by Sheila Dunning | Jun 17, 2014
 The old cliché is “April showers bring May flowers”, but April deluges create weak plants and yellow grass. You were following the UF/IFAS recommendations and waited until April 15th to fertilize. You followed the Urban Turf Rule and applied a low-phosphate fertilizer with slow-release nitrogen. Yet, your grass is yellow and the shrubs haven’t put on any new growth. What happened? The 18” + of rainfall that we experienced at the end of April flushed nearly everything out of the soil, including any fertilizer you applied. Nitrogen and potassium are highly leachable. Phosphorus is also depleted under saturated soil conditions.
The old cliché is “April showers bring May flowers”, but April deluges create weak plants and yellow grass. You were following the UF/IFAS recommendations and waited until April 15th to fertilize. You followed the Urban Turf Rule and applied a low-phosphate fertilizer with slow-release nitrogen. Yet, your grass is yellow and the shrubs haven’t put on any new growth. What happened? The 18” + of rainfall that we experienced at the end of April flushed nearly everything out of the soil, including any fertilizer you applied. Nitrogen and potassium are highly leachable. Phosphorus is also depleted under saturated soil conditions.
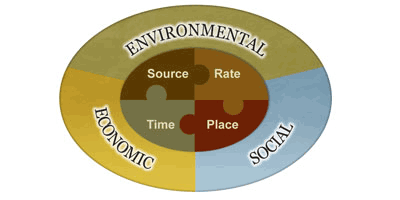
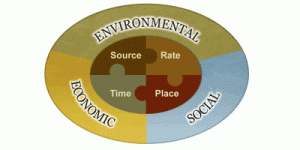
If you haven’t submitted a soil test since the storm, now is the time to do so. It’s time to apply a summer fertilizer, but it needs to address all the nutrient deficiencies created from the excess rain. Soil test kits can be obtained from your County Extension office. When you get the results from the University of Florida Lab, it is important to remember the 4 Rs when applying fertilizer. It needs to be the Right Source, applied at the Right Rate, at the Right Time, and over the Right Place.
Best Management Practices (BMPs) have been developed to allow individuals to make conscientious decisions regarding fertilizer selection that will reduce the risk of water contamination. The Right Source for a BMP-compliant fertilizer is one that contains a portion of slow-release (water insoluble) nitrogen with little to no phosphorus, and a potassium level similar to the nitrogen percentage (e.g. 15-0-15, that contains 5% coated nitrogen). However, a soil test is the only way to accurately identify the specific nutrients your landscape is lacking. Many soil tests indicate a need for phosphate and currently it is illegal to apply more than 0.25 pounds per 1,000 sq. ft. without a soil test verifying the need.
Next, the fertilizer must be applied at the Right Rate. In order to do that, you must know the square footage of your property and how much you can spread using the settings on your equipment. Individuals walk at varied speeds and the product recommended rates are based on 1,000 sq.ft. areas. For information on calibrating application equipment refer to  the publication, “How to Calibrate Your Fertilizer Spreader”. Using the 15-0-15 fertilizer mentioned earlier, the Right Rate for one application would be 3 pounds per 1,000 sq.ft.. That 35 pound bag is all that is needed for a nearly 12,000 sq.ft. yard (a large corner lot).
the publication, “How to Calibrate Your Fertilizer Spreader”. Using the 15-0-15 fertilizer mentioned earlier, the Right Rate for one application would be 3 pounds per 1,000 sq.ft.. That 35 pound bag is all that is needed for a nearly 12,000 sq.ft. yard (a large corner lot).
The Right Time for applying fertilizer is when the plants are actively growing and beginning to show nutrient deficiencies. Summer, when rainfall and irrigation is frequent, is often a typical application time. The Right Place is only on living plant areas. Be cautious to avoid getting fertilizer on the sidewalk, driveway and street. A deflector on your spreader is very helpful. Otherwise, be sure to sweep or blow the fertilizer back onto the grass or into the landscape beds. Avoid having fertilizer end up in any water body.

by Roy Carter | Jun 10, 2014

Blueberry. Photo credit: Eric Zamora, UF IFAS.
Blueberries are native to Eastern North America. They are one of the few crop plants that originated here. The rabbiteye blueberry occurs mostly in certain river valleys in Northern Florida and Southeastern Georgia. The high bush blueberry is native to the eastern third of the United States and Southeastern Canada. Florida is rich in other native species. The woods and swamps of Florida are populated with at least eight wild blueberry species. No area of the state lacks wild blueberries, except where soil pH is above 6.0.
The two types of blueberries grown in Florida are Southern highbush and rabbiteye. The earliest ripening southern highbush varieties ripen about 4 to 6 weeks earlier than the earliest rabbiteye varieties grown at the same location.
Some rabbiteye varieties recommended for our area are: Alice blue, Beckyblue, Climax, Bonita, Brightwell, Chaucer and Tifblue. Some recommended Southern Highbush varieties are: Blue Crisp, Gulf Coast, Jewel, Sharpblue, Santa Fe, Star and Misty.
Blueberries need a fairly acid soil; a pH range of 4 to 5 is suggested. Blueberries grown on alkaline or deep sands will grow poorly. If you need to lower the soil pH before planting, mix in some acidic peat moss.
Blueberries have a shallow, fibrous root system. That means plants should be placed in the ground about an inch deeper than they were growing in the nursery. Rabbiteye blueberries grow poorly in soils with excessive drainage. But they won’t tolerate too much moisture for long periods of time either.
Blueberries are very sensitive to fertilizers. During the first growing season, no mineral fertilizer should be added at all. In the second season, apply about two ounces of an acidic fertilizer per plant. Blueberries can use the same fertilizer as camellias and azaleas, but be careful not to overdo it. Excessive amounts of fertilizer will kill the plants.
Before planting blueberries, you should cultivate the soil by plowing or roto tilling to a depth of at least six inches. Dig a hole large enough so that the roots won’t be crowded. Lightly pack the soil around the roots and water thoroughly. Keep in mind that newly set plants need a good water supply.
Bare-root bushes should be transplanted during the winter months; container grown bushes can be transplanted anytime. The first year after planting, the blossoms should be removed to help the bush grow more quickly.
Pruning is an important part of blueberry culture. It promotes the growth of strong wood, and rids the tree of weak twiggy growth. The strong wood growth is necessary for good fruit production.
Believe it or not, the worst pests of blueberries are birds. You need to protect your bushes with some kind of netting, or employ the old fashioned scarecrow to do the job. It you don’t protect your bushes, you can count on the birds getting to the fruit before you do.
Other than birds, rabbiteye blueberries have few pest or disease problems. Powdery mildew can occur on bushes that don’t get full sun, but this problem can be easily controlled with a sulfur spray. Bud mites, thrips, fruitworms, and defoliating insects can sometimes be a problem.
Weeds will compete with young blueberry bushes for nutrients and water, so keep the beds as free of weeds as possible. Mulches are good for controlling weed growth. If necessary, there are herbicides available.
For more information please see:
Blueberry Gardener’s Guide
by Blake Thaxton | Jun 10, 2014
In this age of tablets, smart phones, and whatever they come up with next, even the gardener can benefit from new technology. Although gardening and landscaping to beautify our surroundings is a way to connect with the past, there are many new tools that are ready to help! Here are a few web sites and phone apps that may prove useful to the gardener.
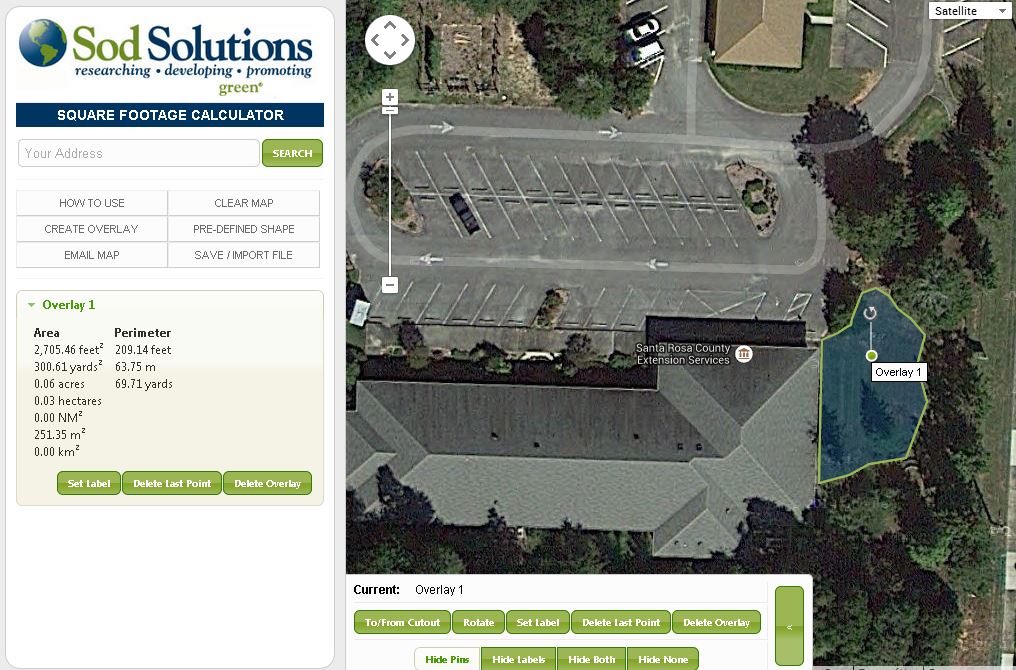
Sod Solutions has made it easy to know how much sod you need to order by using a mapping system to create overlays that measure square footage. Measuring square footage can prove tough for irregularly shaped beds or turf lawns. This website can help measure accurately so one can also apply the correct amount of herbicides, pesticide, or fertilizer. The website can be difficult for the technology challenged among us. An easy solution is to find anyone under the age of 15 and they should be able to help!
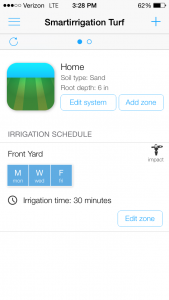
The Smartirrigation Turf app is designed to help homeowners with automatic irrigation systems in scheduling their watering times correctly. This app takes everything into account from soil type to local weather conditions. For example, you set a watering schedule for Zone X of 15 minutes every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. Then, it does not rain for an extended period of time. Because your lawn does not get the supplemental rain that was predicted, the app may tell the home owner to change the setting to 25 minutes. To read more about using the app correctly, click on the link above.
Other apps that might prove useful are:
- NCSU Lawn Care App – An App by North Carolina State University all about lawn care.
- SoilWeb for Iphone – Produced by The California Soil Resource Lab that will tell you what kind of soil you are standing on.
- Leaf Snap – Developed by Columbia University, University of Maryland, and Smithonian Institution. The app uses visual recognition software to identify plants by taking pictures of its leaves.

by Mary Salinas | Jun 10, 2014

A mimosa tree invader in a natural area. Photo by Mary Derrick, UF IFAS.
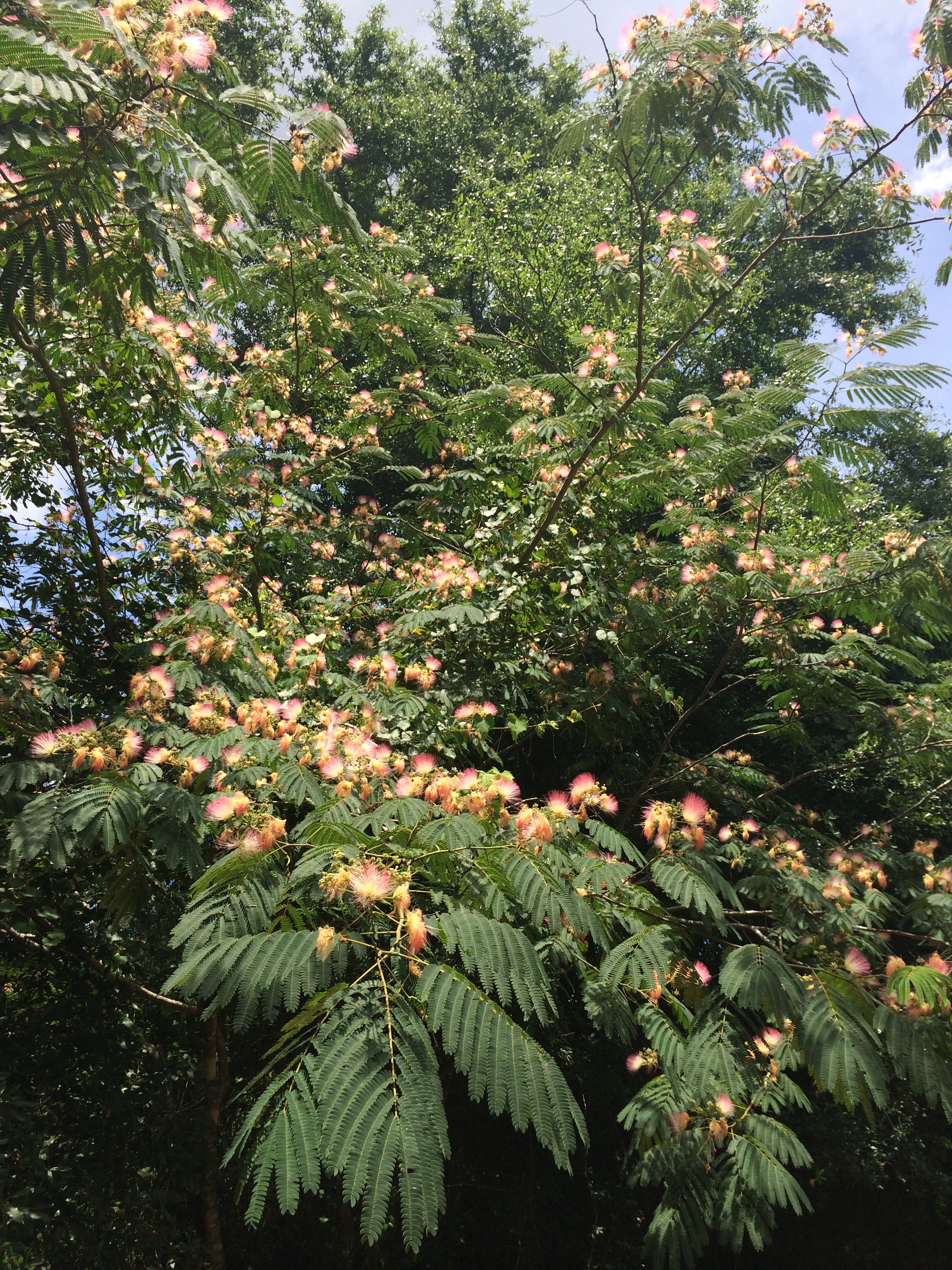
All along the roadsides and in home landscapes this time of year, a profusion of fluffy pink blossoms are adorning trees known as Mimosa, or Albizia julibrissin. This native of China was introduced to home landscapes in this country in the 1700’s to enjoy the fragrant, showy flowers and fine, lacy foliage. However, there is a dark side to this lovely tree. After blooming, it produces an abundance of pods each containing 5 to 10 seeds. Seeds can be spread by wildlife and water; this is evidenced by the appearance of mimosa trees along the roadways, streams and in our natural areas. The seeds can also remain dormant for many years, allowing seedlings to keep sprouting up long after the mother tree is gone.
Mimosa has been categorized as an invasive exotic plant in Florida as it has not only naturalized, but is expanding on its own in Florida native plant communities. This expansion means that our native plants in natural areas get crowded out by the mimosa as it reproduces so prolifically.

Bloom and foliage of the invasive mimosa tree. Photo by Mary Derrick, UF IFAS.
[important]The Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council (FLEPPC) publishes a list of non-native plants that have been determined to be invasive. Click here for the most recent 2013 list![/important]
The first step in controlling this pest plant is to remove existing plants in the landscape. Cutting it down at soil level and immediately painting the stump with a 25% solution of glyphosate or triclopyr should do the trick. Other details and control methods can be found here.
There are some native trees that make excellent alternatives to Mimosa such as fringe tree (Chionanthus virginicus), silverbell (Halesia carolina) and flowering dogwood (Cornus florida).
For more information:
Albizia julibrissin: Mimosa
UF IFAS Center for Aquatic and Invasive Plants: Mimosa

by Larry Williams | Jun 3, 2014

Glistening webbing formed by tree cattle (psocids) Photo credit: Doug Caldwell, University of Florida
Many people are noticing small insects on trunks and branches of their trees. When disturbed, these insects move in a group and are commonly called tree cattle because of this herding habit. They are ¼ inch brownish-black insects with white markings.
Some people assume that these insects will injure their trees but they are harmless. They could be considered beneficial.
These insects are called psocids (pronounced so-cids). They have numerous common names including tree cattle and bark lice. They feed on lichen, moss, algae, fungi, spores, pollen and the remains of other insects found on the tree’s bark. As a result, they are sometimes referred to as bark cleaners.
Tree cattle may form webbing. This webbing is tight against the tree’s trunk and/or limbs. It appears suddenly. The webbing is used as a protection from weather and predators. Underneath you may find psocids.
The glistening webbing may attract a person’s attention resulting in the tree being visually inspected from top to bottom. A dead branch or other imperfections in the tree may be noticed and then wrongly blamed on the tree cattle. I’ve talked to homeowners that sprayed their trees with insecticides or that hired pest control businesses to treat the trees as a result of finding the webbing/psocids. One person told me that he cut down a tree after finding tree cattle. He wrongly assumed that these insects were pests that might move through the area and kill trees. He thought he was doing a good thing.
Adult female psocids lay eggs in clusters on leaves, branches and tree trunks. After hatching, the immature insects (nymphs) remain together under their silk webbing. Adults have wings which are held roof-like over their body. Nymphs are wingless. Psocids usually have several generations per year in Florida.
After seeing the webbing and/or insects, many people insist on spraying insecticides because they believe these insec

Under the webbing live hundreds of psocids. Photo credit: UF/IFAS Jim Castner
ts are damaging their trees. But as mentioned, they are bark cleaners and do not damage trees. If the silk webbing is considered unsightly, a heavy stream of water from a garden hose can be used to wash insects and webbing off infested trees. If nothing is done, the webbing usually goes away in several weeks.
Psocids can be found on many rough-barked hardwood trees and palms. Occasionally, they may be found on wood siding, fence posts or similar areas.

 The old cliché is “April showers bring May flowers”, but April deluges create weak plants and yellow grass. You were following the UF/IFAS recommendations and waited until April 15th to fertilize. You followed the Urban Turf Rule and applied a low-phosphate fertilizer with slow-release nitrogen. Yet, your grass is yellow and the shrubs haven’t put on any new growth. What happened? The 18” + of rainfall that we experienced at the end of April flushed nearly everything out of the soil, including any fertilizer you applied. Nitrogen and potassium are highly leachable. Phosphorus is also depleted under saturated soil conditions.
The old cliché is “April showers bring May flowers”, but April deluges create weak plants and yellow grass. You were following the UF/IFAS recommendations and waited until April 15th to fertilize. You followed the Urban Turf Rule and applied a low-phosphate fertilizer with slow-release nitrogen. Yet, your grass is yellow and the shrubs haven’t put on any new growth. What happened? The 18” + of rainfall that we experienced at the end of April flushed nearly everything out of the soil, including any fertilizer you applied. Nitrogen and potassium are highly leachable. Phosphorus is also depleted under saturated soil conditions. the publication, “How to Calibrate Your Fertilizer Spreader”. Using the 15-0-15 fertilizer mentioned earlier, the Right Rate for one application would be 3 pounds per 1,000 sq.ft.. That 35 pound bag is all that is needed for a nearly 12,000 sq.ft. yard (a large corner lot).
the publication, “How to Calibrate Your Fertilizer Spreader”. Using the 15-0-15 fertilizer mentioned earlier, the Right Rate for one application would be 3 pounds per 1,000 sq.ft.. That 35 pound bag is all that is needed for a nearly 12,000 sq.ft. yard (a large corner lot).