
by Donna Arnold | Sep 30, 2024

Photo Credit: Danielle S. Williams
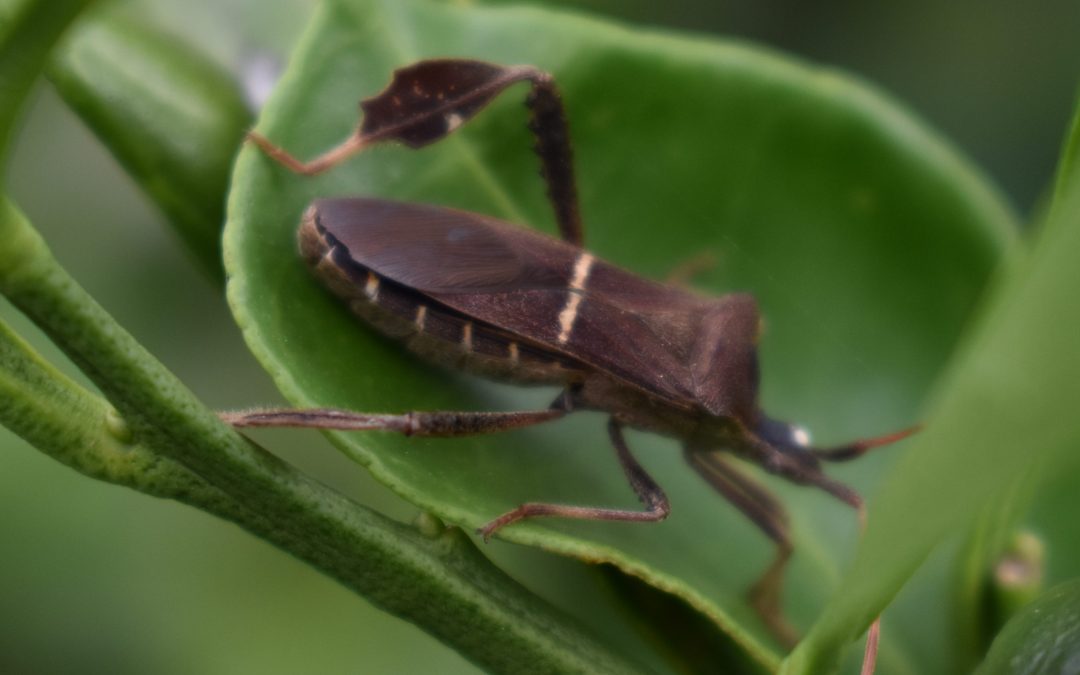
Florida is home to at least nine species of insects from the genus Leptoglossus, some of which possess “foliaceous hind tibiae,” but only Leptoglossus phyllopus has earned the common name “leaf-footed bug.” This insect, a close relative of the stink bug, plays a fascinating yet problematic role in gardens. The nymphs are bright orange, while the adults are brown with a distinct flattened, leaf-shaped structure on their hind legs. Unfortunately, both stages of the leaf-footed bug are notorious pests, causing significant damage to buds, flowers, fruits, and seeds.

Photo Credit: Jennifer Carr
These pests feed on a wide variety of plants, including tomatoes, peaches, blueberries, beans, okra, and sunflowers. Their feeding activity can cause yellow and brown spots, misshapen fruits, and shriveled produce, depending on the severity and timing of the infestation.
In the fall, leaf-footed bugs can gather on warm windowsills or home siding. They can sometimes find openings in homes and get inside, but they don’t cause any damage indoors and don’t deposit eggs. Adult leaf-footed bugs also seek shelter in weedy areas or beneath layers of mulch and debris. They lay their eggs in neat rows on the undersides of leaves or along stems, with eggs hatching within 5 to 7 days. The nymphs then mature in approximately 25 to 30 days, leading to a rapid increase in population.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies are highly effective for controlling leaf-footed bugs. IPM involves a combination of cultural, physical/mechanical, biological, and—when necessary—chemical control methods. Following the IPM triangle approach, gardeners can start with the least harmful methods (like cultural practices) and gradually escalate to chemical controls if needed, depending on the infestation threshold. Early scouting and intervention are crucial to preventing the population from escalating throughout the growing season.
Though there are only a few organic pesticides that effectively manage leaf-footed bugs, proactive steps like hand-picking and reducing overwintering sites can help curb their numbers in the following year. For larger infestations, homeowners might consider using pyrethroids, which should be applied according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Leaf-footed bugs are also susceptible to insecticidal soaps and other pyrethroid-based products available at most garden retailers.
A word of caution: Some beneficial insects, such as assassin bugs, resemble the orange nymphs of leaf-footed bugs. Be sure to correctly identify these insects to avoid harming species that are beneficial to your garden.
For more information about leaf-footed bugs and effective control measures click on the link below or contact your local Extension office for more details.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/in229

by Abbey Smith | Sep 4, 2024
Even though it’s still 98 degrees outside, it’s the time of the year to be looking ahead to plan a fall garden. With the optimal climate of Northwest Florida, the fall season offers gardeners a time to refresh their plots and prepare for another productive season. Here’s a guide to make the most of the fall gardening season!
Site Prep for Fall Gardens
When transitioning from summer to fall, it is important to prep the area where a new crop will be placed. It’s best to remove all dead material from your spring garden so it will not spread disease or bacteria to the new plants. You also may consider adding nutrients to the soil after it has been tilled for fall vegetables. The best method to know how much to add into the soil is by first taking a soil sample. The soil sample results will show what is readily available for vegetables going in the ground and will give you a baseline of how much fertilizer or organic amendments to add. The fall season is also one of the best times of the year to prioritize soil health. Another way to do this in the off season is to incorporate a cover crop into your gardening regimen. For more information on cover crops please visit: https://nwdistrict.ifas.ufl.edu/hort/2023/10/19/cover-crops-in-the-garden/

UF/IFAS Photo by Tyler Jones.
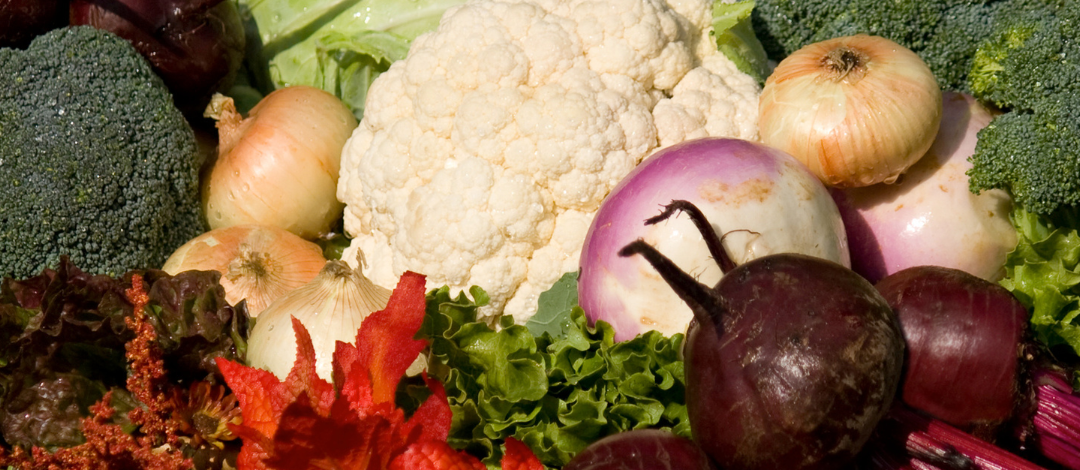
What Vegetables Do I Plant in the Fall?
The “cool” temperatures of a Florida fall make it very ideal for a variety of cool-season vegetables. Vegetables can be classified a hardy, semi-hardy, and tender based on their abilities to withstand freeze conditions, cold temperatures, or high heat. That is how can put vegetables in warm-season and cool-season groups. Tender vegetables are considered short season and are typically seen in spring and summer months. Examples of tender vegetables are potatoes, tomatoes, and squash. Semi-hardy vegetables are mostly frost-tolerant but cannot withstand freezing temperatures. Examples are carrots, leafy greens like Swiss chard and Bok Choy, peas such as sugar snaps, and celery. Lastly, hardy vegetables are a true cool-season vegetable that is frost-tolerant and can withstand freezing temperatures up to a certain degree. Examples of hardy vegetables are broccoli, cauliflower, kale, onions, and garlic. To find more information on fall vegetables in northwest Florida, please visit: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/EP451

UF IFAS Photo by Tyler Jones
Fall Garden Maintenance
With the temperatures being cooler in the fall months, your garden vegetables will require less water. It is best to water your garden early in the morning to allow the soil to dry out during the day. Doing this will prevent fungal growth and root rot. Utilizing mulch will also help conserve soil moisture, regulate the soil the temperature from the cool weather, and suppress weeds. Even through the winters are typically mild in Florida, it is still best to have a freeze protection plan for your garden. Using row covers or frost blankets will help shield your garden when the temperatures drop.
As you enjoy your fall garden, planning ahead for winter and spring will also set you up for success. Research what crops will follow best behind your fall harvest and consider starting your seeds indoors to get a head start. By embracing these fall gardening tips, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest and a thriving garden throughout the season. Happy Fall!

by Joshua Criss | Aug 12, 2024
Managing your soil is easily the most critical task in gardening. Well-managed soils retain water and nutrients, making them available to your plants, thus enabling them to thrive. It may seem daunting, but with a bit of knowledge, you’ll quickly discover that soil management is much simpler than you thought. Soil management can be broken down into two major topics. The first is the physical properties outlined in a previous article, which may be found here. The second, and arguably more complicated of the two, are those chemical properties that drive plant growth.
The What and Why of Soil pH
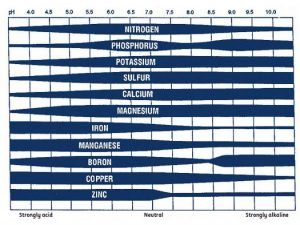
When considering chemical properties, you first need to look at soil pH. This is the measure of acidity or alkalinity within your soil profile. Innate soil pH is a product of the parent material from which your soil has formed, which tends to be slightly acidic on the Panhandle. Testing is the only accurate way to measure your soil’s pH level and buffering capacity. Your county extension office will be happy to facilitate that testing.
So, why is pH so important to plant growth? You’ll want to manage your soil’s pH for two reasons. The first is that soil acidity greatly influences the form that fertilizers and herbicides take in your landscape. Put into context, if you add fertilizers into the soil with an incorrect pH, that fertilizer may not dissolve in the water present. It will thus be unavailable to your plants. Here is another example of putting the right plant in the right place. Some, such as centipedegrass, thrive in a low-nutrition environment created by a low pH, whereas most vegetable plant species and many other landscape species only want a slightly acidic environment. Placing plants that will grow in the natural pH of your soil is a great way to ensure success in your gardens.
UF/IFAS photo
Ok, you’ve tested your soil and discovered it is not optimal for the plants you want to grow. Fear not, as you can take some actions to adjust your soil’s inherent acidity levels. Keep in mind that any changes will be very localized and are temporary. To raise soil pH, you must apply some version of calcium, colloquially called liming. Your calcium source should be based on soil testing, as different types may also add needed nutrients. Most notably, dolomitic lime will change soil pH while adding magnesium. Soil testing will also tell you to provide the buffering capacity of your soil, which will dictate the amount needed to adjust the soil properly. Soil pH may also be lowered through elemental sulfur additions, but this process is very difficult and may become detrimental to plant growth through repeated application. In this instance, it may be preferable to address via plant selection versus pH adjustment.
How Does Soil Hold Onto Water and Nutrition
The other main consideration for soil chemical properties is cation exchange capacity or CEC. Now, this can be a very complicated topic. Put very simply, it refers to your soil’s ability to retain both water and applied nutrients. It’s important to understand as it holds components critical to plant growth in the root zone of said plants. This happens as there are negative charges on the surfaces of clay particles in your soil that latch onto the positive ions of applied fertilizers.
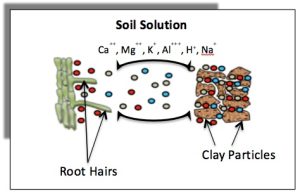
Photo: University of Georgia Extension
So, what about soils low in clay, such as those in Florida? Organic matter will help in this arena. It mimics clay’s properties and will retain nutrients better than your native soil. However, this is not a pass to add endless amounts of compost, as they come with a nutritive load that must be considered in your garden management plan. Adding 1-3 inches worked into your plant root zone is more than enough when establishing new gardens.
Understanding your soil is critical when gardening anywhere. In Florida, where soils are less than optimal, understanding how water and nutrients are retained and used by your plants will help avoid much frustration. For more information on soil management refer to these IFAS documents, or contact your local extension agent for additional information on this and any topic regarding your gardens and more.

by Abbey Smith | Jul 3, 2024

Rain barrel at the teaching demonstration gardens at the Alachua County Extension Office. Photo Credit: Tyler Jones, UF/IFAS
Water is one of the most valuable natural resources and with the ever growing concern of climate change and the hot dry conditions Northwest Florida has already experienced this summer, every drop counts. One way you could combat this issue is by installing a rain barrel at your home. By having a rain barrel on hand, you can reduce stormwater runoff, potentially save money, and improve the health of your plants. Here’s what you need to know:
What is a rain barrel? A rain barrel is a container or storage tank that collects runoff water from a catchment area (a rooftop). They are typically placed under downspouts and capture the water runoff from your home’s gutters. The type of container used to make a rain barrel could be any type, but it cannot have stored chemicals prior to its use as a rain barrel.
Now that we know the definition, why exactly do people use rain barrels? For one, they aid in water conservation. Rain barrels help reduce the amount of potable water used for outdoor purposes, which is important during dry weather spells and areas known for drought conditions. There are also potential cost savings with using a rain barrel. By using the collected rainwater for watering your garden, cleaning outdoor surfaces, or even washing your car, homeowners could potentially reduce their water bills significantly. Having a rain barrel is also a Florida-Friendly way to gardening. Rain barrel usage co-aligns with the Florida-Friendly Landscaping Principles #2: Water Efficiently and #8: Reduce Stormwater Runoff. The use of rain barrels also aligns with sustainable living. It reduces the reliance on municipal water systems and promotes awareness of water usage and conservation.
To install a rain barrel, you will need to obtain a container or “barrel” that is several gallons large to store the water. You can purchase or make one yourself! It will need a secure lid to prevent debris and insects from getting inside. The barrel will need to be placed under a downspout from your home’s roof gutter systems. The ground will need to be level and the barrel could possibly need to be elevated to make accessing the water easier. Once you have placed the rain barrel in the location you want it, you will need to install a rainwater diverter on your downspout. This will help channel the rainwater into the barrel and can be adjusted once the barrel has become full of water. You will also want to install a spigot near the bottom of the rain barrel to access the water and an overflow valve of some sort. The overflow valve will help redirect excess water away from your foundation when the rain barrel becomes full. Maintenance of a rain barrel is generally very low but you need to check regularly for debris in the water and ensure all the mechanisms are functioning like they should be.
How can you use the water collected in a rain barrel? The most obvious answer would be to water your garden and outdoor plants. Rainwater is perfect for watering the lawn, your flowers, and vegetable gardens. The water quality of collected rainwater is often more beneficial for plants as it is non-chlorinated water. Rainwater is also great for indoor plants too as it decreases the amount of mineral build-up that can occur from using tap water.
By installing a rain barrel at your home, you are taking a small leap with significant environmental impact. It is an easy, cost-effective way to reduce your utility bills, conserve water, and contribute to sustainable living. For more information on rain barrels and how to install one, please visit:
https://ffl.ifas.ufl.edu/ffl-and-you/home-landscapes/diy/rain-barrels/
https://sfyl.ifas.ufl.edu/lawn-and-garden/saving-and-using-rainwater/
https://blogs.ifas.ufl.edu/browardco/2019/07/01/florida-friendly-landscaping-adopting-water-conservation-practices-with-rain-barrels/
*This article was written with the aid of ChatGPT AI Services.*

by Daniel J. Leonard | Jul 3, 2024
While the Florida Panhandle isn’t considered a true tropical climate, now that the summer rains have started, it sure feels tropical outside. To create high performing colorful containers in these conditions, it’s wise to pick plants that hail from tropical climes – one of my favorites is Crossandra (Crossandra infundibuliformis).
Native to tropical Sri Lanka and India, Crossandra is built for hot, humid conditions. An evergreen subshrub growing about 3’ tall in its native range, Crossandra sports glowing orange flower clusters held high on stems that rise above deep green, glossy foliage – a very striking combination. These showy orange flowers arrive once temperatures heat up in the early summer and continue emerging en masse until cool nights stop the show in fall. While deadheading spent flowers can enhance Crossandra’s free-flowering nature, I haven’t found it totally necessary to ensure consistent flowering. In addition to being beautiful, Crossandra’s flower clusters are also attractive to a wide variety of pollinators, including butterflies and dragonflies.

Crossandra growing in partial shade on a patio. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
Adding to Crossandra’s appeal, the species couldn’t be easier to grow if you give it the right conditions. Crossandra prefers to be sited in areas that receive ample sunlight but also get a reprieve from the hottest afternoon rays. This year, I grew one on a deck that receives sun from about 10 am – 2 pm and is then provided filtered shade from a large tree the rest of the afternoon; these conditions seem to be ideal. Crossandra performs best in moist, well-drained soil, making potting mix an excellent option. Daily watering in the summer combined with our (hopefully) frequent rainfall in July and August keeps it wilt-free. I also apply slow-release fertilizer at planting and then supplement with liquid fertilizer periodically throughout the summer. This, combined with regular irrigation, promotes healthy, vigorous growth, and allows the flower show to continue uninterrupted until cool weather finally draws the curtains.
Crossandra is a versatile plant in container gardens, shining in either the role of filler in larger containers or as a solo specimen plant in its own container. In mixed containers, play off of Crossandra’s orange flowers with partial sun foliage plants like Coleus, Elephant Ears, or Hawaiian Ti, or flowering annuals like Browallia ‘Endless Illumination’, Torenia (Wishbone Flower), Blue Daze, or Purple Heart Plant. While Crossandra does well in mixed containers, as a UF graduate, I prefer to stick it in my favorite blue pot for an orange and blue Gator themed solo container!
Regardless of how you choose to incorporate Crossandra into your garden’s design, it will reward you with summer-long orange flowers in a low-maintenance package. Simply place it in morning to early afternoon sun, give it ample water and adequate fertilizer, and enjoy this Florida Friendly Landscaping approved species. Plant one today!
For more information about Crossandra or any other horticultural topic, contact your local UF/IFAS County Extension office.













