
by Julie McConnell | Sep 28, 2020
 Earlier this summer I talked about getting to know your weeds, so they’ll be easier to control. If you missed that article you can review it here “Why Can’t I Kill Weeds?”
Earlier this summer I talked about getting to know your weeds, so they’ll be easier to control. If you missed that article you can review it here “Why Can’t I Kill Weeds?”
Today we will look at the types of herbicides available so your selection will fit your situation.
Understand your herbicide options. Picking out the appropriate herbicide can be overwhelming. The options seem unlimited when you are standing in the store looking at aisles of containers. By preparing yourself before you shop you can save time and increase your chances of making the most effective selection. Here are some herbicide basics:
- Label interpretation. The pesticide label is a multipage document that describes ingredients, how a pesticide works, application instructions, safety requirements, and other important information for the user. Before applying any pesticide (yes, herbicides are pesticides!) you should read the entire label. Pulling the label off the package in the store may be frowned upon and the print is very small. For this reason, I would recommend looking up a few options before you go shopping and reading the labels online. This allows you to take your time to be sure you understand if it is the appropriate product and you can make your shopping list for personal protective and application equipment before you leave the house. Three important things to look for when selecting your product are active ingredient, labeled site (site includes the location such as residential landscape vs. agricultural crops and the plants it is safe to use on), and targeted pest.
-

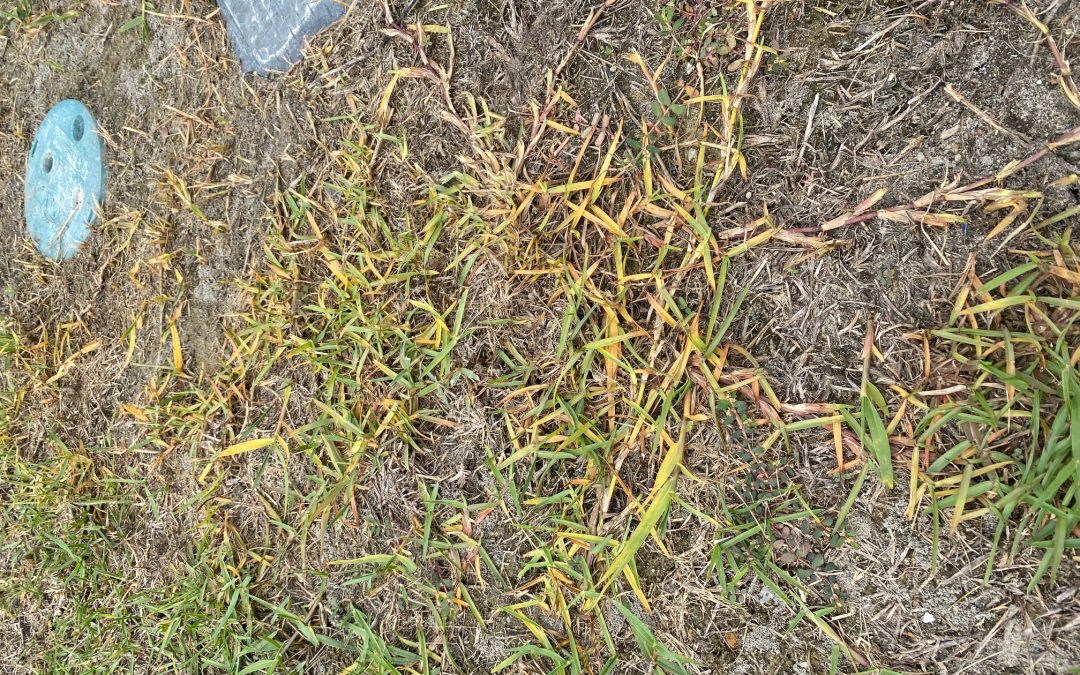
Non-selective, systemic herbicide damage on grass. Photo: J_McConnell, UF/IFAS
Pre-emergent herbicides. Pre-emergent herbicides provide control when applied BEFORE seed germination of your target weed. They do not prevent germination, rather they prevent emergence of shoots and roots essentially inhibiting normal plant growth which eventually results in plant death. It is important to have your product in place during the correct window of time. Typically, 1-2 weeks before germination of your target weed is ideal.
- For warm season annual weeds (crabgrass, goosegrass, sandspur, and spurge are examples) apply pre-emergent herbicides when day temperatures in early spring reach 65-70°F for 4-5 consecutive days. This may be mid-February or as early as January.
- For winter annual weeds (henbit, black medic, geranium, and chickweed are examples) watch for night temperatures in the Fall to reach 55-60°F for several nights in a row to indicate proper application timing.
- Some products are selective to plant types such as grasses, sedges or broadleaf weeds. Other products are more broad-spectrum and are effective on multiple weed types.
- Pre-emergent herbicide should not be used if you intend to plant seed – it will affect your desired plant in addition to the weed! There may also be effects on newly planted lawns or plants, so be sure to read the label closely to avoid damage to non-target plants.
- Post-emergent herbicides. These products are used on weeds that have already emerged, regardless of life cycle (annual, perennial, biennial). This type of herbicide will be applied directly to the weed you are trying to kill. There are a few categories within this group.
- Selective or non-selective.
Selective herbicides work on particular categories of plants: broadleaf, sedge, grass, or woody plant.
Non-selective herbicides can kill any type of plant regardless of category.
- Contact or systemic.
Contact herbicides kill the plant tissue it comes into contact with and does not translocate to the rest of the plant.
Systemic herbicides are translocated throughout the plant to affect more than just the place of absorption. These are ideal for perennial weeds that would regenerate from roots, bulbs, or tubers if the top is damaged or killed.
Effective weed management requires some preparation and research for the best outcome. For help with weed identification and control recommendations, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Office.
Further reading on weeds and herbicides:
Florida Homeowner Herbicide Guide: Considerations, Applications, and Selection
Postemergent Herbicides for Use in Ornamentals
Weed Management Guide for Florida Lawns

by Matt Lollar | May 27, 2019
Nobody likes weeds in their garden. Weeds are not only ugly, they can host insects and diseases that later spread to your garden. This situation commonly occurs when weeds belong to the same plant family as the desired landscape or vegetable species, but some insects and diseases have diverse palettes. For example, I recently witnessed a looper caterpillar on a pokeweed plant.
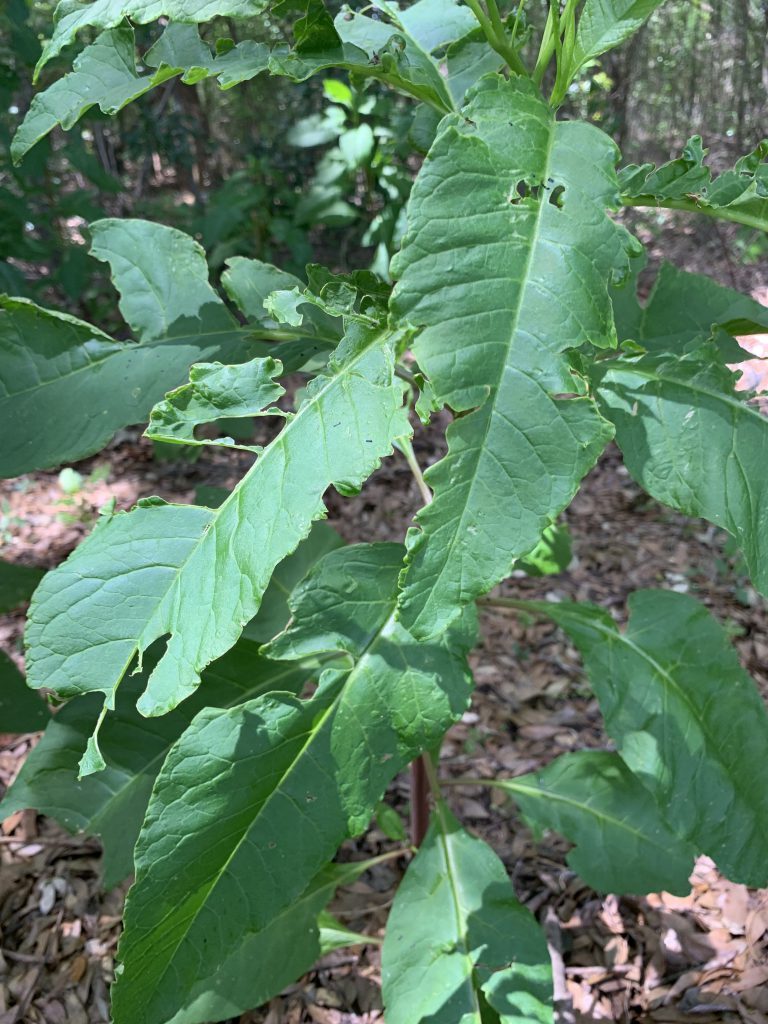

Looper damage on a pokeweed plant. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension at Santa Rosa County
Loopers are common pests of vegetable gardens and in the landscape. Probably the most common loopers found in North Florida gardens are cabbage loopers (Trichoplusia ni) and soybean loopers (Chrysodeixis includens). Cabbage loopers can be found feeding on cabbage, of course, as well as leafy greens, cucumbers, tomatoes, chrysanthemums, and snapdragons. Weeds that attract this looper are lambsquarters, dandelions, and curly dock. Soybean loopers like to feed on sweet potatoes, tomatoes, watermelons, geraniums, and sunflowers. They can also be found feeding on oxalis, kutzu, and lantana.
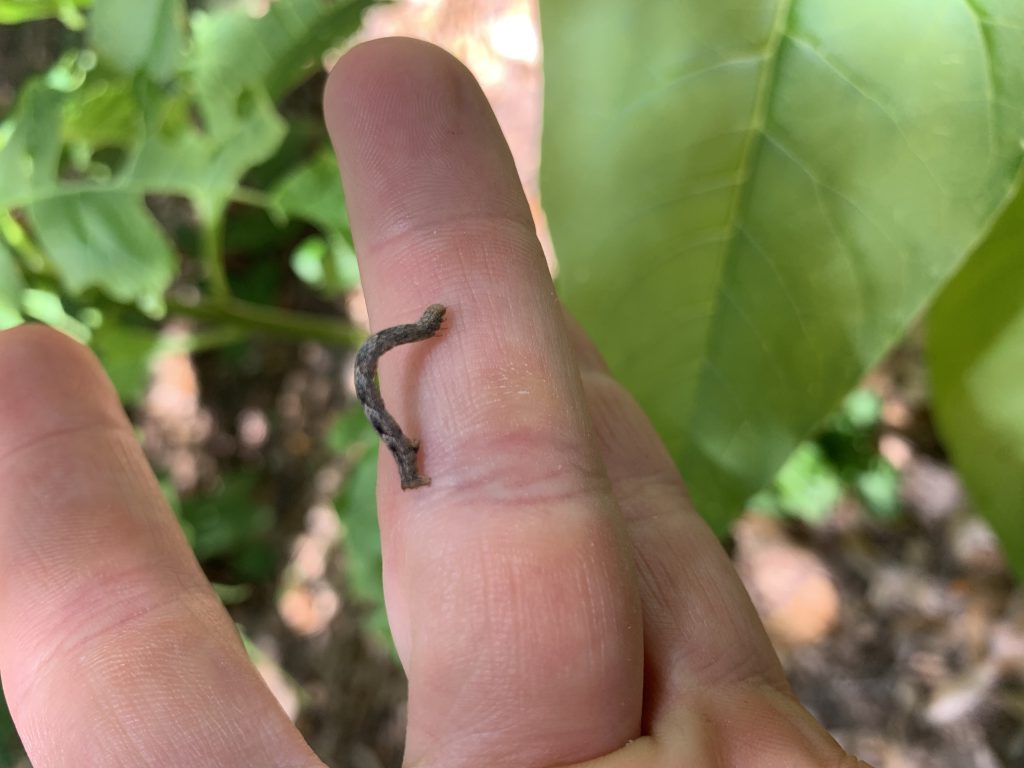

Looper found on pokeweed plant. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension at Santa Rosa County
Although weeds can be hosts for pests, they may be used advantageously. Trap crops can be planted at a garden’s perimeter or windward portion to attract pests away from the desired crop. A trap crop draws the pest crop away from the main crop. The trap crop is then destroyed or sprayed with insecticide when the pest insect is found feeding on it. This allows for a reduction or elimination of insecticidal use on the desired crop. However, it is important that both the trap crop and the desired food crop or ornamental crop are regularly scouted to keep track of pest populations.
For more information on trap crops and other insect and disease diversion methods you can read the EDIS Publication: Intercropping, Crop Diversity and Pest Management.

by Matt Lollar | May 17, 2019
Are you looking for more selective herbicide options for annual beds and around shrubs and trees? The Santa Rosa County Extension Office will be hosting guest speaker Dr. Chris Marble from the UF/IFAS Mid-Florida Research & Education Center on Thursday, May 23. Dr. Marble is a Nationally Renowned Weed Scientist who has published numerous research and extension publications. 2 CEUs available in LCLM, Limited Lawn & Ornamental, Commercial L&O, O&T, Natural Areas, ROW, and Private Ag. Pre-registration fee is $15, or $20 registration at the door the day of the event (includes lunch and resources). Pre-register online at Eventbrite Ticket or bring cash, check, or money order to the Santa Rosa County Extension Office, 6263 Dogwood Dr., Milton, FL before May 23. For additional questions, please contact Matt Lollar at mlollar@ufl.edu or 850-623-3868.
SCHEDULE
9:30 Registration & Welcome
9:45 Presentation Begins
11:30 Question & Answer w/Dr. Marble
11:45 Evaluation & CEUs
12:00 Lunch & Discussion on Glyphosate Registration
12:30 Adjourn

by Larry Williams | Feb 26, 2019

Florida pusley is common summer annual weed. Photo credit: Larry Williams
If weeds were a problem in your lawn last summer, the coming weeks are the time to apply a pre-emergence herbicide to prevent their emergence again this spring and summer.
Timing of a pre-emergence herbicide application for summer annual weeds such as crabgrass should be during February when day temperatures reach 65° to 70°F for four to five consecutive days. This generally coincides with when azaleas and dogwoods first begin to bloom. This in not when these plants are in full bloom but when the first flowers begin to open along the lower branches, particularly on azaleas. Note: This timing is not true for chamberbitter. Chamberbitter requires warmer soil temperatures to germinate. Apply a pre-emergence herbicide during April when battling chamberbitter.
Most pre-emergent type herbicides won’t work when applied after weeds are visible. The product must be applied just before seedlings emerge.
The weeds growing now in local lawns are not summer annuals. Summer annual weed seeds are still dormant awaiting warmer spring temperatures to germinate and emerge.
Most of the weeds in yards now are winter annuals. A few include annual bluegrass, chickweed, henbit, hop clover, lawn burweed and wild geranium.

Winter annual weeds in lawn. Photo credit: Larry Williams
A pre-emergence herbicide should have been applied during October to help prevent these weeds.
A few common summer annual weeds include crabgrass, Florida pusley, chamberbitter, sandspur, spotted spurge and doveweed.
If your lawn has a history of summer annual weeds, one control option is to apply a pre-emergence herbicide. Timing is critical in order for pre-emergence herbicides to work.
Look for lawn pre-emergence products that contain the active ingredients oryzalin, benefin, pendimethalin, DCPA or bensulide.
For season-long weed control, a second application may be needed about six to nine weeks after the initial application. To activate some products, irrigation or rain may be necessary following application. Because pre-emergence products may interfere with lawn grass seed germination, delay re-seeding six to sixteen weeks after application.
Overuse of some types of pre-emergence herbicides can cause a lawn to produce short stubby weak roots. So only apply the product if there is a pest to control – in this case, if you have had a history of summer annual weeds. Otherwise, save your money and time. Use pre-emergence herbicides only on lawns that have been established for at least a year. These products can severely injure newly planted lawns.
It is the user’s responsibility to read and follow all label directions and precautions when using any pesticide, including herbicides.

by Matthew Orwat | Oct 10, 2017

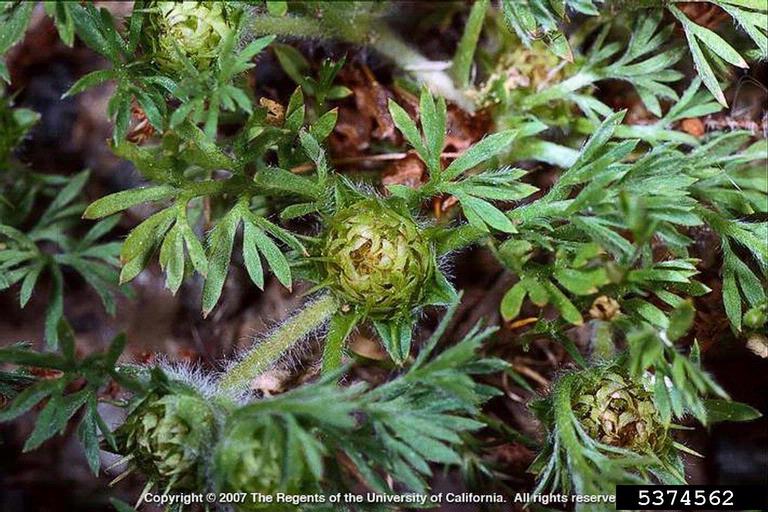
Burweed, Soliva Sessilis. – Image Credit: Joseph M. DiTomaso, University of California – Davis, Bugwood.org. Creative Commons License
On the top of my list of lawn related annoyances is stepping into a patch of burweed, Soliva sessilis, which is in the sunflower family and is also known as spurweed. The leaves are opposite along the stem and sometimes resemble parsley. The main ways in which burweed can irk the casual gardener are sticking to socks, sneaking in with the dog, or littering flower beds with its nuisance. It can also hide in the house and reappear when shoes are removed. This causes pain in both the foot and the ear.
Lawn burweed has been an especially noticeable problem in lawns. Over the years, extension offices throughout Northwest Florida have been fielding many questions and finding solutions to lawn burweed infestations!
Maintaining a healthy vigorous lawn will prevent weeds from taking over. If your lawn is reasonably healthy and only a few instances of this weed exist, try to mechanically remove them and encourage the lawn to outgrow them.
If an infestation of burweed occurred last year on a specific patch of turf, take note. The best time to apply pre-emergent herbicides to control burweed is in October, when nighttime temperatures drop to between 55-60 degrees F for a few consecutive nights. A widely used pre-emergence product for burweed control is isoxaben, which is sold under the brand name of Gallery as well as others. It prevents the weed from emerging from the ground when it germinates and can be used on St. Augustine, centipede, bahia and zoysia lawns, as well as in ornamental shrub beds. In northwest Florida, this herbicide needs to be applied in October for best results. A second application later in the season might be warranted. For more information about control, please consult this excellent article on lawn burweed management.
Now is the time to control burweed before it gets started. As temperatures cool burweed seed will germinate, as it is a winter annual. In cases where it is already coming up, control with post-emergent herbicide may be warranted.
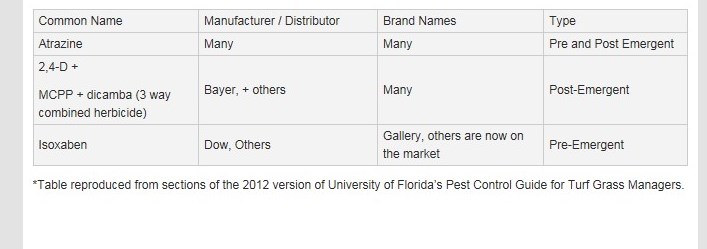
The active ingredients mentioned above are present in a variety of ‘trade name’ products* available from your local garden center, farm supply or co-op. Be sure to read label instructions carefully and contact your local extension office for any assistance. I hope all the northwest Florida lawn managers prevent burweed this fall so that lawns will be burweed free next spring.
Happy Gardening!

 Earlier this summer I talked about getting to know your weeds, so they’ll be easier to control. If you missed that article you can review it here “Why Can’t I Kill Weeds?”
Earlier this summer I talked about getting to know your weeds, so they’ll be easier to control. If you missed that article you can review it here “Why Can’t I Kill Weeds?”










