by Matt Lollar | Jun 4, 2018
Normally we think of rust as something that deteriorates metal, but a number of different fungal rusts can affect plants in the garden. Rust disease can affect corn plants, cedar trees, and even blueberry bushes. Just like the broad range of plant species that can be plagued by rust, there are a number of species of rust fungal spores floating around and ready to infest your garden. This article will focus on leaf rust of blueberry.
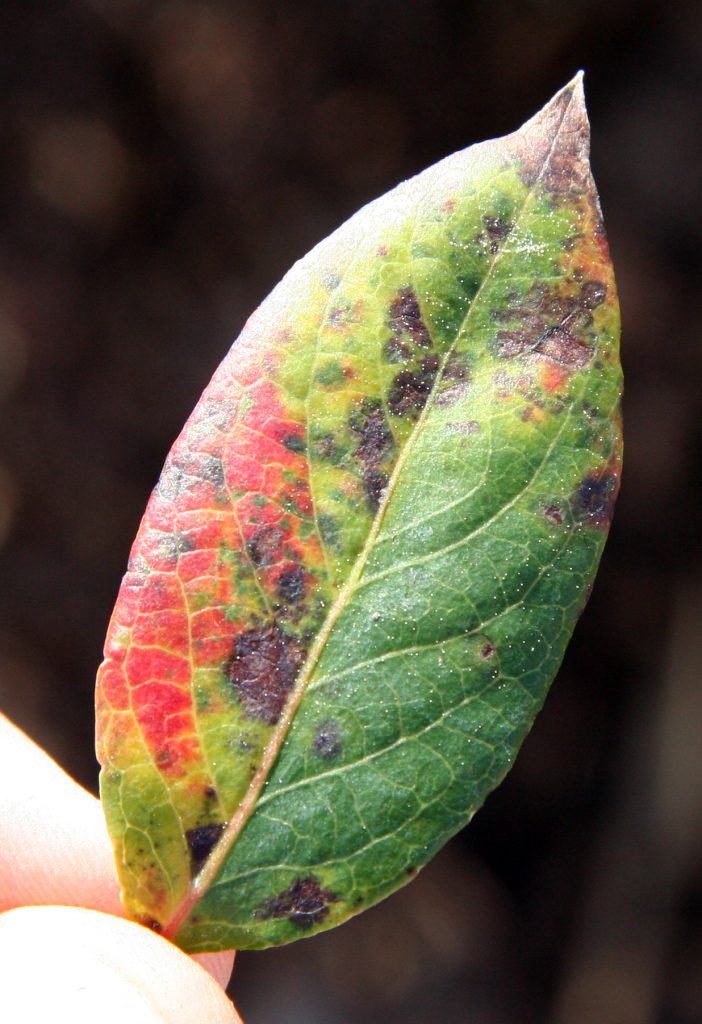

Blueberry leaf rust on the top of a leaf. Photo Credit: Philip Harmon, University of Florida/IFAS Extension.
Leaf rust of blueberry in Florida is caused by the fungus Pucciniastrum vaccinii. Although the common name of the disease is “leaf rust”, the disease can also infect the stems and fruit of blueberry plants. The disease causes small, round spots visible on the tops of leaves. Spots will multiply and the leaves will eventually yellow and fall off. Young stems and green fruit can also become infected as the disease progresses. Bright orange lesions will form on stems and fruit as the thousands of microscopic spores conjoin. The clusters of spores are easily wiped or washed off of plant material. When spores dry out, they become airborne and can be transferred to nearby plants.
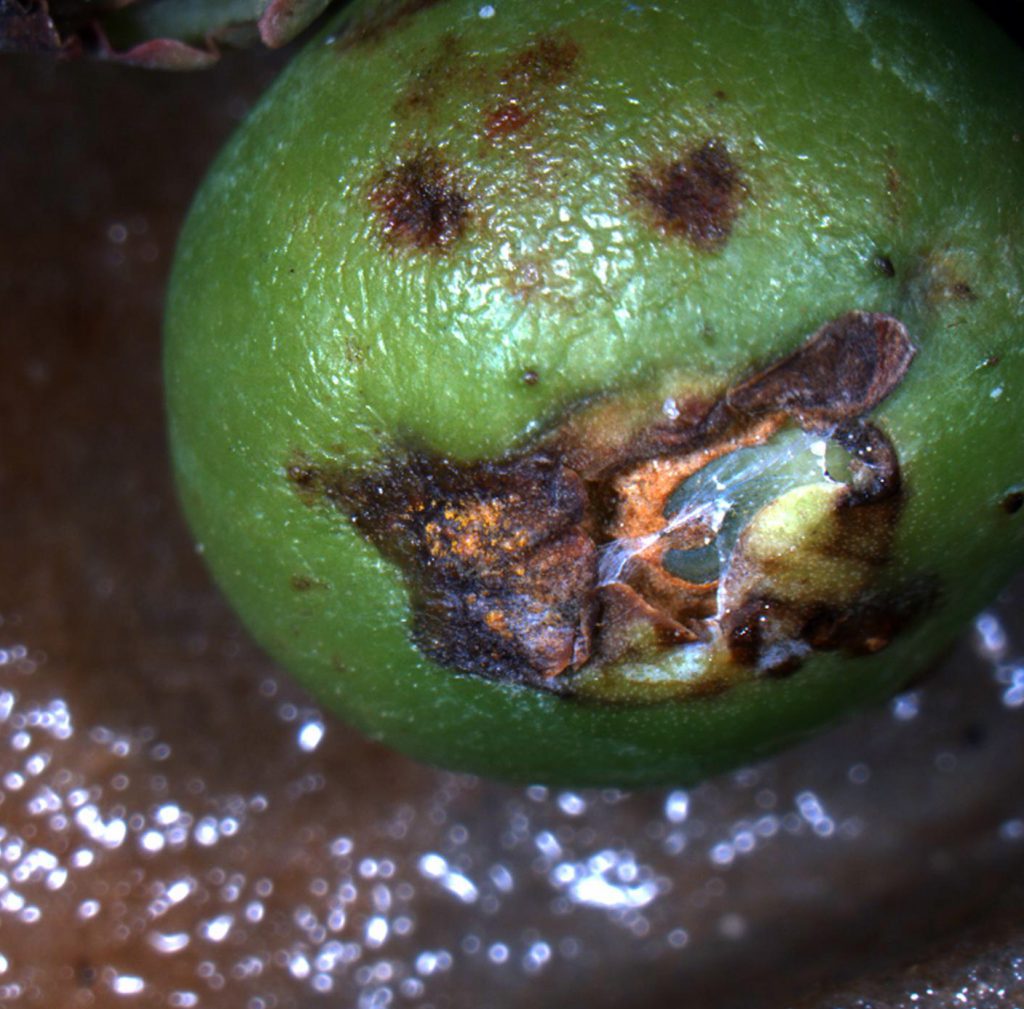

Blueberry leaf rust on fruit. Photo Credit: Philip Harmon, University of Florida/IFAS Extension
The rust fungus thrives in hot, humid, wet conditions. A number of cultural practices can be adopted to reduce disease progression and survival.
-
Irrigation
Disease persistence can be reduced by limiting the amount of water that contacts the plant leaves. Water the base of plants or install drip irrigation for your bushes rather than watering from overhead. If overhead irrigation is the only option, then water plants in the morning rather than in the evening. This allows the leaves to dry out over the course of the day.
-
Pruning
Removal of approximately 25% of the oldest canes in late winter before spring growth begins will stimulate the production of new canes and should result in plants with canes of different ages and will provide a good mix of vigorous branching and fruit production. Moderate summer pruning can also improve yield and shoot growth. When pruning, cut out vigorous shoots that are growing well beyond the desired canopy height and are in the interior portion of the bush. This will promote a more open growth habit and help with air circulation on the remaining plant material. Some vigorous canes developing from the ground and growing on the outside of the bush can be topped to stimulate branching and flower bud formation.
-
Mulch
Pine bark mulch helps with establishment of young plants and helps keep soil pH low in existing plantings. A layer of aged pine bark 3 inches deep extending about 2 feet out from the plants will provide a good growing medium for surface feeder roots. Pine straw can be used if pine bark is unavailable. Mulch also moderates soil temperature, helps keep weeds at bay, and adds organic matter to the soil. Make sure to keep mulch raked back about three inches away from the plant canes to provide good air circulation to the roots.
Hopefully this article has given you some tips to have a good blueberry crop for years to come. For more information on growing blueberries in Florida, please visit the University of Florida/IFAS EDIS Publication: Blueberry Gardener’s Guide.

by Mary Salinas | Feb 16, 2016
As you have read in other articles in this blog, it is too early to fertilize your lawn; however, this is a good time to start fertilizing your citrus to ensure a healthy fruit crop later in the year.

Orange grove at the University of Florida. UF/IFAS photo by Tara Piasio.
Citrus benefits from regular fertilization with a good quality balanced citrus fertilizer that also contains micronutrients. A balanced fertilizer has equal amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium such as a 6-6-6, 8-8-8 or a 10-10-10. The amount of fertilizer to be applied will vary on the formulation; for example you will need less of a 10-10-10 than a 6-6-6 as the product is more concentrated. Always consult the product label for the correct amount to use for your particular trees. Fertilizer spikes are not recommended as the nutrients are concentrated in small areas and not able to be widely available to all plant roots.
The number of fertilizations per year will vary depending on the age of the tree. Trees planted the first year need 6 light fertilizations that year starting in February with the last application in October. In following years, decrease the number of fertilizations by one per year until the fifth year when it is down to 3 fertilizations per year. From then on, keep fertilizing 3 times per year for the life of the tree. Good quality citrus fertilizer will have accurate and specific instructions on the label for the amount and timing of fertilizer application.
Fertilizer should be spread evenly under the tree but not in contact with the trunk of the tree. Ideally, the area under the drip line of the tree should be free of grass, weeds and mulch in order for rain, irrigation and fertilizer to reach the roots of the tree and provide air movement around the base of the trunk.
If you have not in recent years, obtain a soil test from your local extension office. This can detect nutrient deficiencies, which may be corrected with additional targeted nutrient applications.
For more information:
Citrus Culture in the Landscape
by Matt Lollar | Jan 27, 2016
We may be suffering from the recent low temperatures, but temperate fruit trees such as peaches and apples require a period of cold weather in order to become cold hardy and produce a good crop.
What is Cold Hardiness?
Cold hardiness is the ability of a plant to survive low temperatures. However, every cold event is fairly unique with variables such as when the low temperatures occur (early vs. late winter), how quickly the temperature drops, the temperatures in the days leading up to the event, and the length of time the low temperatures are sustained.
Cold Acclimation
Cold acclimation is the development of freezing tolerance in plants. Three fall environmental factors contribute to cold acclimation in fruit trees. Plant will develop 10 to 15 degrees of cold tolerance when the leaves sense shorter day lengths. Metabolic activity is increased when days are short and temperatures are between 60°F days and 40°F nights. The second factor occurs when lows reach the 20s, which can make trees up to 10 degrees hardier. The final factor occurs when temperatures dip to near zero, which fortunately for us does not occur very often.
Trees remain hardy during the winter as long as temperatures remain fairly stable. However, de-acclimation occurs in reaction to warm temperatures. This explains the winter flowering which occurred this past December. A cold snap may not injure trees unless it immediately follows a period of mild temperatures.

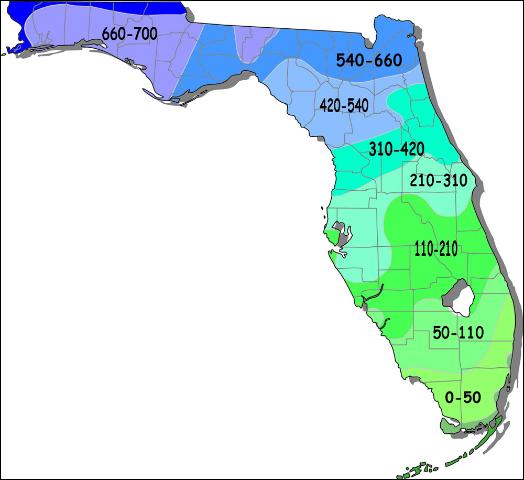
Florida Average Chill Hours Map – UF/IFAS Extension
Chilling Requirement
The cold weather and gradual cold acclimation are necessary to a tree’s accumulation of chill hours which is necessary for steady fruit yields. Chill hours are the accumulation of hours when temperatures are between 32°F and 45°F. The yearly average chill hour accumulation in Northwest Florida is between 660 and 700 hours. The apple varieties recommended for our area (‘Anna’, ‘Dorsett Golden’, and ‘TropicSweet’) have a chilling requirement of 250 to 300 hours. Some of the peach varieties recommended for our area (‘Flordacreast’, ‘Flordaking’, and ‘Gulfsnow’) have a chilling requirement of 350 to 400 hours. Please note the risk of planting these varieties because their chilling requirements are lower than our average chill hour accumulation. The varieties listed are for example, but other available varieties are suitable for our area.
Whether you like winter weather or not, just remember the satisfaction of eating fresh fruit in the summer. To track this year’s chill hours from the warmth of your home, please visit the AgroClimate tool at http://agroclimate.org/tools/Chill-Hours-Calculator/.

by Matthew Orwat | Nov 24, 2015

Satsuma fruit, harvested with their stem intact to ensure longevity when stored. Image Credit: Dr. Pete Andersen
The satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu) is a popular dooryard fruit tree, and emerging crop, across the Florida Panhandle. 100-150 years ago it was a major cash crop for the region, with boxcar loads being shipped to the Northeast during the months of October-December. Due to a series of hard freezes in the 1950s and a shift in land use from produce production to timber, the satsuma industry was effectively dead in northwest Florida until recent years, when several entrepreneurial growers have invested time and effort in bringing back this delicious citrus to the commercial scene.
Throughout this time, many homeowners have enjoyed this historic citrus, dressing many a Thanksgiving table with its beautiful bright orange fruit. Satsumas contain few seeds, are generally sweet and very easy to peel. They are part of the mandarin group of citrus, and somewhat resemble canned mandarin oranges in shape and flavor. The cooler the fall temperatures (above freezing) the sweeter the fruit will be at harvest.
Mature trees are hardy down to 14-18 º F when budded to a cold hardy rootstock such as trifoliate orange or swingle. Young trees need to be protected from temperatures below the mid 20s, and fruit will be ruined if exposed to any freezing temperatures below “light frost” conditions. Commercial growers use protective techniques, such as microirrigation, to protect their fruit if freezing temperatures threaten harvest.
This Thanksgiving, if you do not have a satsuma tree of your own, seek out a local producer and buy a case of satsumas for the holiday season !
For more information on growing and harvesting satsuma mandarins consult “The Satsuma Mandarin – HS195“, produced for your benefit by UF / IFAS Extension.






