
by Carrie Stevenson | Jan 17, 2020

4H youth assist an IFAS Extension agent in planting a tree. UF/IFAS Photo: Josh Wickham.
This week, we celebrate Florida’s Arbor Day. “What?” you may say—“Isn’t Arbor Day in the spring?” Well, yes and no. National Arbor Day is celebrated in the spring (April 24 this year), usually within a day or two of Earth Day. However, because of the wide range of climatic environments throughout the United States, each state has its own date based on ideal growing conditions. As it stands, Florida’s is the 3rd Friday in January, as we are situated so very far south. Alabama and Georgia, where so many of us north Floridians experience similar weather, hold their Arbor Days in late February.
Contrary to popular opinion, the optimal planting time for trees in not in the spring, but in fall and winter. Planting during dormancy allows trees to focus their energy resources on growing healthy roots. In the coming spread, a steady supply of warmth, sunshine, and pollinators bring on leaf growth, flowers, and fruit.
Check with your local Extension offices, garden clubs, and municipalities to find out if there is an Arbor Day event near you! Several local agencies have joined forces to organize tree giveaway and sales events in observance of Florida’s Arbor Day.
Friday, January 17th
Okaloosa County: UF/IFAS Okaloosa County, in partnership with the Florida Forest Service, the Niceville Senior Center and the Kiwanis Club of Niceville-Valparaiso, will give away trees beginning at 9 a.m., until all trees are gone. Niceville Senior Center, 201 Campbell Drive. A UF/IFAS Extension agent will conduct a tree planting demonstration and UF/IFAS Master Gardener volunteers will be available to answer questions about planting and growing trees in North Florida.
Saturday, January 18th
Walton County Master Gardener Volunteer Tree and Plant Sale
A wide variety of plants and trees will be offered: shade trees, ornamentals, citrus, flowering, tropical, fruits, nuts, berries, shrubs, grasses, vines, palms, and ferns.
Time: 9 a.m. to noon
UF/IFAS Extension Walton County
DeFuniak Springs, FL
Escambia County: UF/IFAS Extension Escambia County is partnering with the Escambia County Water Quality and Land Management Department and the Florida Forest Service for the annual Tree Giveaway. Events begin with a tree planting demonstration at 8:45 and conclude by noon (or until the trees are all distributed, two per household). Beulah Middle School, 6001 Nine Mile Road, Pensacola.
Jackson County: Tree give-away Saturday, January 18 at 9 am at Florida Forest Service work center at 3973 Kynesville Rd, Marianna
Wakulla County: UF/IFAS Wakulla County Master Gardeners are hosting a tree giveaway.
Saturday, January 25th
Leon County: UF/IFAS Extension Leon County Master Gardeners will assist with the county’s Arbor Day tree planting at 9 a.m. Martha Wellman Park, 5317 W. Tennessee St., Tallahassee.

by Laura Tiu | Jan 10, 2020

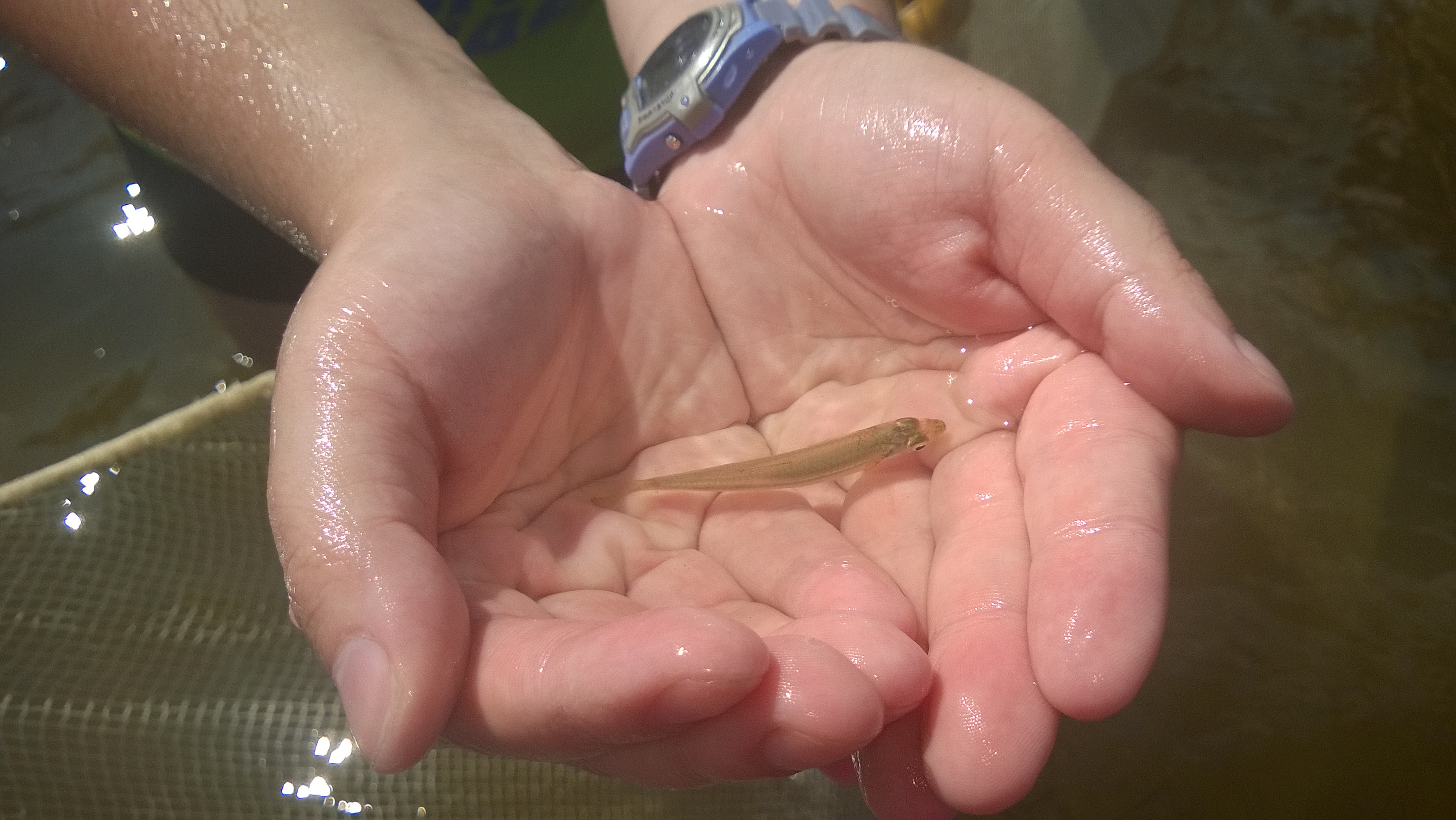
A 4-H youth at Camp Timpoochee Marine Camp dissecting a lionfish.
Are you interested in learning about marine life, going fishing, or exploring the underwater world with a mask and snorkel? If so, this is the camp for you! This local education opportunity for budding marine scientists will be happening this summer at Camp Timpoochee in Niceville, FL. The camps enable participants to explore the marine and aquatic ecosystems of Northwest Florida; especially that of the Choctawhatchee Bay. Campers get to experience Florida’s marine environment through fishing, boating snorkeling, games, STEM (science, technology, engineering & math) activities and other outdoor adventures. University of Florida Sea Grant Marine Agents and State 4-H Staff partner to provide hands-on activities exploring and understanding the coastal environment.
Florida Sea Grant has a long history of supporting environmental education for youth and adults to help them become better stewards of the coastal zone. This is accomplished by providing awareness of how our actions affect the health of our watersheds, oceans and coasts and marine camp is a great opportunity for sharing that information. Many of the Sea Grant youth activities use curriculum developed by the national Sea Grant program and geared toward increasing student competency in math, science, chemistry and biology. The curriculum is fun and interesting!
Registration opens Monday, January 13th at 11:00 am CST. The camps fill up quickly, so early registration is encouraged. Marine Camp is open to 4-H members and non 4-H members between the ages of 8-12 (Junior Camp) and ages 13-17 (Senior Camp). In the summer of 2020, there will be one Senior camp, June 22-26, and two Junior Camps, July 13-17 and July 20-24. The cost for Senior Camp is $350 for the week and $300 for Junior Camp.

Sampling the benthic community at Timpoochee.
If Marine Camp sounds interesting to someone you know, visit the Camp Timpoochee website at http://florida4h.org/camps_/specialty-camps/marine/ for the 2020
dates and registration instructions. A daily snack from the canteen and a summer camp T-shirt are included in the camp fees, along with three nutritious meals per day prepared on site by our certified food safety staff. All cabins are air-conditioned. So many surprises await at marine camp, come join the fun.

by Sheila Dunning | Oct 10, 2019
 Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be.
Over 1.8 million Monarch butterflies have been tagged and tracked over the past 27 years. This October these iconic beauties will flutter through the Florida Panhandle on their way to the Oyamel fir forests on 12 mountaintops in central Mexico. Monarch Watch volunteers and citizen scientists will be waiting to record, tag and release the butterflies in hopes of learning more about their migration and what the 2019 population count will be.
This spring, scientists from World Wildlife Fund Mexico estimated the population size of the overwintering Monarchs to be 6.05 hectacres of trees covered in orange. As the weather warmed, the butterflies headed north towards Canada (about three weeks early). It’s an impressive 2,000 mile adventure for an animal weighing less than 1 gram. Those butterflies west of the Rocky Mountains headed up California; while the eastern insects traveled over the “corn belt” and into New England. When August brought cooler days, all the Monarchs headed back south.
What the 2018 Monarch Watch data revealed was alarming. The returning eastern Monarch butterfly population had increased by 144 percent, the highest count since 2006. But, the count still represented a decline of 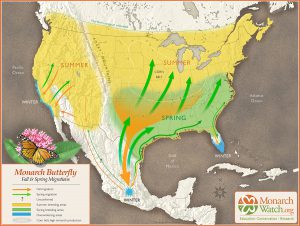 90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing.
90% from historic levels of the 1990’s. Additionally, the western population plummeted to a record low of 30,000, down from 1.2 million two decades ago. With estimated populations around 42 million, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began the process of deciding whether to list the Monarch butterfly as endangered or threatened in 2014. With the additional information, FWS set a deadline of June 2019 to decide whether to pursue the listing.
Scientists estimate that 6 hectacres is the threshold to be out of the immediate danger of migratory collapse. To put things in scale: A single winter storm in January 2002 killed an estimated 500 million Monarchs in their Mexico home. However, with recent changes on the status of the Endangered Species Act, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has delayed its decision until December 2020. One more year of data may be helpful to monarch conservation efforts.
 Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.
Individuals can help with the monitoring and restoring the Monarch butterflies habitat. There are two scheduled tagging events in Panhandle, possibly more. St. Mark’s National Wildlife Refuge is holding their Butterfly Festival on Saturday, October 26 from 10a.m. to 4 p.m. Henderson Beach State Park in Destin will have 200 butterflies to tag and release on Saturday, November from 9 – 11 a.m. Ask around in the local area. There may be more opportunities.
There is something more you can do to increase the success of the butterflies along their migratory path – plant more Milkweed (Asclepias spp.). It’s the only plant the Monarch caterpillar will eat. When they leave their hibernation in Mexico around February or March, the adults must find Milkweed all along the path to Canada in order to lay their eggs. Butterflies only live two to six weeks. They must mate and lay eggs along the way in order for the population to continue its flight. Each generation must have Milkweed about every 700 miles. Check with the local nurseries for plants. Though orange is the most common native species, Milkweed comes in many colors and leaf shapes.

by Ray Bodrey | Apr 17, 2019
Soon, two important ecological surveys will begin in Gulf County, concerning both diamondback terrapins and mangroves.
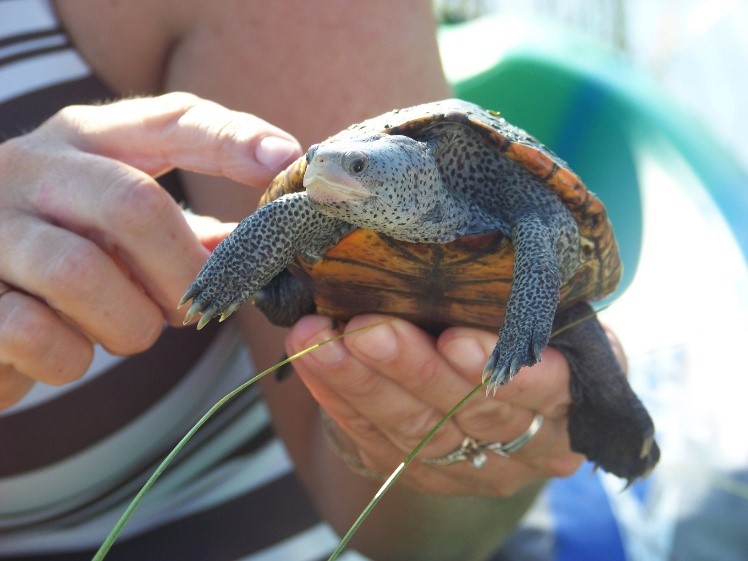
Florida is home to five subspecies of diamondback terrapin, three of which occur exclusively in Florida. Diamondback terrapins live in coastal marshes, tidal creeks, mangroves, and other brackish or estuarine habitats. However, the diamondback terrapin is currently listed as a Species of Greatest Conservation Need (SGCN).
Diamondback terrapin populations, unfortunately, are nationally in decline. Human activities, such as pollution, land development and crabbing without by-catch reduction devices are often reasons for the decline, but decades ago they were almost hunted to extinction for their tasty meat. The recent decline has raised concern of not only federal agencies, but also organizations and community groups on the state and local levels. Diamondback Terrapin range is thought to have once been all of coastal Florida, including the Keys.

Figure 1: Diamondback Terrapin.
Credit: Rick O’Connor, UF/IFAS Extension & Florida Sea Grant, Escambia County.
Mangroves, a shoreline plant species of south Florida, are migrating north and are now being found in the Panhandle. Both red and black mangroves have been found in St. Joseph Bay. Mangroves establishment could be an important key to a healthy bay ecosystem, as a factor in shoreline restoration and critical aquatic life habitat.
Currently there is a significant data gap for both diamondback terrapin and mangrove populations. Therefore, there is a great need to conduct assessments to learn more about their geographic distribution.

Figure 2. Black Mangrove in St. Joseph Bay.
Credit: Ray Bodrey, UF/IFAS Extension & Florida Sea Grant, Gulf County.
The Forgotten Coast Sea Turtle Center is partnering with UF/IFAS Extension & Florida Sea Grant to assist in surveying and monitoring diamondback terrapins and mangroves in St. Joseph Bay, and we need your help! UF/IFAS Extension & Florida Sea Grant Agent’s Rick O’Connor and Ray Bodrey are providing a training workshop for volunteers and coordinating surveys for St. Joseph Bay. Terrapin surveys require visiting an estuarine location where terrapin nesting sites and mangrove plants are highly probable. Volunteers will visit their assigned locations at least once a week during the months of May and June and complete data sheets for each trip. Each survey takes about two hours, and some locations may require a kayak to reach.
If you are interested in volunteering for these important projects, we will hold a training session on Monday, April 22nd at 1:00 p.m. ET at the Forgotten Coast Sea Turtle Center (located at 1001 10th Street, Port St. Joe).
For more information, please contact:
Ray Bodrey, UF/IFAS Extension Gulf County, Extension Director
rbodrey@ufl.edu
(850) 639-3200
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.
by Sheila Dunning | Jan 4, 2019

Tree planting in Mary Esther
The best time to plant a tree is twenty years ago. The second best time is for Arbor Day. Florida recognizes the event on the third Friday in January, but planting any time before spring will establish a tree quickly. Arbor Day is an annual observance that celebrates the role of trees in our lives and promotes tree planting and care. As a formal holiday, it was first observed on April 10, 1872 in the state of Nebraska. Today, every state and many countries join in the recognition of trees impact on people and the environment. Trees are the longest living organisms on the planet and one of the earth’s greatest natural resources. They keep our air supply clean, reduce noise pollution, improve water quality, help prevent erosion, provide food and building materials, create shade, and help make our landscapes look beautiful. A single tree produces approximately 260 pounds of oxygen per year. That means two mature trees can supply enough oxygen annually to support a family of four. The idea for Arbor Day in the U.S. began with Julius Sterling Morton. In 1854 he moved from Detroit to the area that is now the state of Nebraska. J. Sterling Morton was a journalist and nature lover who noticed that there were virtually no trees in Nebraska. He wrote and spoke about environmental stewardship and encouraged everyone to plant trees. Morton emphasized that trees were needed to act as windbreaks, to stabilize the soil, to provide shade, as well as, fuel and building materials for the early pioneers to prosper in the developing state. In 1872, The State Board of Agriculture accepted a resolution by J. Sterling Morton “to set aside one day to plant trees, both forest and fruit.” On April 10, 1872 one million trees were planted in Nebraska in honor of the first Arbor Day. Shortly after the 1872 observance, several other states passed legislation to observe Arbor Day. By 1920, 45 states and territories celebrated Arbor Day. Richard Nixon proclaimed the last Friday in April as National Arbor Day during his presidency in 1970. Today, all 50 states in the U.S. have official Arbor Day, usually at a time of year that has the correct climatological conditions for planting trees. For Florida, the ideal tree planting time is January, so Florida’s Arbor Day is celebrated on the third Friday of the month. Similar events are observed throughout the world. In Israel it is the Tu B Shevat (New Year for Trees). Germany has Tag des Baumes. Japan and Korea celebrate an entire week in April. Even, Iceland one of the most treeless countries in the world observes Student’s Afforestation Day. The trees planted on Arbor Day show a concern for future generations. The simple act of planting a tree represents a belief that the tree will grow and some day provide wood products, wildlife habitat erosion control, shelter from wind and sun, beauty, and inspiration for ourselves and our children.

Trees provide us with benefits including serving as a sound barrier, stormwater abatement, and of course fresh air and oxygen
“It is well that you should celebrate your Arbor Day thoughtfully, for within your lifetime the nation’s need of trees will become serious. We of an older generation can get along with what we have, though with growing hardship; but in your full manhood and womanhood you will want what nature once so bountifully supplied and man so thoughtlessly destroyed; and because of that want you will reproach us, not for what we have used, but for what we have wasted.”
~Theodore Roosevelt, 1907 Arbor Day Message

by Sheila Dunning | Jan 19, 2018
 The Florida Master Naturalist Program is an adult education University of Florida/IFAS Extension program. Training will benefit persons interested in learning more about Florida’s environment or wishing to increase their knowledge for use in education programs as volunteers, employees, ecotourism guides, and others.
The Florida Master Naturalist Program is an adult education University of Florida/IFAS Extension program. Training will benefit persons interested in learning more about Florida’s environment or wishing to increase their knowledge for use in education programs as volunteers, employees, ecotourism guides, and others.
Through classroom, field trip, and practical experience, each module provides instruction on the general ecology, habitats, vegetation types, wildlife, and conservation issues of Coastal, Freshwater and Upland systems. Additional special topics focus on Conservation Science, Environmental Interpretation, Habitat Evaluation, Wildlife Monitoring and Coastal Restoration. For more information go to: http://www.masternaturalist.ifas.ufl.edu/ Okaloosa and Walton Counties will be offering Upland Systems on Thursdays from February 15- March 22. Topics discussed include Hardwood Forests, Pinelands, Scrub, Dry Prairie, Rangelands and Urban Green Spaces. The program also addresses society’s role in uplands, develops naturalist interpretation skills, and discusses environmental ethics. Check the website for a Course Offering near you :http://conference.ifas.ufl.edu/fmnp/
















