
by Matt Lollar | Nov 8, 2018
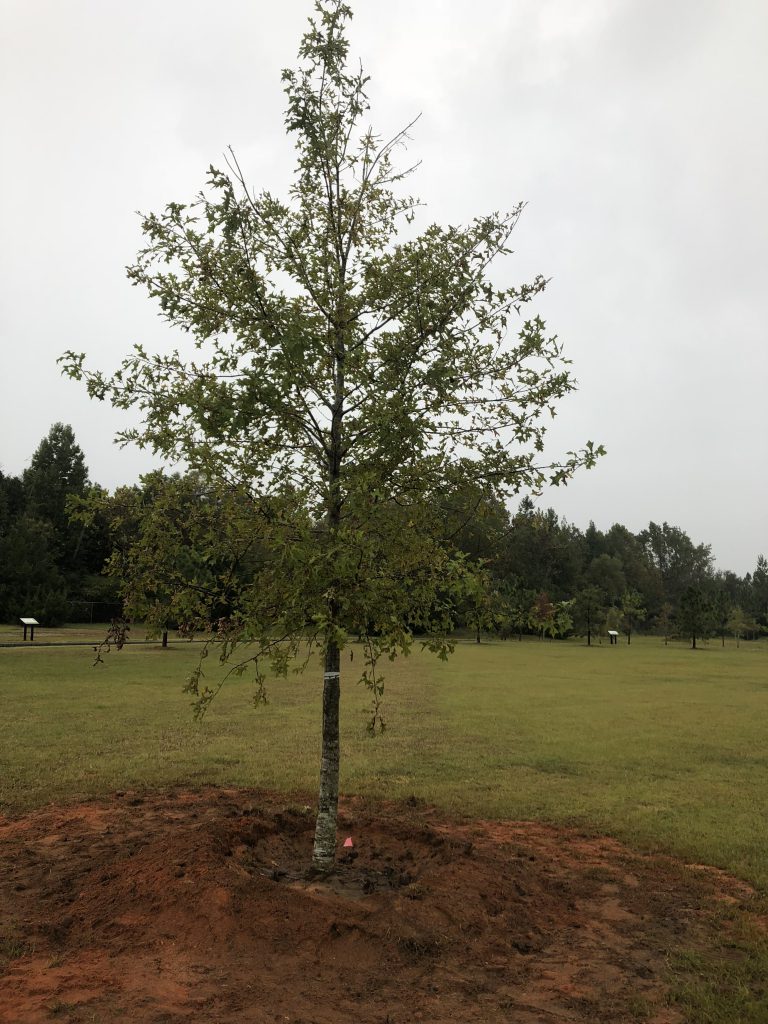

A planted tree with water retention berm. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
Often, Extension agents are tasked with evaluation of unhealthy plants in the landscape. They diagnose all sorts of plant problems including those caused by disease infection, insect infiltration, or improper culture.
When evaluating trees, one problem that often comes to the surface is improper tree installation. Although poorly installed trees may survive for 10 or 15 years after planting, they rarely thrive and often experience a slow death.
Fall is an excellent time to plant a tree in Florida. A couple of weeks ago beautiful Nuttal Oak was planted at Bagdad Mill Site Park in Santa Rosa County, FL. Here are 11 easy steps to follow for proper tree installation:
- Look around and up for wire, light poles, and buildings that may interfere with growth;
- Dig a shallow planting hole as wide as possible;
- Find the point where the top-most root emerges from the trunk;
- Slide the tree carefully into the planting hole;
- Position the point where the top-most root emerges from the trunk slightly above the landscape soil surface;
- Straighten the tree in the hole;
- Remove synthetic materials from around trunk and root ball;
- Slice a shovel down in to the back fill;
- Cover the exposed sides of the root ball with mulch and create water retention berm;
- Stake the tree if necessary;
- Come back to remove hardware.
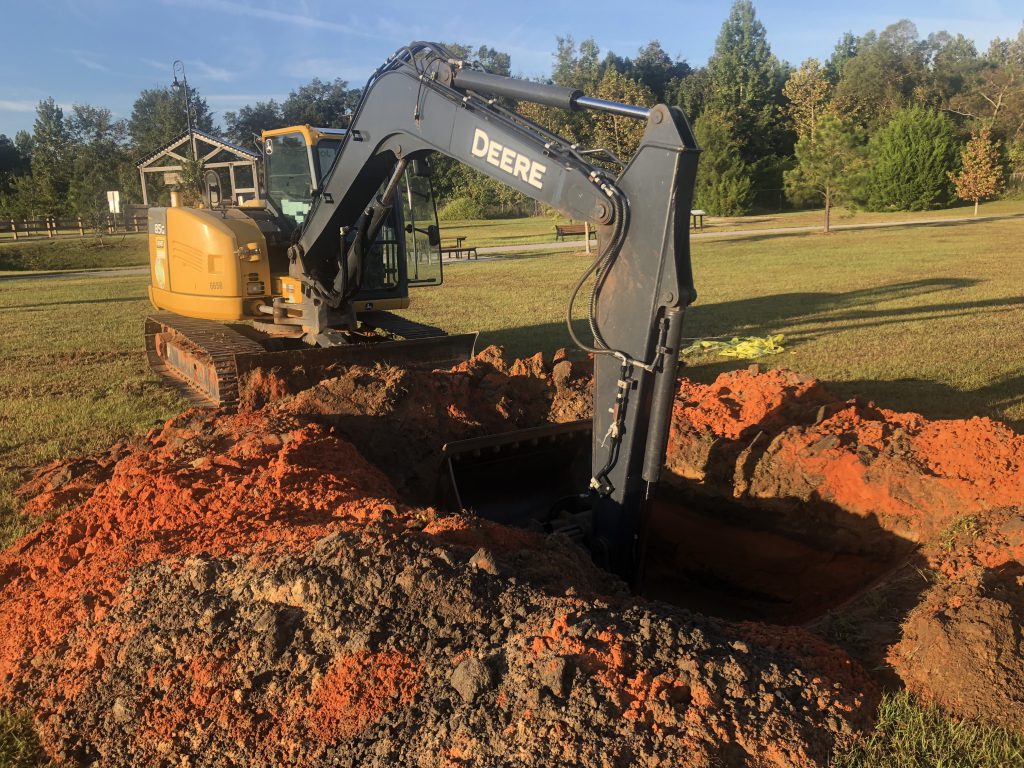

Digging a properly sized hole for planting a tree. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
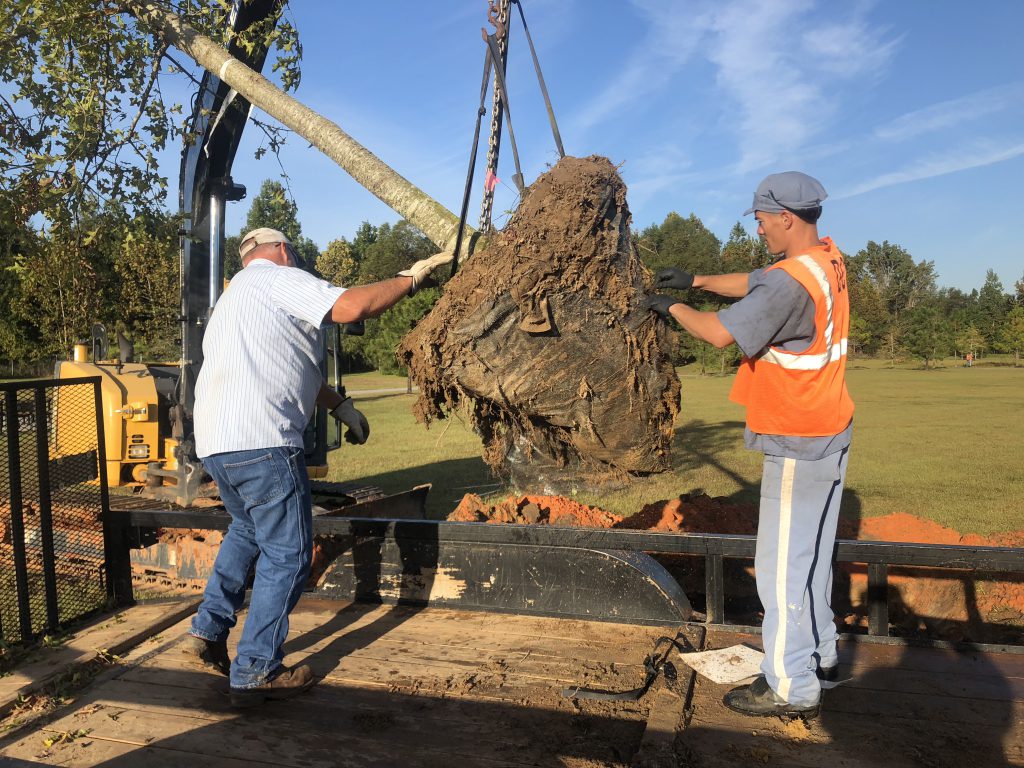

Removing synthetic material from the root ball. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
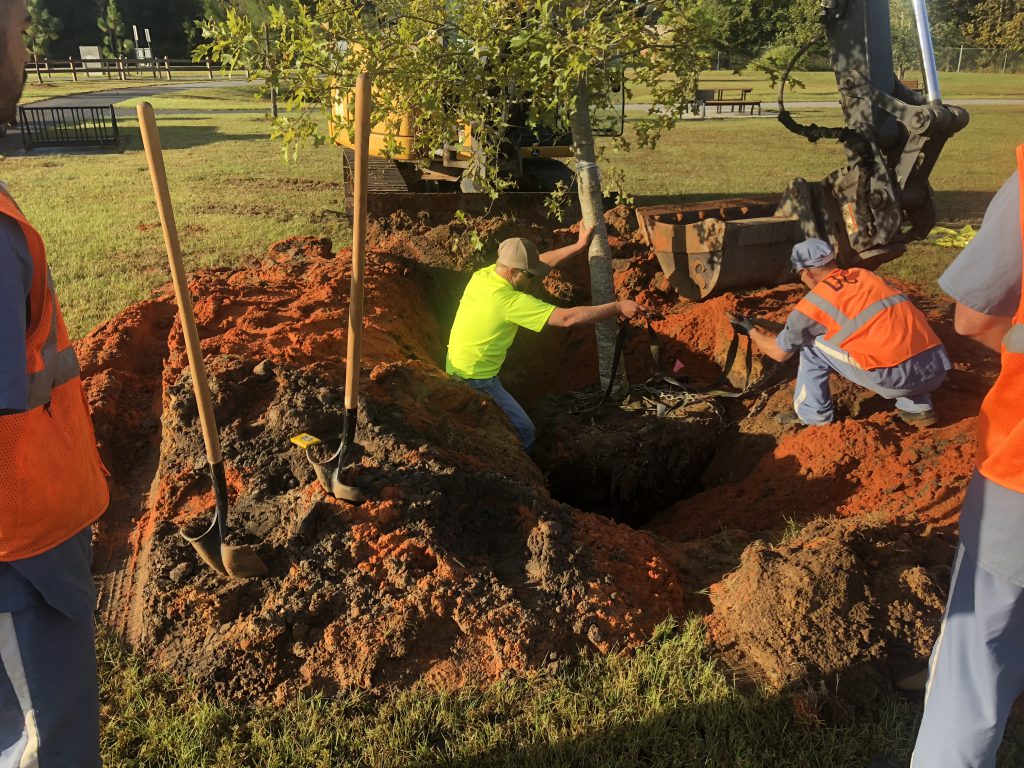

Straightening a tree and adjusting planting height. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida – Santa Rosa County
For more detailed information on planting trees and shrubs visit this UF/IFAS Website – “Steps to Planting a Tree”.
For more information Nuttall Oaks visit this University of Arkansas Website.

by Matt Lollar | Sep 6, 2018
A few months ago I visited a property that had been renovated to clean up some limbs that were in danger of falling on the house. Pruning tree limbs that are in danger of hitting a structure is always a good idea, but it’s important to look at the impacts this practice may have on the rest of a landscape. Any time the light profile of a landscape is changed, current and future plant selection must be considered. One often seen example occurs when trees grow to full size and shade out the lush lawn that’s underneath. However, in this case, removal of limbs allowed more light to shine on some beautiful, old camellia bushes.
Camellia Planting and Care
Camellias do best in locations that receive filtered sunlight and are protected from the wind. They like acidic, well-drained soils. Trees and shrubs are generally planted 2″ to 3″ above the soil grade. (2″ to 3″ of root ball should be exposed above the soil grade when the tree/shrub is planted.) To help improve root oxygen exposure and help prevent a root rot situations, camellias can be planted slightly shallower than the previously stated recommendation. For more plant establishment guidelines, please visit: UF/IFAS Planting and Establishing Trees Guide
Scenario and Diagnosis
As mentioned above, the property in question was visited to diagnose sick camellia bushes. Upon further inspection of the property, asking about recent changes to the landscape, and inspecting the bushes, it was clear that the camellias were receiving too much sunlight. Sunlight damage was expressed by large brown sunscald spots on the yellowing leaves.
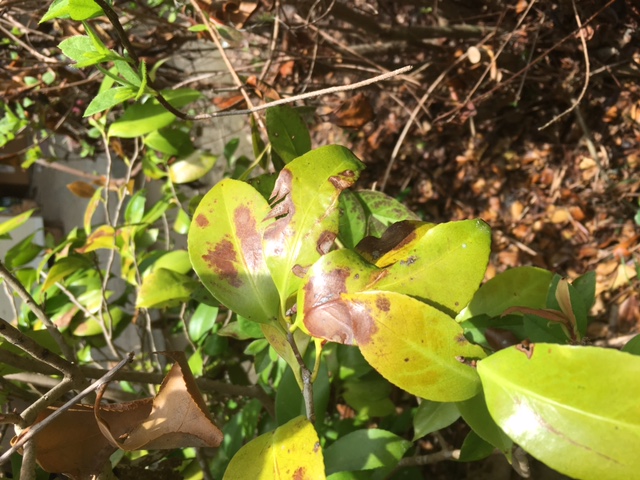

Sunscald damage on camellia leaves. Photo Credit: Jed Dillard
The camellias had also been pruned incorrectly. Camellias require minimal pruning. They are normally pruned to control size or promote a tree form structure if desired. Any pruning should be done before flower buds form in late summer.

An incorrectly pruned camellia bush. Photo Credit: Jed Dillard
Solution
The best solution in this scenario was to dig up the affected camellias and move them to a location with more shade. Sun loving shrubs were suggested as options to replace the camellia bushes. It’s important to note that Camellia sasanqua cultivars are usually more tolerant of sunlight than Camellia japonica cultivars. The recommendations were based on the Florida Friendly Landscaping principle of “Right Plant, Right Place”.
If you’re trying to find the right plants for you own yard, then you should check out the Florida Friendly Landscaping Interactive Plant Database. The database gives you plant selection options for each area of your yard based on location in the state, plant type, and soil and light conditions.

by Carrie Stevenson | Jan 17, 2017
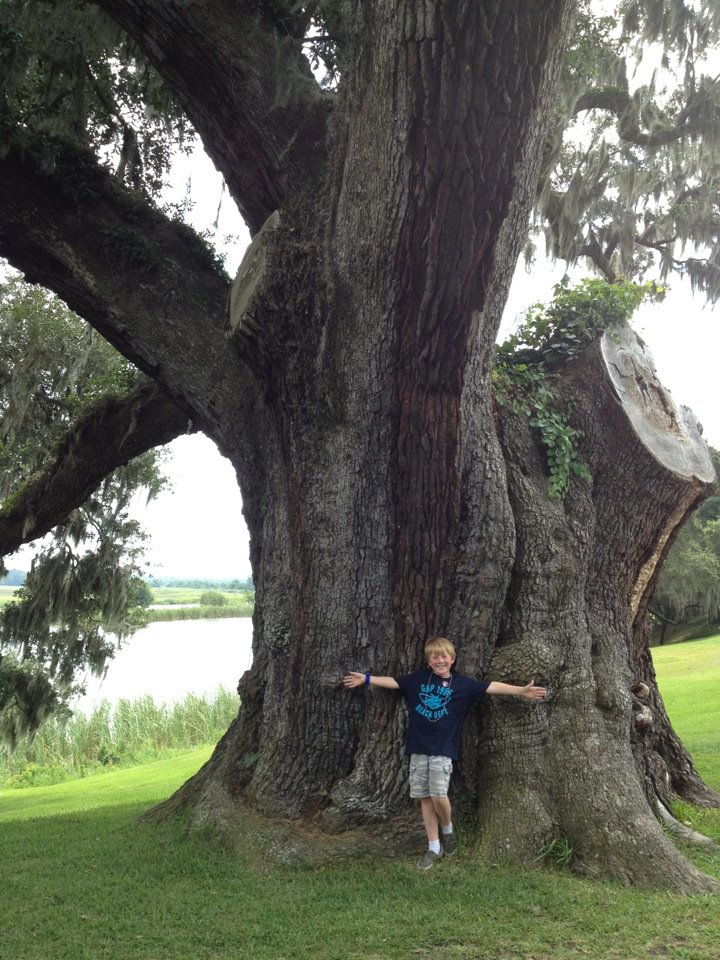
Arbor Day has a 145-year history, started in Nebraska by a nature-loving newspaper editor named J. Sterling Morton who recognized the many valuable services trees provide. The first Arbor Day was such a big success that Mr. Morton’s idea quickly spread nationwide–particularly with children planting trees on school grounds and caring for them throughout the year. Now, Arbor Day is celebrated around the world in more than 30 countries, including every continent but Antarctica. We humans often form emotional attachments to trees, planting them at the beginning of a marriage, birth of a child, or death of a loved one. Trees have tremendous symbolic value within cultures and religions worldwide, so it only makes sense that people around the world have embraced the idea of celebrating a holiday focused solely on trees.

Ancient trees like this live oak have an important place in our cultural history. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
In addition to their aesthetic beauty and valuable shade in the hot summers, trees provide countless benefits: wood and paper products, nut and fruit production, wildlife habitat, stormwater uptake, soil stabilization, carbon dioxide intake, and oxygen production. New research is even showing that trees can communicate throughout a forest, sharing “information” and nutrients through a deeply connected network of roots and fungi that can increase the resiliency of an entire forest population. And if you’re curious of the actual dollar value of a single tree, the handy online calculator at TreeBenefits.com can give you an approximate lifetime value of a one growing in your own backyard.
While national Arbor Day is held the last Friday in April, Arbor Day in Florida is always the third Friday of January. Due to our geographical location further south than most of the country, our primary planting season is during our relatively mild winters. Trees have the opportunity during cooler months to establish roots without the high demands of the warm growing season in spring and summer.
To commemorate Arbor Day, many local communities will host tree giveaways, plantings, and public ceremonies. In the western Panhandle, the Florida Forest Service, UF/IFAS Extension, and local municipalities have partnered for several events, listed here. As the Chinese proverb goes, “The best time to plant a tree was twenty years ago. The second best time is now.”
For more information on local Arbor Day events and tree giveaways in your area, contact your local Extension Office or County Forester!

by Blake Thaxton | Nov 3, 2016
It was a hot summer that has continued into Fall. We hope cooler temperatures are on their way to the panhandle of Florida. Fall can be a great time to spruce up your landscape with some new shrubs.

Image Credit UF / IFAS
It may be time for your landscape to receive a mini-makeover and to get a new look. Perhaps some strategically placed shrubs will be what makes an outdoor living space pop. Proper selection and installation is key to future health of new shrubs.
Selection
There are several factors that need to be considered before installing new shrubs to the landscape. Selecting plants carefully, based on the following points, will help with long-term success of the plant:
- Climate – Be sure that the species are climate appropriate.
- Environment – Study the light level, acidity, and drainage of the planting site.
- Space – Account for the mature size of the plant before planting. This will eliminate the possible need for plant removal if space is not adequate.
- Inspect the plant – Check for mechanical injury (scars and open wounds), cold injury, condition and shape of the canopy, and examine the root system.
Installation
Now that essential considerations have been made, it is time to give the shrub the best chance for survival with proper installation techniques. Fall and winter is an ideal time for planting shrubs. The roots can develop before the tops begin to grow in spring. The following are keys to proper establishment of container shrubs.
- Root ball preparation – Remove the container from the root ball and inspect for circling roots. If there are circling roots than make three or four cuts vertically to cut the roots. Pull some of the roots away so they will take on a new growth direction (massage the roots). Also find the top most roots, as sometimes they are covered by extra potting media. Remove the extra potting media so the top most roots are exposed and become the top of the root ball.
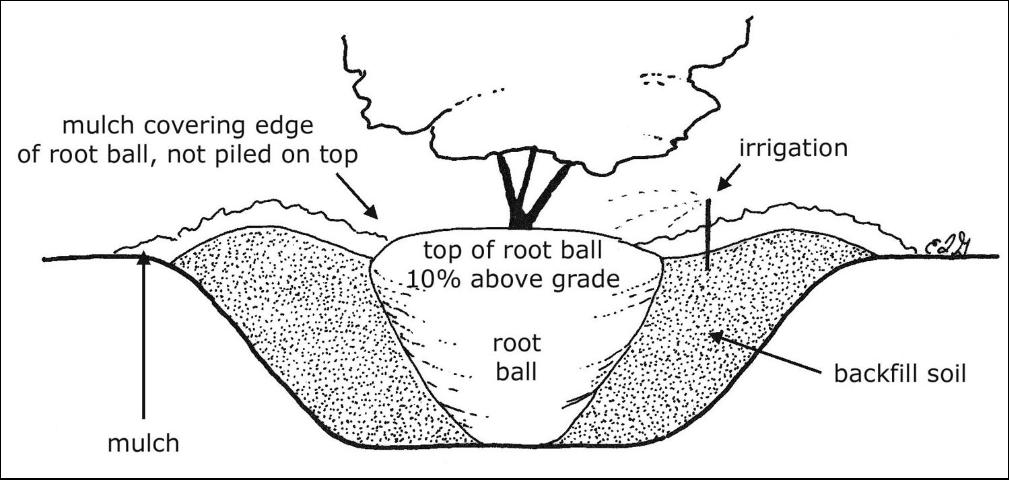
Image Credits: UF/IFAS, Edward F. Gilman
- Wider is better – Dig the hole two or three times the diameter of the root ball.
- Proper depth – Make sure to dig the hole 10% less than the height of the root ball. In poorly drained soils dig the hole 25% less than the height of the root ball. The top most roots should be slightly above the native soils.
- Backfill – Fill the hole with existing soil half way and tamp the soil to settle. Again fill the rest of the hole with the existing soil and tamp again to settle the soil. Do not place any backfill soil or mulch over the root ball as it is crucial that water and air are able to be in contact with the roots.
- Aftercare – Irrigate daily for the first two weeks, followed by every other day for the next two months, and weekly until the shrub is established (For <2 inch caliper shrubs).
If these key points are followed regarding selection and installation, the shrubs will be well on their way to becoming established in the landscape. If you would like read more in detail about installation please read the following:
Specifications for Planting Trees and Shrubs in the Southeastern U.S.
Literature:
Gilman, E.F., (2011, August) Specifications for Planting Trees and Shrubs in the Southeastern U.S.. Retrieved from: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep112
Black, R.J. and Ruppert, K.C., (1998) Your Florida Landscape, A complete guide to planting & maintenance. Gainesville, FL: University Press of Florida.

by Julie McConnell | Jun 2, 2015

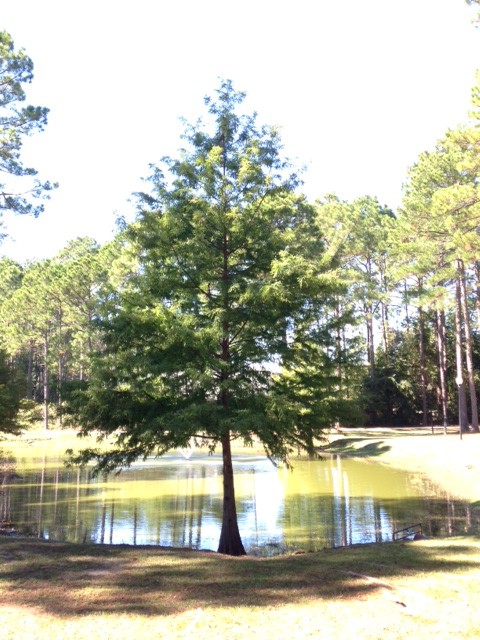
Bald cypress growing at the edge of a pond. Photo: Julie McConnell, UF/IFAS
Considering planting a tree in your landscape, but not sure what will do well?
Baldcypress, Taxodium distichum, is one tree you should consider for your Florida landscape. This deciduous conifer is native to North America and is suited to a wide variety of situations, even difficult ones!
Baldcypress is found naturally along stream banks and in swampy areas, but also performs well in dry situations once established. Not many trees can tolerate standing water or flooding situations, but baldcypress is well adapted to these tough spots. In areas that flood or remain wet the tree will form “knees” that project out of the ground and add a beautiful feature – just don’t plan to mow in areas where these develop. Not restricted to wet areas, baldcypress also performs well as a street tree or in limited root zone situations such as parking lot islands.
This tough tree has a soft, delicate leaf texture and interesting globular cones that start out green then turn brown as they mature. The foliage is light green through the spring and summer then turns a coppery gold before the needles fall in the winter. The trunk has a reddish color that is also attractive and will grow branches low to the ground, but can easily be maintained with a clear trunk in a street tree form.
Baldcypress will grow in full sun to part shade and is adapted to all soil types except highly alkaline (over 7.5 pH). Sand, loam, clay, or muck can all sustain this native tree. Few pests bother baldcypress, but it can be affected by bagworms and mites. Mature size can be in excess of 100 feet, but trees typically grow 60-80 feet tall in Florida.
For more information:
Taxodium distichum: Baldcypress














