by Danielle S. Williams | May 7, 2020

‘Early Pride’ Tangerine. Photo courtesy of Danielle Sprague.
Citrus is not only a vital part of our economy in Florida but it’s also a major component in our landscapes. Having grown up in the major grapefruit producing region of Florida, the citrus industry is near to my heart. So for me, it is very exciting to see all of the interest in the citrus industry in North Florida despite the devastation the industry is facing in South Florida. With many folks spending more time outdoors and working in the landscape, I wanted to share some ways homeowners can enjoy citrus in their landscape all while protecting the future of the citrus industry in North Florida!
First thing’s first…identification!
It’s important to be aware of some of the major pests and diseases affecting citrus. Fortunately for us in the Panhandle, many of the major pests and diseases troubling citrus to the south haven’t become quite as widespread in our area, and with your help we can keep it that way! Regularly scouting the citrus in your landscape and detecting any major pests or diseases early will be very important to prevent it from spreading.
The first major disease all Floridians should be aware of is citrus greening. Citrus greening or huanglongbing (HLB) is the major disease affecting the citrus industry worldwide. It is a bacterial disease caused by the bacteria Candidatus Liberibacter. The bacterium is spread from tree to tree by a tiny insect known as the Asian citrus psyllid. Psyllids spread the disease by feeding on infected trees and moving on to non-infected trees. Once the tree is infected, there’s little hope for survival as there is no cure for citrus greening.
Citrus greening can be difficult to diagnose as it can be easily confused with nutrient deficiency. Symptoms of citrus greening include yellowing of the veins and a blotchy mottle pattern. Nutrient deficiencies tend to have a symmetrical pattern on each side of the leaf vein whereas citrus greening is asymmetrical. Overall, a tree infected with citrus greening will appear unhealthy with discolored leaves, a thin canopy, and reduced fruit production.

Citrus Canker presenting on a leaf. Photo courtesy of Danielle Sprague.
Another disease to be on the lookout for is citrus canker. Citrus is also caused by a bacterial pathogen but is spread primarily though wind, rain and human movement. Citrus canker is highly contagious and can spread very rapidly. Transporting infected plant material from an area where canker is present is the primary means of spreading the pathogen.
Purchase from a certified nursery!
One of the absolute most important things you can do if you are planting citrus is to purchase your trees from a certified citrus nursery! A certified nursery has been inspected by the state to confirm that the nursery is producing clean, disease free trees. Citrus trees grown in a certified nursery will have a tag with the name of the nursery, registration number, the tree variety, and rootstock.
When buying a tree from a secondary retailer, you will want to be sure to examine the tree for any signs and symptoms of pests and diseases. A healthy tree will have dark green leaves, a smooth trunk and show no signs of wilt.

Certified nursery label. Photo courtesy of Danielle Sprague.
Other ways to protect citrus:
- Learn how to properly care for citrus trees. Proper watering an fertilization will make them less susceptible to pest and disease.
- Report any suspected pest and diseases to the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS) Division of Plant Industry by calling 1-888-397-1517
- Don’t bring back plants or fruit into Florida! They could introduce new pests and diseases.
Keeping the Panhandle free of citrus greening and citrus canker will play a major role in the success of the citrus industry in North Florida. For assistance with pest and disease identification or for more information, contact your local Extension agent.

by Larry Williams | Apr 23, 2020
One of the things to do while stuck at home due to COVID-19 restrictions, is to look for caterpillars and butterflies in your landscape. I’ve noticed giant swallowtail butterflies (Papilio cresphontes) a little early this year. The giant swallowtail is one of the largest and most beautiful butterflies in our area. Its larval stage is known as the orangedog caterpillar. This unusual name comes from the fact that it feeds on young foliage of citrus trees.

Orangedog caterpillar. Photo credit: Donald Hall, University of Florida
The orangedog caterpillar is mostly brown with some white blotches, resembling bird droppings more than a caterpillar. When disturbed, it may try to scare you off by extruding two orange horns that produce a pungent odor hard to wash off.
I’ve had some minor feeding on citrus trees in my landscape from orangedog caterpillars. But I tolerate them. I’m not growing the citrus to sell. Sure the caterpillars eat a few leaves but my citrus trees have thousands of leaves. New leaves eventually replace the eaten ones. I leave the caterpillars alone. They eat a few leaves, develop into chrysalises and then emerge as beautiful giant swallowtail butterflies. The whole experience is a great life lesson for my two teenagers. And, we get to enjoy beautiful giant swallowtail butterflies flying around in our landscape and still get plenty of fruit from the citrus trees. It is a win, win, win.
In some cases, the caterpillars can cause widespread defoliation of citrus. A few orangedog caterpillars can defoliate small, potted citrus trees. Where you cannot tolerate their feeding habits, remove them from the plant. But consider relocating the caterpillars to another area. In addition to citrus, the orangedog caterpillars will use the herb fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) and rue (Ruta graveolens) as a food source. Some butterfly gardens plant citrus trees to provide food for orangedog caterpillars so that they will have giant swallowtail butterflies. So you could plan ahead and grow some fennel, rue or find a butterfly garden in your area for the purpose of relocating the larvae.

Yellow giant swallowtail butterfly on pink garden phlox flowers. Photo credit: Larry Williams
The adult butterflies feed on nectar from many flowers, including azalea, bougainvillea, Japanese honeysuckle, goldenrod, dame’s rocket, bouncing Bet and swamp milkweed. Some plants in this list might be invasive.
Keep in mind that mature citrus trees can easily withstand the loss of a few leaves. If you find and allow a few orangedog caterpillars to feed on a few leaves of a mature citrus tree in your landscape, you and your neighbors might get to enjoy the spectacular giant swallowtail butterfly.
More information on the giant swallowtail butterfly is available online at http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in134.
by Matt Lollar | Feb 14, 2018
Register today for the 2018 Panhandle Fruit & Vegetable Conference! The Panhandle Fruit & Vegetable Conference is scheduled for February 19th & 20th. On the 19th we will go on an afternoon farm tour in Baldwin County, AL that will end with dinner (included) at Auburn University’s Gulf Coast Research and Extension Center in Fairhope. Educational sessions with guest speakers from University of Florida, Auburn University, and Texas A&M University will be held on February 20th where topics will include Citrus Production, Vegetable Production, Protected Ag Production, Marketing/Business, Food Safety, and Fruit & Nut Production. A full list of topics can be found here. Fifty dollars (plus $4.84 processing fee) covers the tour and dinner on the 19th and educational sessions, breakfast, and lunch on the 20th! The complete agenda is now available. Use your mouse or finger to “click” on the image below for full screen viewing.
Make sure to register by Wednesday, February 14th! – Registration Link

by Mary Salinas | May 11, 2017

Citrus canker symptoms on twigs, leaves and fruit. Photo by Timothy Schubert, FDACS
In November 2013, citrus canker was found for the first time in the Florida panhandle in Gulf Breeze in southern Santa Rosa County. The Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS) tested and confirmed the disease on grapefruit trees in a residential landscape. Since that time, citrus canker has been confirmed on citrus trees at 27 more locations in Gulf Breeze. To my knowledge it has not been found in any other location in the panhandle. Not yet.

Citrus canker lesions on leaves are raised, rough and visible on both sides of the leaf. Photo by Timothy Shubert, FDACS.
Citrus canker is a serious bacterial disease that only infects citrus trees. It will not infect any other plant species nor is it a threat to human health. This highly contagious disease has no cure as yet. Severely affected trees experience substantial leaf and premature fruit drop and serve as a source for infecting other citrus in the area. The disease spreads through wind, rain and transportation of infected plant material from other locations.
We do not know how the disease came to infect trees in our region. The disease could have been spread through infected fruit or trees brought here from areas where the disease is established, such as central or south Florida.
What should you do if you suspect your citrus is infected with this disease?

Citrus canker lesions can appear in the mines left by the citrus leafminer pest. Photo by Timothy Schubert, FDACS
- Look at Homeowner Fact Sheet: Citrus Canker for more information.
- Leave the tree in place in your yard and call the Division of Plant Industry at FDACS at 1-888-397-1517 for a free inspection and testing of your citrus trees.
- Consult your local Horticulture Extension Agent for more information and control/removal strategies.
- Proper removal of infected trees is recommended to prevent the spread of citrus canker but is not mandatory.
For more information please see:
Save Our Citrus Website
UF IFAS Gardening Solutions: Citrus
Citrus Culture in the Home Landscape
UF IFAS Extension Online Guide to Citrus Diseases

by Carrie Stevenson | Mar 2, 2017
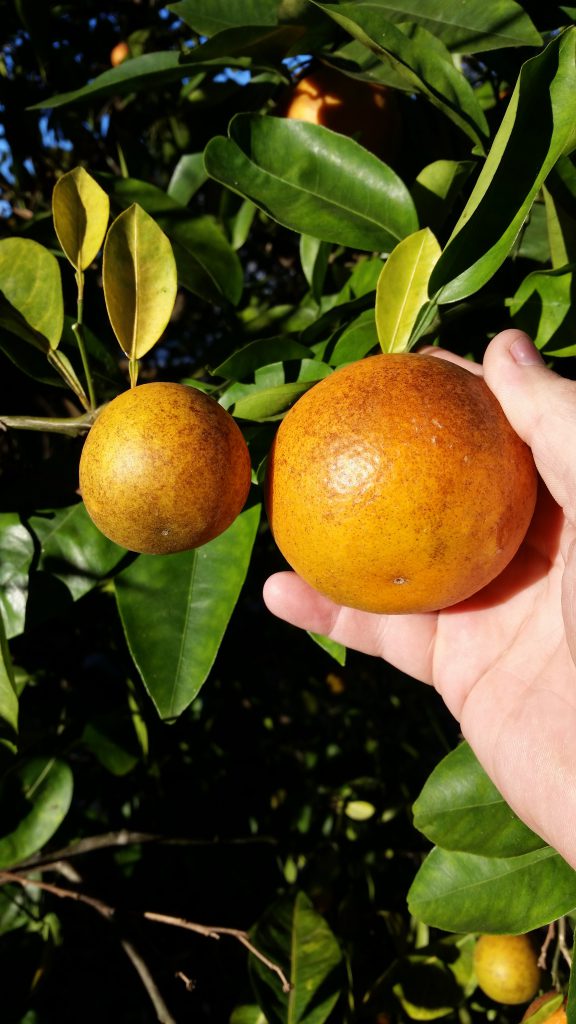

Small Fruit vs Normal
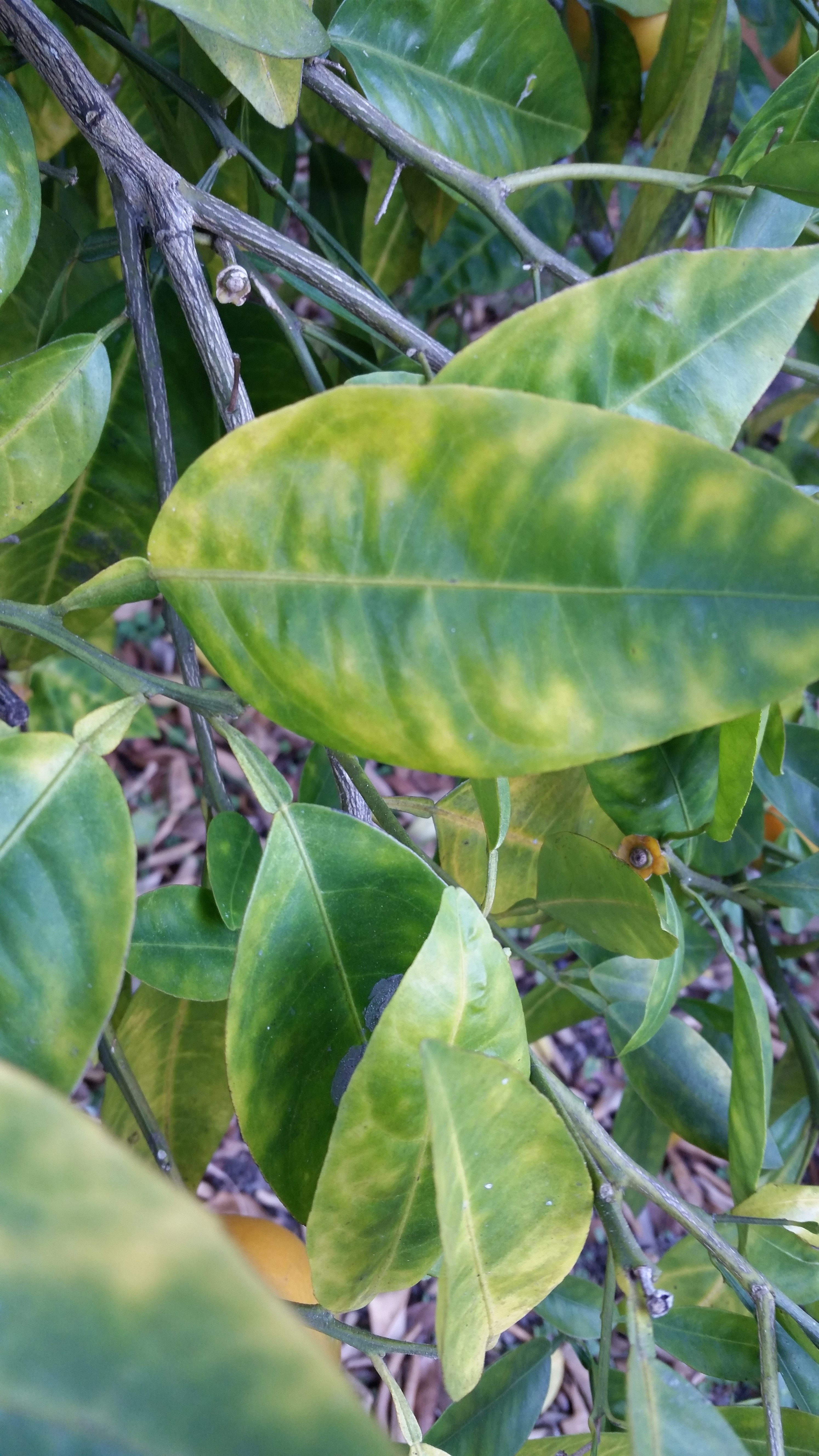
If we look at the big picture when it comes to invasive species, some of the smallest organisms on the planet should pop right into focus. A microscopic bacterium named Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus, the cause of Citrus Greening (HLB), has devastated the citrus industry worldwide. This tiny creature lives and multiplies within the phloem tissue of susceptible plants. From the leaves to the roots, damage is caused by an interruption in the flow of food produced through photosynthesis. Infected trees show a significant reduction in root mass even before the canopy thins dramatically. The leaves eventually exhibit a blotchy, yellow mottle that usually looks different from the more symmetrical chlorotic pattern caused by soil nutrient deficiencies.
One of the primary vectors for the spread of HLB is an insect called the Asian citrus psyllid. These insects feed by sucking juices from the plant tissues and can then transfer bacteria from one tree to another. HLB has been spread through the use of infected bud wood during grafting operations also. One of the challenges with battling this invasive bacterium is that plants don’t generally show noticeable symptoms for perhaps 3 years or even longer. As you would guess, if the psyllids are present they will be spreading the disease during this time. Strategies to combat the impacts of this industry-crippling disease have involved spraying to reduce the psyllid population, actual tree removal and replacement with healthy trees, and cooperative efforts between growers in citrus producing areas. You can imagine that if you were trying to manage this issue and your neighbor grower was not, long-term effectiveness of your efforts would be much diminished. Production costs to fight citrus greening in Florida have increased by 107% over the past 10 years and 20% of the citrus producing land in the state has been abandoned for citrus.
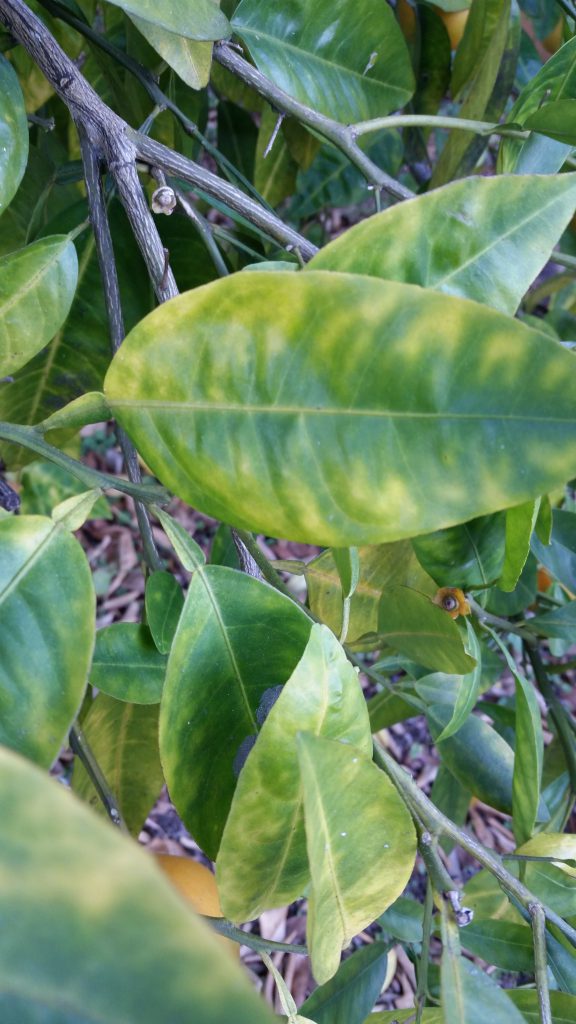

Classic blotchy mottle in Leaves
Many scientists and citrus lovers had hopes at one time that the Florida Panhandle would be protected by our cooler climate, but HLB has now been confirmed in more than one location in backyard trees in Franklin County. The presence of an established population of psyllids has yet to be determined, as there is a possibility infected trees were brought in.
A team of plant pathologists, entomologists, and horticulturists at the University of Florida’s centers in Quincy and Lake Alfred and extension agents in the panhandle are now considering this new finding of HLB to help devise the most effective management strategies to combat this tiny invader in North Florida. With no silver-bullet-cure in sight, cooperative efforts by those affected are the best management practice for all concerned. Vigilance is also important. If you want to learn more about HLB and other invasive species contact your local UF/IFAS Extension office.

Asymmetrical Fruit

Typical nutrient deficiencies observed in leaf, on trees with heavy fruit load. Not related to Citrus Greening (HLB)
Article by: Erik Lovestrand, UF/IFAS Franklin County Extension Director/Florida Sea Grant Agent

by Matthew Orwat | Feb 14, 2017
 Dooryard citrus enthusiasts may be uncertain about late winter management of Satsuma and other citrus trees. Several questions that have come in to the Extension Office recently include:
Dooryard citrus enthusiasts may be uncertain about late winter management of Satsuma and other citrus trees. Several questions that have come in to the Extension Office recently include:
- Should I prune my trees?
- Why are the leaves yellow?
- How soon should I fertilize?
The focus of this article is to provide some answers to these common questions.
Should I prune my trees?
This is a complicated question that is best answered with “it depends…” Pruning is not necessary for citrus, as it is in many temperate fruits, to have excellent production quality and quantity. Citrus trees perform excellently with minimal pruning. The only pruning necessary for most citrus is removing crossing or rubbing branches while shaping young trees, removing dead wood, and pruning out suckers from the root-stock. Homeowners may choose to prune citrus trees to keep them small, but this will reduce potential yield, since bigger trees produce more fruit.
Often, maturing Satsuma trees produce long vertical branches. It is tempting to prune these off, since they make the tree look unbalanced. To maximize yield, allow these branches to weep with the heavy load of fruit until they touch the ground. This allows increased surface area for the tree, since the low areas around the trunk are not bare. Additionally, weeds are suppressed since the low branches shade out weed growth. The ground under the trees remains bare, thus allowing heat from the soil to radiate up during cold weather events. The extra branches around the trunk offer added protection to the bud union as well. If smaller trees are desired for ease of harvest, ‘flying dragon’ root-stock offers dwarfing benefits, so that the mature scion cultivar size will only grow to 8-10 feet tall.
Heavy fruit loads were produced in many home gardens throughout Northwest Florida last year. When fruiting is heavy, citrus trees translocate nitrogen and other nutrients from older leaves to newer growth and fruit. Therefore, temporary yellowing may occur and last until trees resume growing in the spring. Remember, never fertilize after early September, since fertilizing this late in the year can reduce fruit quality and increase potential for cold injury. If a deficiency, as in the photo above persists through spring, consider a soil test, or consult a citrus production publication to determine if additional fertilizer should be added to your fertilizer program.
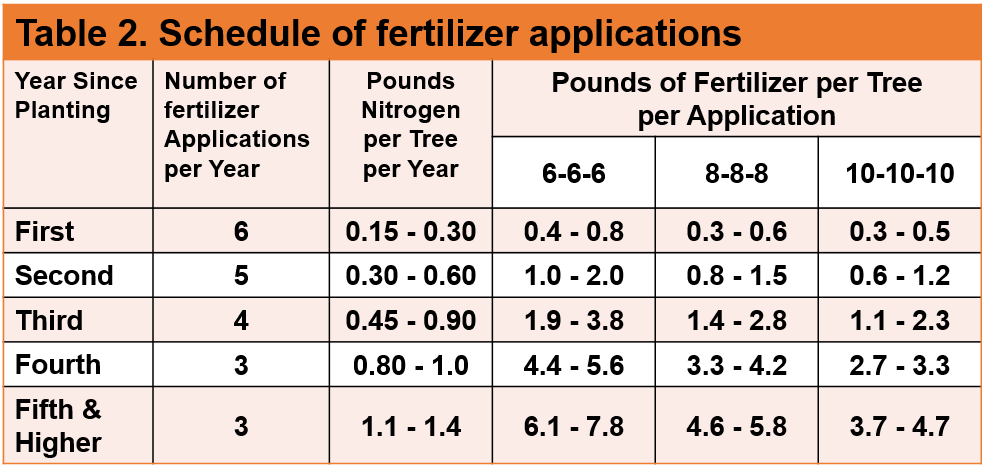
How soon should you fertilize?
Although most Florida citrus publications recommend fertilizing citrus in February, they don’t take into account the potential for late frost in the Panhandle. Thus it makes more sense to wait until mid-March for the first fertilizer application in this region. Citrus trees don’t require a fertilizer with a high percentage of nitrogen, so it is best for fruit quality if an analysis of around 8-8-8 with micro-nutrients is used. Fertilizer should be applied in the drip-line of the tree, not around the trunk. The drip-line of a mature tree is generally considered to extend one foot from the trunk out to one foot from the edge of the furthest branch tip from the trunk. For fertilizer quantity recommendation see the chart below.
Through awareness of the unique managements techniques inherent to dooryard citrus production in the Panhandle, home gardeners are offered an opportunity to provide their friends and family with a substantial portion of their annual citrus !
For more information on this topic please use the following link to the UF/IFAS Publication: