
by Carrie Stevenson | Nov 3, 2017

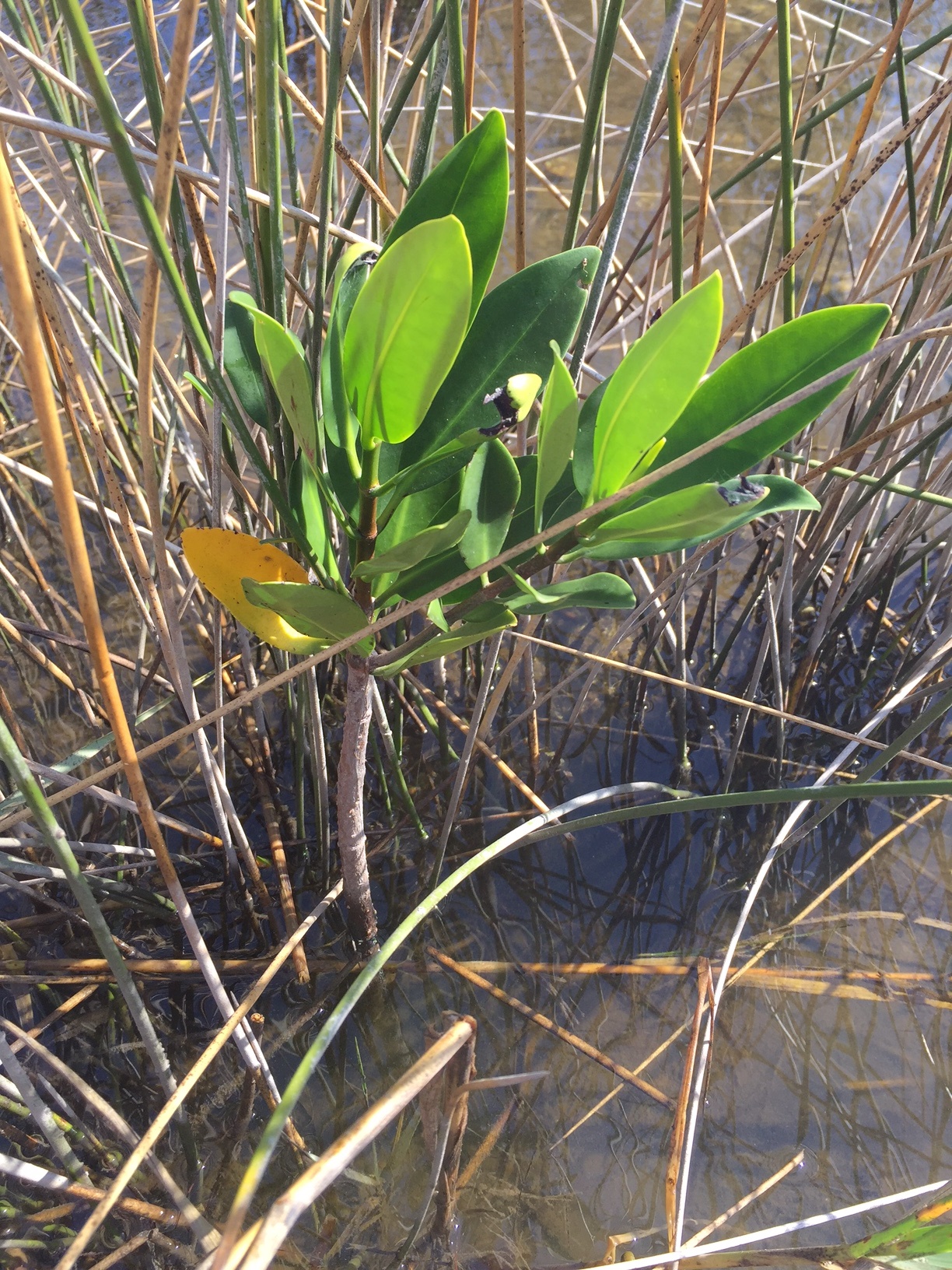
Red mangrove growing among black needlerush in Perdido Key. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
Discovering something new is possibly the most exciting thing a field biologist can do. As students, budding biologists imagine coming across something no one else has ever noticed before, maybe even getting the opportunity to name a new bird, fish, or plant after themselves.
Well, here in Pensacola, we are discovering something that, while already named and common in other places, is extraordinarily rare for us. What we have found are red mangroves. Mangroves are small to medium-sized trees that grow in brackish coastal marshes. There are three common kinds of mangroves, black (Avicennia germinans), white (Laguncularia racemosa), and red (Rhizophora mangle).
Black mangroves are typically the northernmost dwelling species, as they can tolerate occasional freezes. They have maintained a large population in south Louisiana’s Chandeleur Islands for many years. White and red mangroves, however, typically thrive in climates that are warmer year-round—think of a latitude near Cedar Key and south. The unique prop roots of a red mangrove (often called a “walking tree”) jut out of the water, forming a thick mat of difficult-to-walk-through habitat for coastal fish, birds, and mammals. In tropical and semi-tropical locations, they form a highly productive ecosystem for estuarine fish and invertebrates, including sea urchins, oysters, mangrove and mud crabs, snapper, snook, and shrimp.
Interestingly, botanists and ecologists have been observing an expansion in range for all mangroves in the past few years. A study published 3 years ago (Cavanaugh, 2014) documented mangroves moving north along a stretch of coastline near St. Augustine. There, the mangrove population doubled between 1984-2011. The working theory behind this expansion (observed worldwide) is not necessarily warming average temperatures, but fewer hard freezes in the winter. The handful of red mangroves we have identified in the Perdido Key area have been living among the needlerush and cordgrass-dominated salt marsh quite happily for at least a full year.

Key deer thrive in mangrove forests in south Florida. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
Two researchers from Dauphin Island Sea Lab are planning to expand a study published in 2014 to determine the extent of mangrove expansion in the northern Gulf Coast. After observing black mangroves growing on barrier islands in Mississippi and Alabama, we are working with them to start a citizen science initiative that may help locate more mangroves in the Florida panhandle.
So what does all of this mean? Are mangroves taking over our salt marshes? Where did they come from? Are they going to outcompete our salt marshes by shading them out, as they have elsewhere? Will this change the food web within the marshes? Will we start getting roseate spoonbills and frigate birds nesting in north Florida? Is this a fluke due to a single warm winter, and they will die off when we get a freeze below 25° F in January? These are the questions we, and our fellow ecologists, will be asking and researching. What we do know is that red mangrove propagules (seed pods) have been floating up to north Florida for many years, but never had the right conditions to take root and thrive. Mangroves are native, beneficial plants that stabilize and protect coastlines from storms and erosion and provide valuable food and habitat for wildlife. Only time will tell if they will become commonplace in our area.
If you are curious about mangroves or interested in volunteering as an observer for the upcoming study, please contact me at ctsteven@ufl.edu. We enjoy hearing from our readers.

by Carrie Stevenson | Aug 25, 2017

Life on the Gulf Coast can be beautiful, but has its share of complications. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
Life on the coast has tremendous benefits; steady sea breezes, gorgeous beaches, plentiful fishing and paddling opportunities. Nevertheless, there are definite downsides to living along it, too. Besides storms like Hurricane Harvey making semi-regular appearances, our proximity to the water can make us more vulnerable to flooding and waterborne hazards ranging from bacteria to jellyfish. One year-round problem for those living directly on a shoreline is erosion. Causes for shoreline erosion are wide-ranging; heavy boat traffic, foot traffic, storms, lack of vegetation with anchoring roots, and sea level rise.
Many homeowners experiencing loss of property due to erosion unwittingly contribute to it by installing seawalls. When incoming waves hit the hard surface of the wall, energy reflects back and moves down the coast. Often, an adjacent homeowner will experience increased erosion and bank scouring after a neighboring property installs a seawall. This will often lead that neighbor to install a seawall themselves, transferring the problem further.

Erosion can damage root systems of shoreline trees and grasses. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
Currently, south Louisiana is experiencing significant coastal erosion and wetlands losses. The problem is compounded by several factors, including canals dredged by oil companies, which damage and break up large patches of the marsh. Subsidence, in which the land is literally sinking under the sea, is happening due to a reduced load of sediment coming down the Mississippi River. Sea level rise has contributed to erosion, and most recently, an invasive insect has caused large-scale death of over 100,000 acres of Roseau cane (Phragmites australis). Add the residual impacts from the oil spill, and you can understand the complexity of the situation.
Luckily, there are ways to address coastal erosion, on both the small and large scale. On Gulf and Atlantic beaches, numerous coastal communities have invested millions in beach renourishment, in which offshore sand is barged to the coast to lengthen and deepen beaches. This practice, while common, can be controversial because of the cost and risk of beaches washing out during storms and regular tides. However, as long as tourism is the #1 economic driver in the state, the return on investment seems to be worth it.
On quieter waters like bays and bayous, living shorelines have “taken root” as a popular method of restoring property and stabilizing shorelines. This involves planting marsh grasses along a sandy shore, often with oyster or rock breakwaters placed waterward to slow down wave energy, and allow newly planted grasses to take root.
Locally in Bayou Grande, a group of neighbors were experiencing shoreline erosion. Over a span of 50 years, the property owners used a patchwork of legally installed seawalls, bulkheads, rip rap piles, private boat ramps, piers, mooring poles and just about anything else one can imagine, to reduce the problem. Over time, the seawalls and bulkheads failed, lowering the property value of the very property they were meant to protect and increasing noticeable physical damage to the adjacent properties.”

Project Greenshores is a large-scale living shoreline project in Pensacola. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
In 2011, a group of neighboring property owners along the bayou decided to take action. After considering many repair options, the neighbors decided to pursue a living shoreline based on aesthetics, long-term viability, installation cost, maintenance cost, storm damage mitigation and feasibility of installation. By 2017, the living shoreline was constructed. Oyster shell piles were placed to slow down wave energy as it approached the transition zone from the long fetch across the bayou, while uplands damage was repaired and native marsh grasses and uplands plants were restored to slow down freshwater as it flowed towards the bayou. Sand is now accruing as opposed to eroding along the shoreline. Wading shorebirds are now a constant companion and live oysters are appearing along the entire 1,200-foot length. Additionally the living shoreline solution provided access to resources, volunteer help, and property owner sweat equity opportunities that otherwise would have been unavailable. An attribute that has surprisingly appeared – waterfront property owners are now able to keep their nicely manicured lawns down to within 30 feet of the water’s edge. At that point, the landscape immediately switches back to native marsh plants, which creates a quite robust and attractive intersection. (Text and information courtesy Charles Lurton).
Successes like these all over the state have led the Florida Master Naturalist Program to offer a new special topics course on “Coastal Shoreline Restoration” which provides training in the restoration of living shorelines, oyster reefs, mangroves, and salt marsh, with focus on ecology, benefits, methods, and monitoring techniques. Keep an eye out for this course being offered near you. If you are curious about living shorelines and want to know more, reach out to the Florida Department of Environmental Protection Ecosystem Restoration section for help and read through this online document.

by Rick O'Connor | Aug 11, 2017
Our first POL program will happen this week – August 17 – at the Navarre Beach snorkel reef, and is sold out! We are glad you all are interested in these programs.
Well! We have another one for you. The Natural Resource Extension Agents from UF IFAS Extension will be holding a two-day water school at St. Joseph Bay. Participants will learn all about the coastal ecosystems surrounding St. Joe Bay in the classroom, snorkeling, and kayaking. Kayaks and overnight accommodations are available for those interested. This water school will be September 19-20. For more information contact Extension Agent Ray Bodrey in Gulf County or Erik Lovestrand in Franklin. Information and registration can be found at https://stjosephbay-waterschool.eventbrite.com.


by Rick O'Connor | Jul 29, 2017
ARTICLE BY DR. MATT DEITCH; water quality specialist – University of Florida Milton
Summer is a great time for weather-watching in the Florida panhandle. Powerful thunderstorms appear out of nowhere, and can pour inches of rain in an area in a single afternoon. Our bridges, bluffs, and coastline allow us to watch them develop from a distance. Yet as they come closer, it is important to recognize the potential danger they pose—lightning from these storms can strike anywhere nearby, and can cause fatality for a person who is struck. Nine people were killed by lightning strike in Florida in 2016 alone, more than in any other state. Because of the risk posed by lightning, my family and I enjoy these storms up-close from indoors.

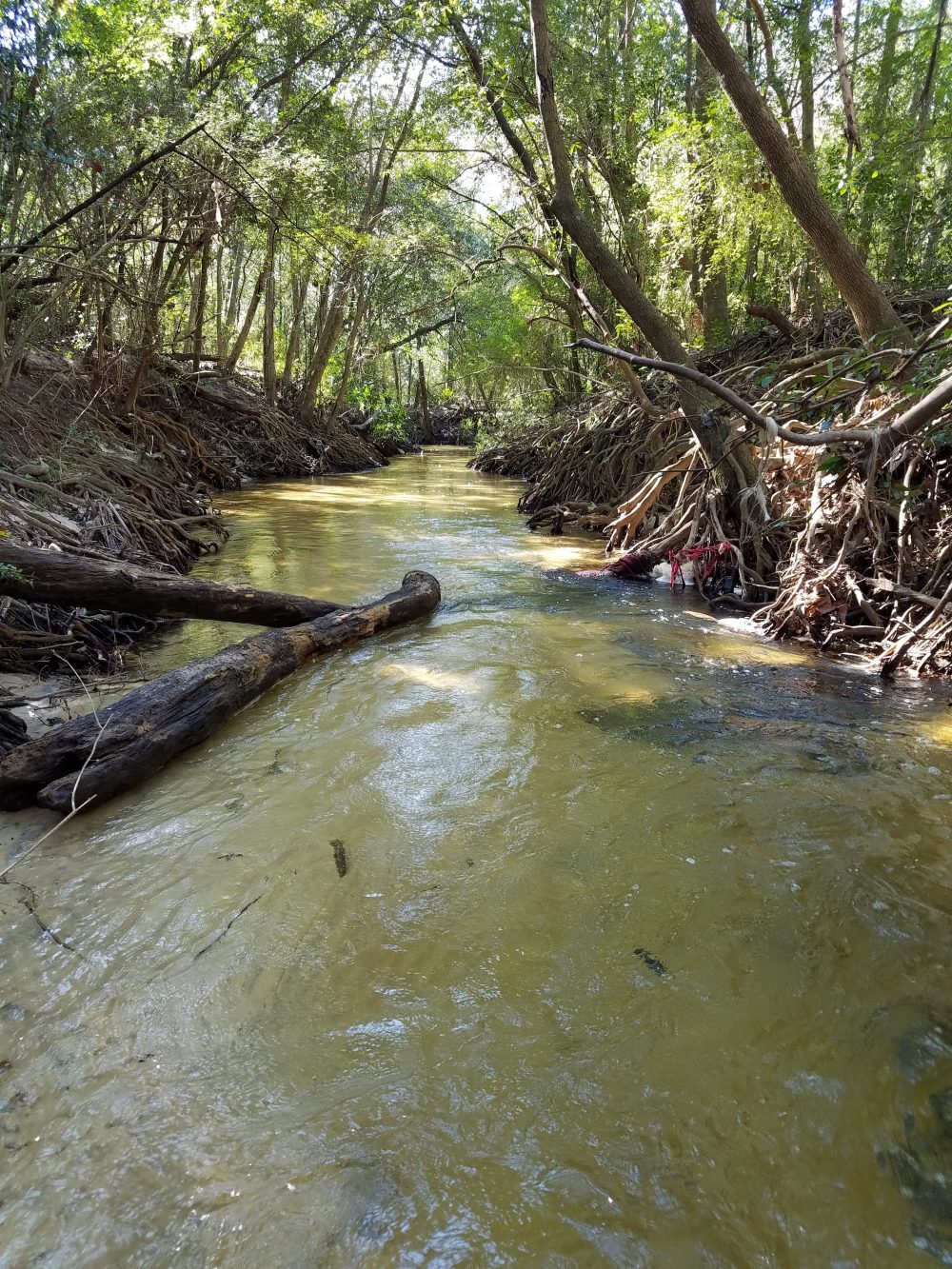
Carpenter’s Creek in Pensacola
Photo: Dr. Matt Deitch
A fraction of the rain that falls during these storms is delivered to our bays, bayous, and estuaries through a drainage network of creeks and rivers. This streamflow serves several important ecological functions, including preventing vegetation encroachment and maintaining habitat features for fish and amphibians through scouring the streambed. High flows also deposit fine sediment on the floodplain, helping to replenish nutrients to floodplain soil. On average, only about one-third of the water that falls as rain (on average, more than 60 inches per year!) turns into streamflow. The rest may either infiltrate soil and percolate into groundwater; or be consumed and transpired by plants; or evaporate off vegetation, from the soil, or the ground surface before reaching the soil. Evaporation and transpiration play an especially large role in the water cycle during summer: on average, most of the rain that falls in the Panhandle occurs during summer, but most stream discharge occurs during winter.
The water that flows in streams carries with it many substances that accumulate in the landscape. These substances—which include pollutants we commonly think of, such as excessive nutrients comprised of nitrogen and phosphorus, as well as silt, oil, grease, bacteria, and trash—are especially abundant when streamflow is high, typically during and following storm events. Oil, grease, bacteria, and trash are especially common in urban areas. The United States EPA and Florida Department of Environmental Protection have listed parts of the Choctawhatchee, St. Andrew, Perdido, and Pensacola Bays as impaired for nutrients and coliform bacteria. Pollution issues are not exclusive to the Panhandle: some states (such as Maryland and California) have even developed regulatory guidelines in streams (TMDLs) for trash!
Many local and grassroots organizations are taking the lead on efforts to reduce pollution. Some municipalities have recently publicized efforts to enforce laws on picking up pet waste, which is considered a potential source of coliform bacteria in some places. Some conservation groups in the panhandle organize stream debris pick-up days from local streams, and others organize volunteer citizens to monitor water quality in streams and the bays where they discharge. Together, these efforts can help to keep track of pollution levels, demonstrate whether restoration efforts have improved water quality, and maintain healthy beaches and waterways we rely on and value in the Florida Panhandle.

Santa Rosa Sound
Photo: Dr. Matt Deitch
by Rick O'Connor | Sep 23, 2016
Humans have been settling on, and around, coastal estuaries since they first arrived in the panhandle over 10,000 years ago. These bodies of water have provided food and recreation as long as anyone can remember. They are a magnet for those looking to build homes or businesses – and we continue to be attracted to them today.

Black Needlerush is one of the species of marsh grasses that live in brackish conditions.
Estuaries are defined as semi-enclosed bodies of water where fresh and sea water mix. The point where the freshwater enters is called the head of the bay; the point where seawater enters is called the mouth. Seawater is denser than freshwater so during incoming tides the saline water tends to “wedge” it’s way into the upper estuary along the bottom. Under certain conditions, it is possible to catch freshwater fish near the surface and marine species on the bottom at the same location. The mixture of fresh and seawater makes for an interesting cocktail of salinities termed brackish water – which is required for the development of almost 90% of the commercially valuable seafood species we enjoy. This ecosystem supports stands of vegetation which are also important in the development of some species – some of these systems are the most biologically productive on the planet.
We are lucky to have several large estuaries along the Florida panhandle. All of our bays are what are called drowned river valleys. Most are very wide and pretty shallow, with the highest average depth being 17 feet in Choctawhatchee Bay. The rivers that feed these estuaries begin in states north of us and bring with them needed freshwater and nutrients. Each of the panhandle estuaries is unique and provides different resources for their neighboring communities. Below is a breakdown of some of these characteristics. This information was provided by GulfBase.org.
| Bay |
Surface Area (km2) |
Drainage Area (km2) |
Avg. Daily Inflow (m3/sec) |
Avg. Depth (m) |
Avg. Salinity (ppt) |
Area of Wetlands (km2) |
Area of Submerged Vegetation (km2) |
| Perdido |
130 |
3,100 |
62 |
3.0 |
15 |
688 |
ND |
| Pensacola |
370 |
18,100 |
328 |
4.0 |
23 |
991 |
32 |
| Choctawhatchee |
334 |
14,000 |
241 |
5.0 |
25 |
1,133 |
12 |
| St. Andrews |
243 |
2,800 |
127 |
4.0 |
31 |
1,016 |
53 |
| St. Joseph ND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Apalachicola |
554 |
53,100 |
824 |
3.0 |
22 |
2,396 |
36 |
| Apalachee |
412 |
11,900 |
150 |
3.0 |
30 |
2,813 |
130 |
You can see some of our estuaries have large areas and tremendous amounts of freshwater inflow. Others not so much, the bays with less freshwater inflow have higher salinities – and support a different ecology than the others. Is one better than the other?… no… certainly our ancestors understood this. Higher salinities meant more seagrass, scallops, and urchins – certain species of fish and maybe even marine turtles could be found here. Lower salinities meant a different group of fish, oysters, and crabs. It’s all good! Residents should benefit from what the bay provides – and not try to make “your bay” more like “another bay”.
They have suffered some over the years – discharge containing organic and inorganic chemicals have tainted some drinking water supplies as well as reduce valuable aquatic resources. Increased sediments from development have darkened the waters reducing light and reducing submerged plants. Heavily fishing and recreation have impacted both the habitats and the species that inhabit them. Through the efforts of universities, government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private citizens many of the problems have been addressed – and recovery is occurring… but there is still more to do.
National Estuaries Week is a chance for all who live in the panhandle to realize how important these bodies of water are to our locally economy and to our quality of life. We hope you will appreciate them and do your part to help protect them. HAPPY NATIONAL ESTUARIES WEEK!

by Laura Tiu | Sep 23, 2016

Rocky Bayou Aquatic Preserve – Choctawhatchee Bay, Niceville, Florida – Photo by Laura Tiu
September 17-24, 2016 was the nation’s 28th time to celebrate America’s coasts and estuaries during National Estuaries Week. This week helps us to remember to appreciate the challenges these coastal ecosystems face, along with their beauty and utility.
Estuaries, semi-enclosed bodies of water with both fresh and saltwater, dot the Gulf Coast of the United States from Brownsville Texas to Key West, Florida. These estuaries are important as they serve as drainage basins for many of the large river systems, and play a significant role in the nation’s seafood industry.
Florida’s six major Panhandle estuaries, which includes Perdido Bay, Pensacola Bay (including Escambia Bay), Choctawhatchee Bay, St. Andrew Bay, St. Joseph Bay and Apalachicola Bay, are unique ecosystems teeming with life and diversity. Critical habitat includes important seagrass beds that support both the larval and adult stages of fish and invertebrates. In Choctawhatchee Bay, there is also critical foraging habitat for the federally protected Gulf sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi) and stream habitat for the endangered Okaloosa darter.
Choctawhatchee Bay is in Okaloosa and Walton counties in the Florida Panhandle. It is approximately 30 miles long and from three and a half to six miles wide, with a total area of 129 square miles. It is relatively shallow varying from 10 to 40 feet deep. Large portions of the western half of Choctawhatchee Bay are militarily restricted (Eglin Airforce Base). The Bay is fed by the Choctawhatchee River and numerous small creeks that feed into several bayous. The only opening to the Gulf of Mexico is the East Pass, which ironically is at the Western end of the Bay in Destin, Florida. This is where the saltwater and freshwater mix.
Continued industrial and residential development in the watershed regions that drain into many of these estuaries has impacted them in a number of ways. Pollution comes from storm water runoff, lawns, industry and farms. The shorelines are impacted by development, which causes sedimentation and in turn loss of vegetation. This reduces water clarity and habitat for wildlife.
Many organizations work to protect this estuary and reach out to others through education, restoration, and recreation events. Choctawhatchee Basin Alliance (CBA) is one such organization committed to ensuring sustainable utilization of the Choctawhatchee River and Bay. They, working with their partners, provide leadership for the stewardship of the Bay. Alison McDowell, director of the CBA, notes that 75-85% of commercially and recreationally important species that are caught in the Gulf spend part of their lifecycle in the Bay. McDowell says a key factor in the Bay’s health is monitoring the water quality and reducing erosion, and the Oyster Reef Restoration program started in 2006 does just that.
There are often opportunities for the general public to join in some of the conservation efforts taking place in the Bay. For more information, like the Okaloosa or Walton County Extension Facebook page.

Kayaking Choctawhatchee Bay – Photo by Laura Tiu
















