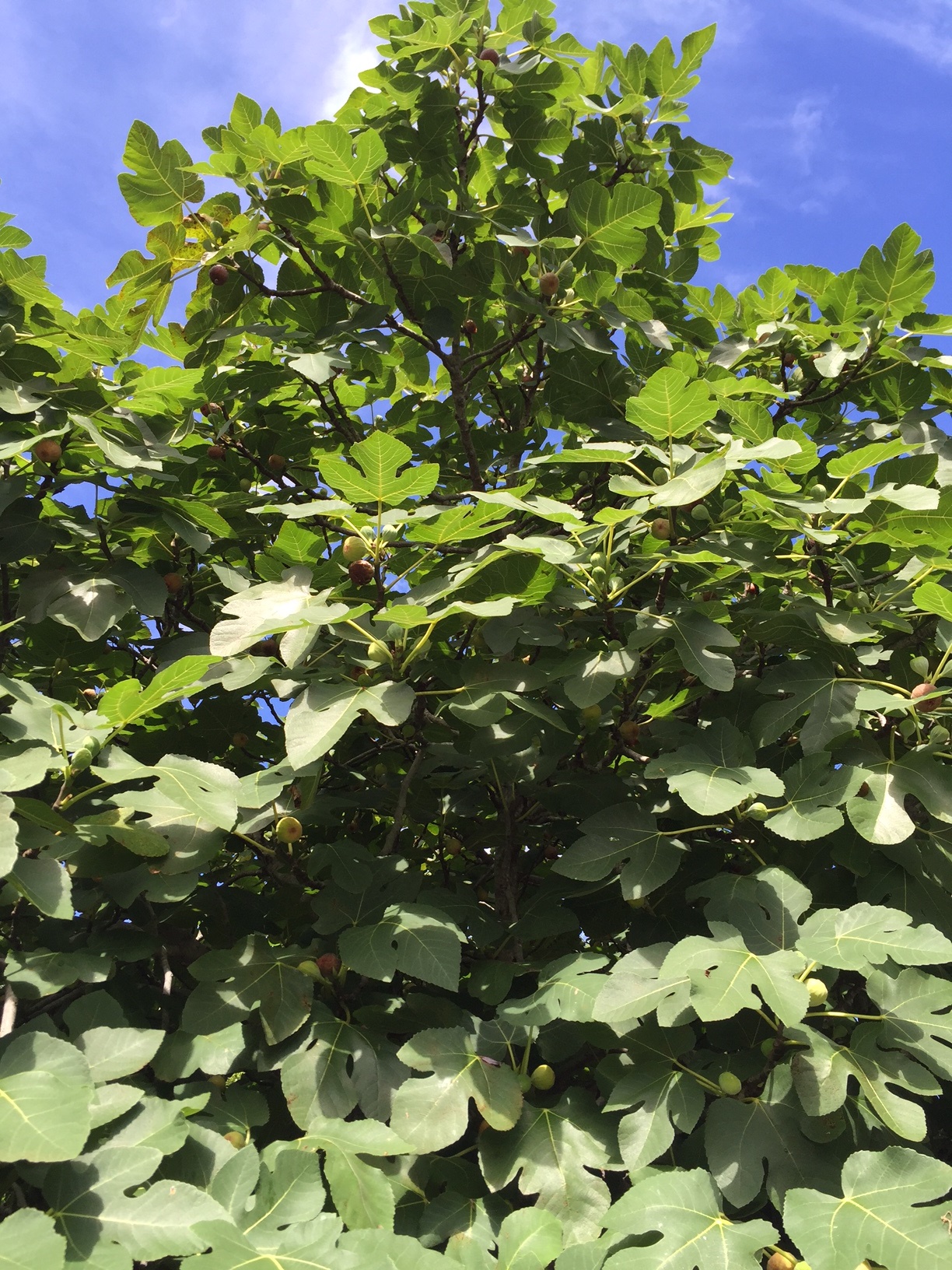
Hopefully, by this time of year, most north Florida gardeners have harvested their figs and are enjoying fig preserves or fig bars. But if you’ve noticed your fig leaves dropping a little early, it may be a sign of the fungal disease Fig Rust (Cerotelium fici).
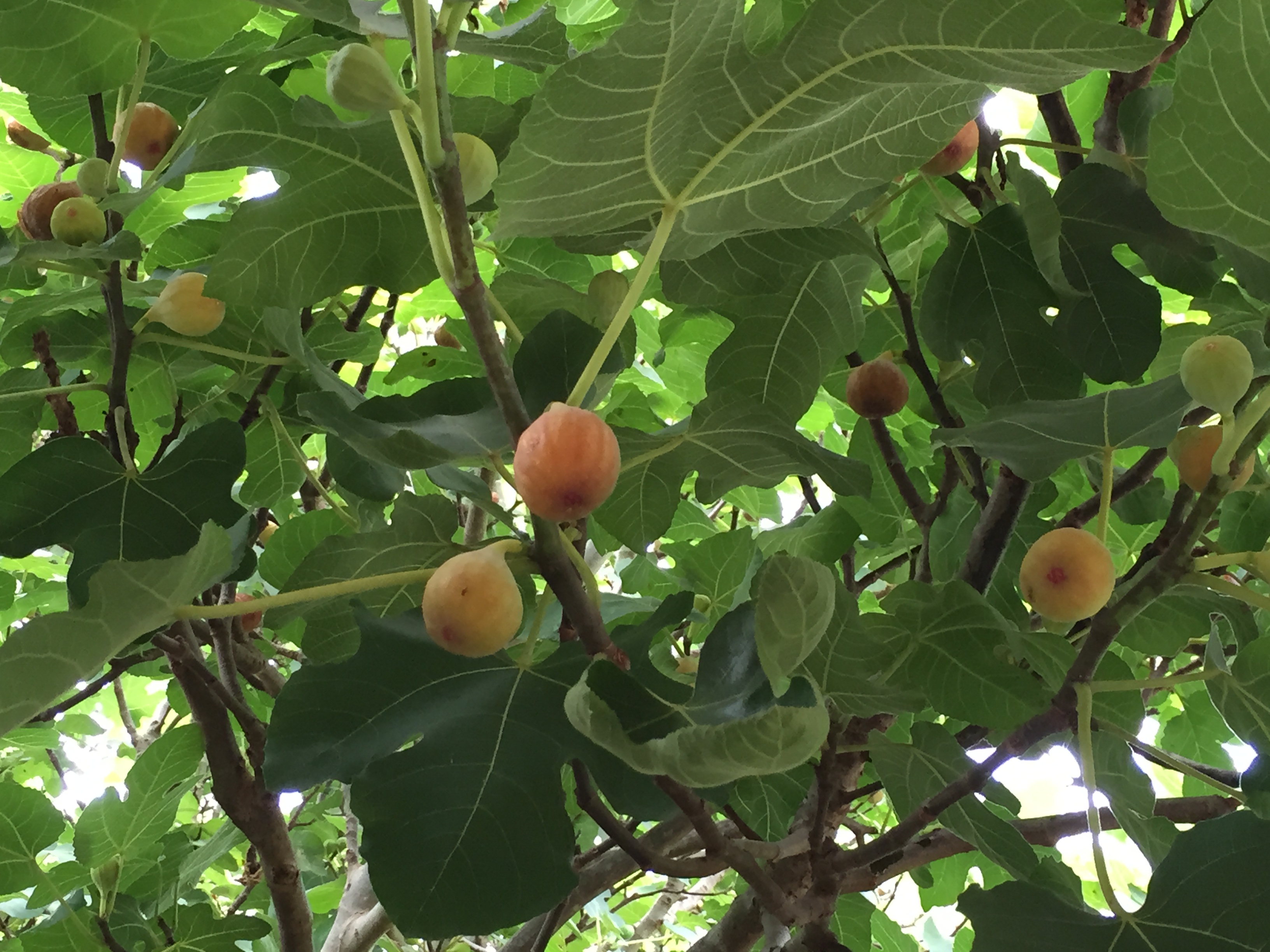
Figs are a great fruit tree for the north Florida home garden. Not only do they provide a tasty reward (if you can keep the birds and squirrels away), but they are fairly easy to maintain and are bothered by relatively few pests and diseases. One of the few diseases that can be common, however, is fig rust, especially when conditions are favorable. In the case of fig rust, a fungus, warm humid weather is what it likes and well, we have plenty of that.
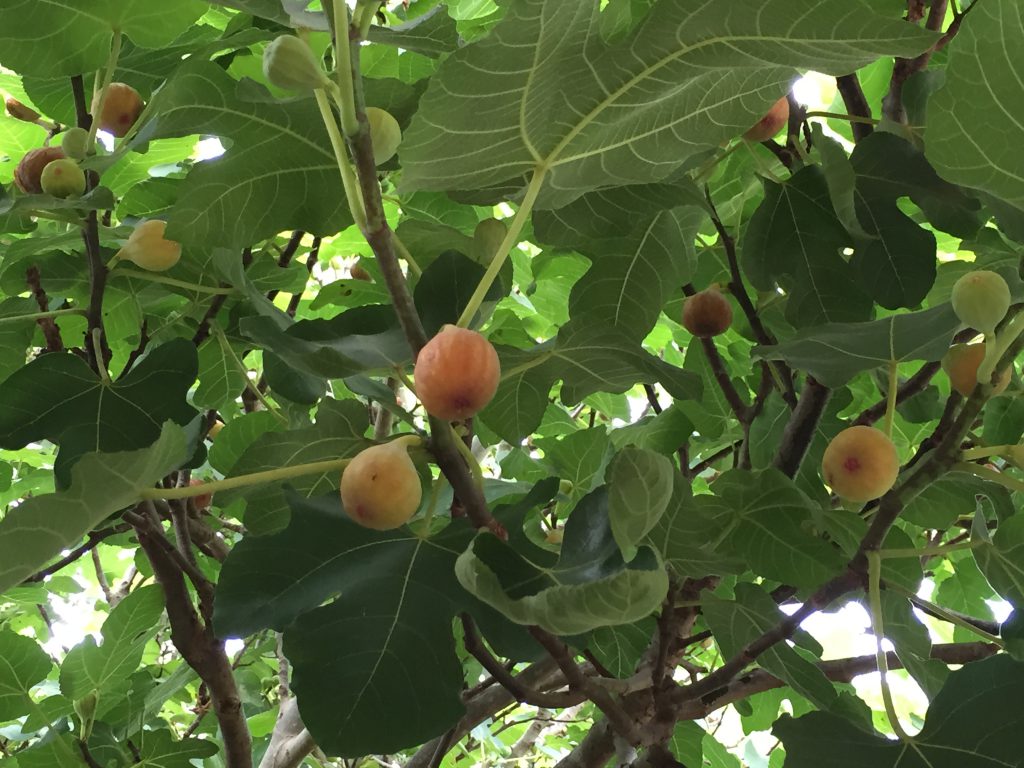

Figs are a great fruit tree for North Florida. Credit: Mary Derrick, UF/IFAS.
The first signs of the fig rust disease are small yellow to yellow-green spots/lesions on the upper surface of the leaf that turn a reddish-brown color as they get larger. A heavy infestation causes the leaves to turn yellow and drop early. While fig rust does not injure the fruit, repeat occurrences of premature leaf drop can adversely affect the overall health of the tree, resulting in yield loss. Another concern is that if the leaves drop too early, the tree will flush out with new growth heading into winter. This new growth can be injured by early freezes and cause a loss of fruit the following season.

Fig rust on leaves. Credit: UF/IFAS.
What can you do to prevent and/or cure fig rust? Unfortunately, once you see the yellowish-green/reddish-brown spots on the leaves, it’s too late to provide any control. As always, proper cultural practices can help. Pruning the tree to provide adequate airflow keeps the leaves as dry as possible during our humid summers. Remember to prune fig trees in Florida after fruit harvest, not in the dormant season, since fruit is borne on previous year’s growth. Another cultural control to prevent fig rust is to rake diseased leaves out from under the tree. The fungal spores in the fallen leaf litter pass the disease on to next year’s leaves. Other cultural controls include providing adequate moisture and placing a healthy dose of mulch around the tree. Figs require minimal fertilizer. Using a general complete fertilizer with micronutrients (such as a 10-10-10), young trees should receive 1 cup (1/2 pound) and mature trees 4-8 cups (2-4 pounds) per year.
There are currently no chemical controls approved for fig rust in Florida. The classic Bordeaux mix is recommended by various authors to be used as a preventative fungicide during the dormant season, before the lesions appear on the leaves. The Bordeaux mixture is a mix of copper sulfate, lime, and water in a 1:1:10 ratio and is considered an organic pesticide. This mix has been used since the late 19th century and was discovered by accident after botanists and farmers realized that grapevines sprayed with the mix to deter theft had less fungal problems. As with any pesticide, be cautious when using. Overuse of copper-based fungicides can cause copper to build up in soils, leading to potential issues to plant and human health.
While figs are generally worry free for our area, fig rust is one disease to be on the lookout for. Good gardening practices can reduce the occurrence of this disease and ensure a bountiful harvest. For questions on growing figs or about the fig rust disease, visit the UF/IFAS EDIS website – edis.ifas.ufl.edu – or contact your local Extension office.

by Larry Williams | Dec 2, 2016
 Billions of leaves blanket the fall landscape and are bagged by hundreds of homeowners to be placed curbside for local trash pick-up.
Billions of leaves blanket the fall landscape and are bagged by hundreds of homeowners to be placed curbside for local trash pick-up.
Many of these leaves could be easily turned into valuable mulch or compost.
Why do all those fall leaves end up in bags to be discarded?
It’s probably because the homeowner is overwhelmed by the volume. For instance, one resident reported raking more than 100 large bags of leaves from his half-acre property. One large oak tree can contain over 250,000 leaves!
Bagged and discarded leaves could become a quality mulch or could be composted.
Homeowners have tools for reducing 100 bags of leaves to 10 in their own backyards.
Shredding and composting can reduce leaf volume by 90 percent and provides a manageable quantity of valuable mulch and an excellent organic source for composting and converting into rich humus to improve garden soil.
Shredded leaves stay seated better on the landscape than whole leaves. They also do a better job of holding moisture in the soil and don’t mat down like whole leaves.
But how do you shred leaves if you don’t have a costly leaf shredder?
All you need is a lawn mower, a little extra time and a concern for the environment. Just put the leaves on the lawn in rows around three feet wide and two feet deep.
Then, with the lawn mower at the highest wheel setting, run over the pile. If the mower has a bag attachment, collecting shredded leaves is a neat and easy task.
Without a bag, the easiest way to collect them is to put a 9-by-12-foot drop cloth parallel to the row of leaves. Then, by running the mower in one direction so the leaves are discharged onto the cloth, cleanup is easier.
Throw the shredded leaves in the compost pile to cut the volume by another 50 percent.
Shredded leaves will shrink within a week and compost faster than whole leaves.
To compost dry leaves, add water, a little garden soil and a cup of garden fertilizer.
For more information on gardening and landscaping, contact the UF/IFAS Extension Office in your County.

by Beth Bolles | Aug 12, 2016
Homeowners and horticulture professionals spend time to develop an attractive ornamental bed only to have weeds take over months or a few years later. One common method in the attempt to prevent weeds is to apply a landscape fabric around plants in beds and place a layer of mulch on top to dress it up. The thought is that this barrier on top of the soil will prevent a large number of weeds from emerging. The fabric physically prevents the growth of weeds form the soil below and blocks sunlight from reaching weed seeds. Available fabrics are labeled as porous to allow air and water to move through them and reach ornamental plant roots.
On paper, landscape fabric sounds like a good idea and it may work for a little while. Over time, soil particles and decomposing mulch fill up the porous spaces in the fabric which prevent air and water from reaching plant roots. Even with irrigation or routine rainfall, plant roots often do not receive the needed water and air for healthy growth. Plants may respond by trying to send roots through fabric seams which breaks down the intended weed barrier. Other plants slowly decline or may die quickly due to water stress or lack of sufficient air movement into the soil.

Fabric may initially prevent some weeds but it can also prevent air and water movement. Photo by Beth Bolles, UF Extension Escambia County
Weed seeds also find their way into the mulch that is on top of the fabric from nearby lawns and landscapes. The next thing you know, you have an entire weed crop growing in the mulch on top of your landscape fabric. Perennial weeds such as torpedograss and purple nutsedge eventually grow through fabrics.

Seeds from annuals like Chamberbitter easily get into mulch from surrounding areas and grow on top of fabrics. Photo by Beth Bolles, UF Extension Escambia County
The best place to consider fabric if you want to install it in the landscape is under mulched paths or other areas without ornamental plantings where a synthetic groundcover is needed. In order to have a healthy root environment for your ornamental bed plants, it is best to keep landscape fabric out of these areas.

by Carrie Stevenson | Jul 26, 2016
Summer is full of simple pleasures—afternoon rainstorms, living in flip flops, and cooling off in a backyard pool. Among these, one of my favorites is walking out my door and picking handfuls of figs right from the tree. Before we planted our tree, my only prior experience with the fruit was a Fig Newton—I’d never eaten an actual fig, much less one picked fresh. Now, they are my favorite fruit.

When ripe, figs are a deep shade of pink to purple. Larger green figs will ripen over the course of a few days. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
Native to Asia Minor and the Mediterranean, figs were introduced to Florida in the 1500’s by Spanish explorers. Spanish missionaries introduced these relatives of the mulberry to California a couple hundred years later. Figs are best suited to dry, Mediterranean-type climates, but do quite well in the southeast. Due to our humidity, southern-growing figs are typically fleshier and can split when heavy rains come through. The biggest threats to the health of the trees are insects, disease (also due to our more humid climate) and root-knot nematodes.

Fig trees can grow quite large and produce hundreds of fruit each year. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
Our tree started out just a couple of feet tall, but 12 years ago we replanted it along a fence in our back yard. It has grown so large (easily 25 feet tall and equally wide) that it hangs over our driveway, making it handy to grab a few as I hop in the car to run errands. The tree is in full sun at the bottom of a slope, and seems to be a satisfied recipient of all the runoff from our backyard. This position has resulted in a thick layer of soil and mulch in which it thrives.
We usually see small green fruit start to appear in early May, becoming fat and ripe by the second half of June. The tree produces steadily through early August, when the tree’s leaves turn crispy from the summer heat and there’s no more fruit to bear. The common fig doesn’t require a pollinator, so only one tree is necessary for production. The fiber-rich fig is also full of calcium, potassium, and vitamins A, E, and K. As it turns out, the “fruit” is actually a hollow peduncle (stem) that grows fleshy, forming a structure called a synconium. The synconium is full of unfertilized ovaries, making a fig a container that holds both tiny flowers and fruit in one.

The insides of a fig show the small flowering structures that form the larger fruit. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
With the hundreds of figs we’ve picked, my family has made fig preserves, fig ice cream, baked figs and of course eaten them raw. We typically beg friends and neighbors to come help themselves—and bring a ladder—because we can’t keep up with the productivity. Often you can tell you’re near our tree from around the block, as the aroma of fermenting fruit baking on the driveway is far-reaching.
No matter what you do with them, I encourage planting these trees in your own yard to take full advantage of their sweet, healthy fruit and sprawling shade. As Bill Finch of the Mobile (AL) botanical gardens has written, “fresh…figs are fully enjoyed only by the family that grows them, and the very best figs are inevitably consumed by the person who picks them.”

by Molly Jameson | Jun 8, 2016
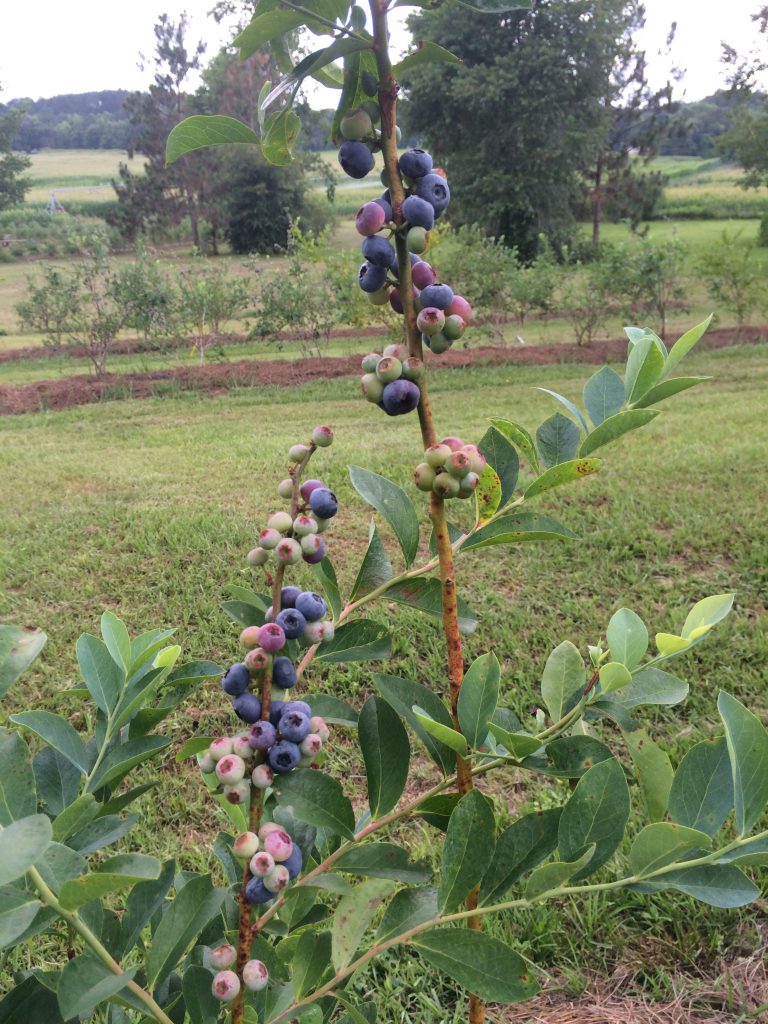

Blueberries beginning to ripen at Blue Sky Berry Farm. Photo by Molly Jameson.
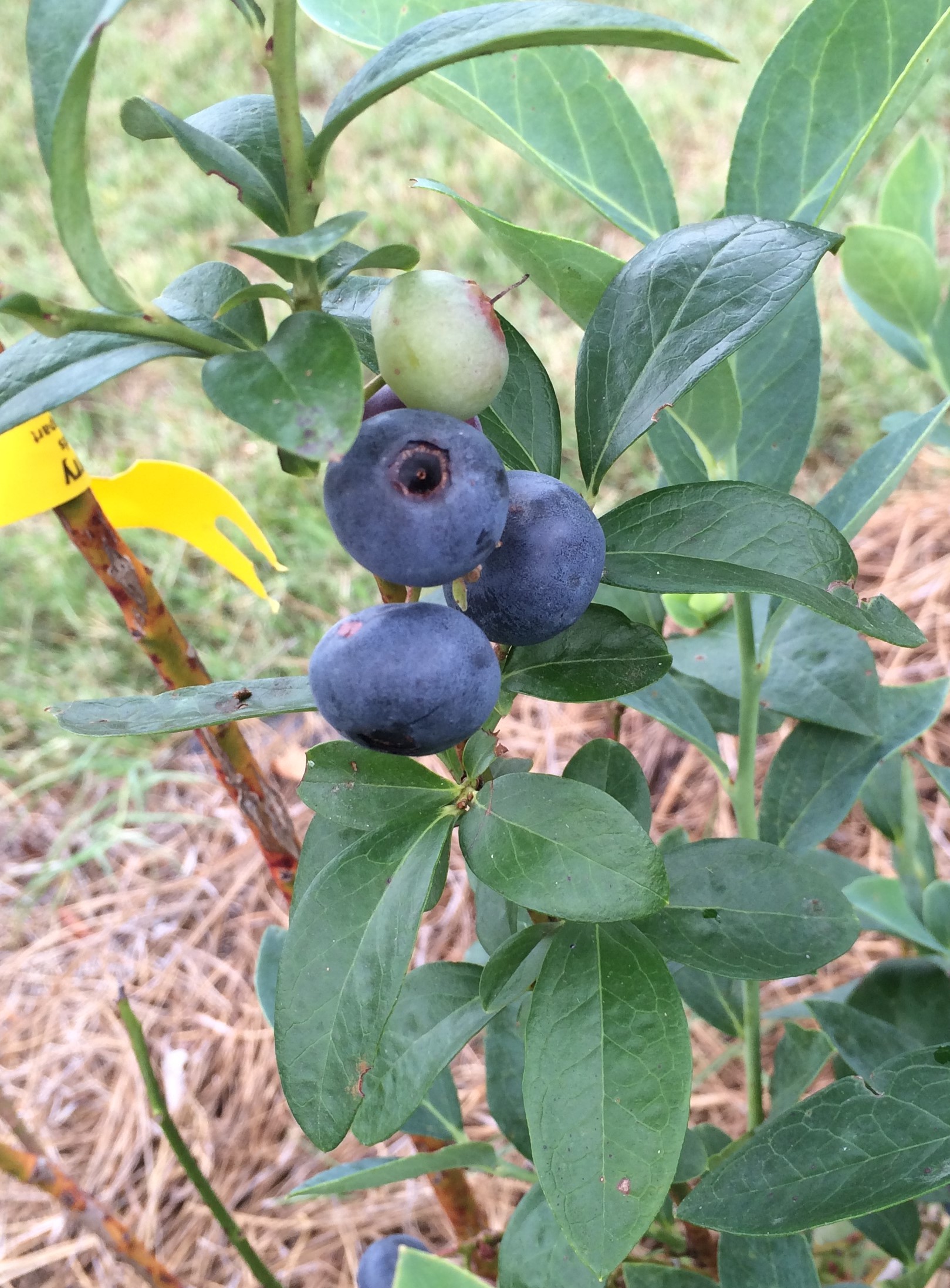
There is something almost magical about picking vibrantly blue blueberries off a bush and eating them fresh. If you watch the blueberries develop, you see them go from shades of pale green and blush red to dark and puffy and bright blue. When a blueberry is ready – you know it!
Blueberries are one of the few crop plants that are actually native to eastern North America. The most popular types are the rabbiteye blueberry (Vaccinium ashei) and the highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum). Both can be found in northern Florida and southern Georgia, and the highbush blueberry can be found as far north as southeastern Canada. There are at least eight other Vaccinium wild blueberry species that can be found in the woods and near swamps in Florida. They are usually smaller and don’t taste quite as sweet as the rabbiteye and highbush, but birds rely on them heavily for forage.
If you’ve never experienced a fresh blueberry right off the bush, then you may want to consider either foraging for wild blueberries, growing your own, or scouting out a local u-pick blueberry farm near you.

Mulch blueberries with pine straw. Photo by Molly Jameson.
Let’s first consider the joys of growing your own. Blueberries require an acidic soil pH, between about 4.0 and 5.5. Lucky for most of us in the Panhandle, our soil pH is largely naturally acidic. If you have pine trees growing in your area, you most likely can grow blueberries. And the pine straw makes an excellent blueberry mulch! There are many rabbiteye cultivars that have been specifically developed to grow well in our hot climate – requiring fewer “chilling hours” than their northern counterparts. Check out varieties such as Powderblue, Brightwell, Tifblue, and Climax. Highbush blueberries can also do well in northern Florida, although they tend to flower early, making them susceptible to late freezes. Try highbush varieties such as Bluecrisp, Emerald, and Star. Each has its own advantages and drawbacks, such as fruit cracking and insect susceptibility. Click here to learn more about growing blueberries in Florida.
If you are not already growing blueberries, and you want fresh blueberries, then be sure to check out a local u-pick near you. This year you may have noticed we had a warm winter, which delayed the onset of blueberry dormancy. This means the crop is hitting its peak about two or three weeks later than normal. But don’t delay – blueberry season in north Florida typically declines by the beginning of July, so the season is upon us!
If you are in the east Panhandle, be sure to check out u-pick operations such as Blue Sky Berry Farm, Myrtle Creek Farm, Green Meadows Farm, and Blueberry Springs Farm.
Blue Sky Berry Farm, which is located just three miles south of the courthouse in Monticello, on 1180 Ashville Highway, is entering its second season as a u-pick, and its bushes have really grown! They use organic fertilizer and grow using sustainable farming methods. Blue Sky Berry Farm anticipates being open Saturdays and Sundays from 8 a.m. to 1 p.m. this summer, but anyone interested in picking blueberries should first check the Blue Sky Berry Farm website (http://www.bskyfarm.com), as it is updated regularly during the season.

‘Titan’ blueberries at Blue Sky Berry Farm. Photo by Molly Jameson.
Green Meadows Farm, located at 177 East Bluebird Road in Monticello, is five acres of USDA certified organic blueberries. The farm is located among the trees and has been designated a Certified Wildlife Habitat by the National Wildlife Federation. It is open Fridays and Saturdays from 7:30 a.m. to noon and 5:00 p.m. to dusk, and Tuesdays from 7:30 a.m. to noon, while the blueberries last.
Myrtle Creek Farm, located at 2184 Tram Road in Monticello, has beautiful blueberry fields that are dappled with shade in the late afternoon and early evening. They currently have u-pick blueberries and blackberries available. They are open during the weekdays and weekends while the blueberries last, but do call ahead (850-997-0533) to check on availability.
Blueberry Springs Farm is located at 383 Wacissa Springs Road in Monticello, and is celebrating their 25th anniversary of harvesting blueberries. They first planted in December of 1991 and had their first harvest in June of 1991. They are open Tuesdays through Sundays 7:00 a.m. to noon and 5:00 p.m. to 7:00 p.m. You can contact Blueberry Springs Farm at (850) 997-1238 for updates, pricing, and directions.
Also check out the Florida Blueberry Growers Association website and the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services u-pick locator to discover u-picks around the state, including grape and blackberry u-picks.
Whether you are foraging for wild blueberries, picking your own blueberries, or visiting a u-pick, be sure to bring along plenty of water, a hat, close-toed shoes, and sunscreen, as blueberry season can be a very hot and sunny time of year! But once you’ve experienced your first taste of hand-picked Florida blueberries, you will be hooked and coming back for more each and every summer!

by Mark Tancig | May 24, 2016
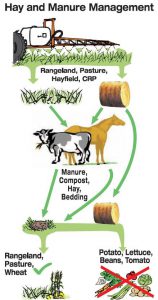
Humans have used animal manures to fertilize food crops for thousands of years. Manures are an organic source of plant nutrients and are often a waste byproduct that must be properly managed when raising animals. Today, many farmers and backyard gardeners continue to use animal manures to provide nutrition to their crops. However, a recent experience at our local extension office brought to our attention the need to know what else, besides nutrients, is in the manure used.
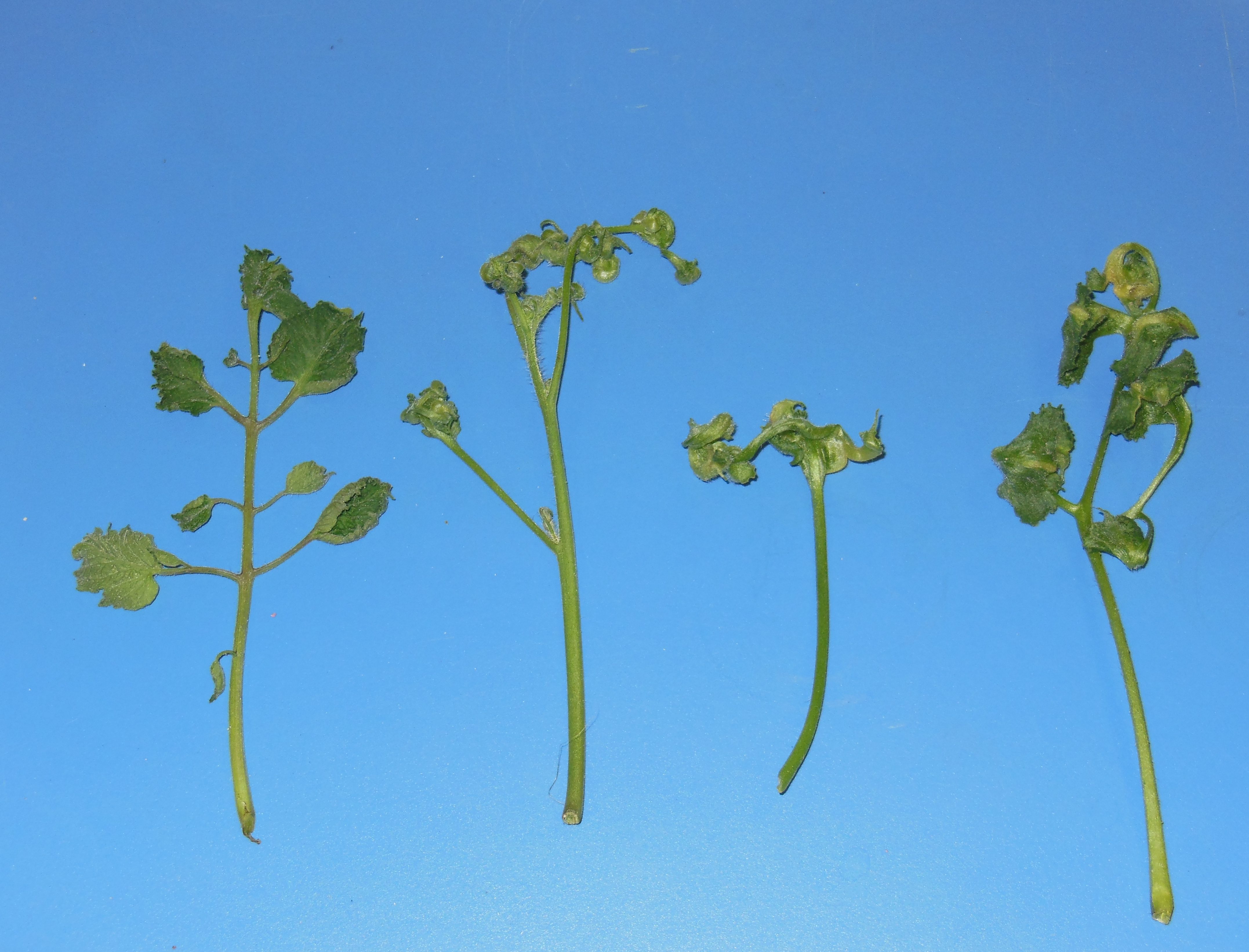
A local backyard gardener brought in samples of tomato plants that had strange new growth. She had purchased the tomato plants, along with other vegetable plants, from a local nursery. When she repotted the tomato plants into larger pots, she added horse manure from her own horses to the soil mix. She then noticed this strange growth on the tomatoes, but not in the other vegetable plants that were repotted without adding horse manure. Herbicide damage was one of the first potential causes we suggested, since the new growth was twisted and distorted, a common symptom of plants that have been sprayed by herbicides. The gardener was sure she had not sprayed any herbicides near these plants, or in the pasture where she keeps her horses.

Herbicide damaged tomato plants. Photo by: Mark Tancig
Photos of the tomato plants were shared with other NW District agents and an agriculture agent with livestock and hay producer experience had the probable answer – herbicide damage due to the horses being fed hay from a hayfield that was treated with a particular herbicide. Interestingly, this agent also had experience with these symptoms after their neighbor had similar issues using manure to fertilize the garden.
Herbicides with the active ingredients picloram or aminopyralid are able to cause this kind of unexpected damage to many gardeners’ crops. Herbicides containing these active ingredients are used in hayfields to control broadleaf weeds. These herbicides are especially effective at controlling hard to manage weeds such as thistle, nightshade, and nettle. They also provide long-lasting weed control. Unfortunately, the persistence of these ingredients extends into the hay, and also persists in the manure and urine of animals who eat hay from treated fields. These ingredients pass through the animal unchanged and remain active as an herbicide. Since many vegetable crops are broadleaf plants, the herbicide’s ingredients cause injury.
So what can a farmer or backyard gardener do to prevent this problem? When purchasing hay for livestock, ask the seller if they know whether the hayfield has been treated with herbicides that contain either picloram or aminopyralid. Most herbicides are known by their common names, rather than their chemical name. If they give you a common name or brand name, the active ingredient can be obtained by contacting your local extension office. If the seller can’t tell you, then, as a precaution, do not use the manure to fertilize broadleaf vegetable crops. The same question should be asked if purchasing hay for mulch as well. Composting the manure or hay does not break down the active ingredient, and may even concentrate it.
While we continue to use animal manures to fertilize our crops as our ancestors did, it’s important to remember that many of the tools and products we use today are much more advanced. These advanced products require that we stay informed of all precautions, use them responsibly, and, in this case, inform end users of any precautions. Remember to always read and follow the label and ask questions. And if a science-based answer is what you’re looking for, your local extension office is a good place to go!
Warning from herbicide label.



















