
by Matt Lollar | Jun 23, 2020
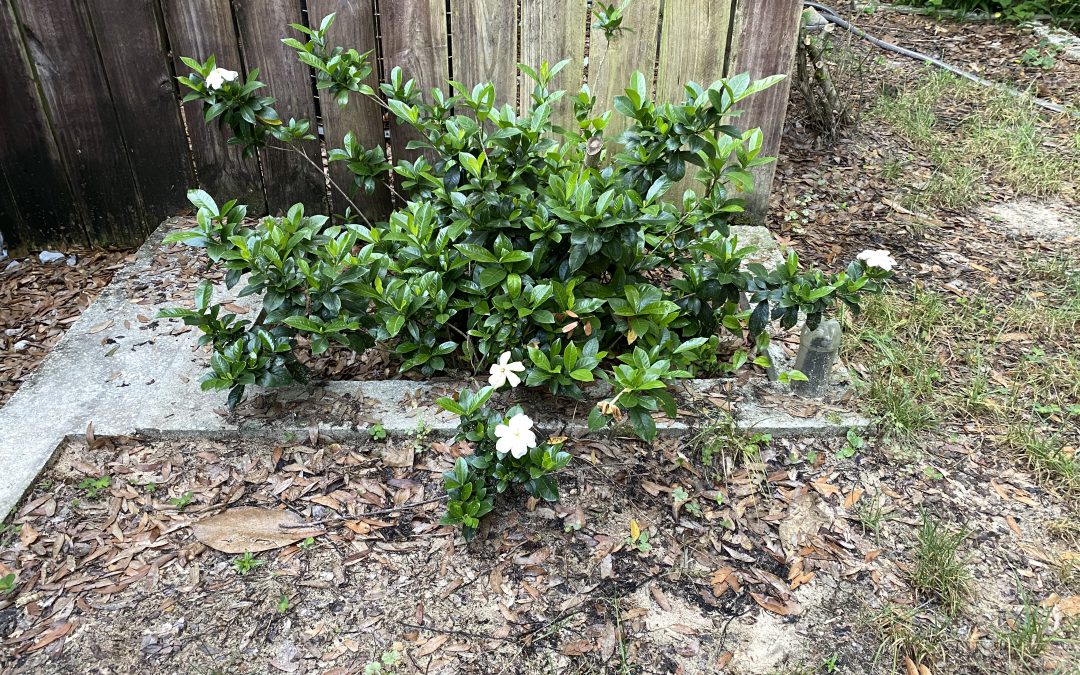
I live in the woods, so I mainly have a “natural” landscape. I remove trees, shrubs, and weeds as I see fit, but for the most part things just grow wild. However, there are a few spots in the yard where the previous owners did a little landscaping. Unfortunately, these spots have become a bit overgrown. One spot in particular features some gardenia plants around the HVAC units. At first, I was a little hesitant to prune these shrubs because they provide some shade to the units. However, they have become overgrown and I know they will grow back. I was patient to wait for them to finish flowering.

A gardenia shrub that has become a bit overgrown. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
As you can see in the photo above, this gardenia has become a bit leggy. It is important to also note the good amount of branching and new growth at the base of the plant. There are a few pruning options available for shaping shrubs such as hedging/terminal pruning, selective pruning, and renewal pruning. While a tree form gardenia can be attractive, it wasn’t desired in this situation. This particular case called for renewal pruning to improve the form of the plant. Renewal pruning is probably the easiest type of pruning, because it requires the least amount of thinking. It basically involves removing the majority of old growth.

A gardenia shrub that has been renewal pruned. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
The picture above is of the same shrub that has been pruned heavily. Not only have the older, leggy branches been removed, but some of the newer growth has been removed to allow for better air circulation within the shrub. This will help reduce the incidence of disease.
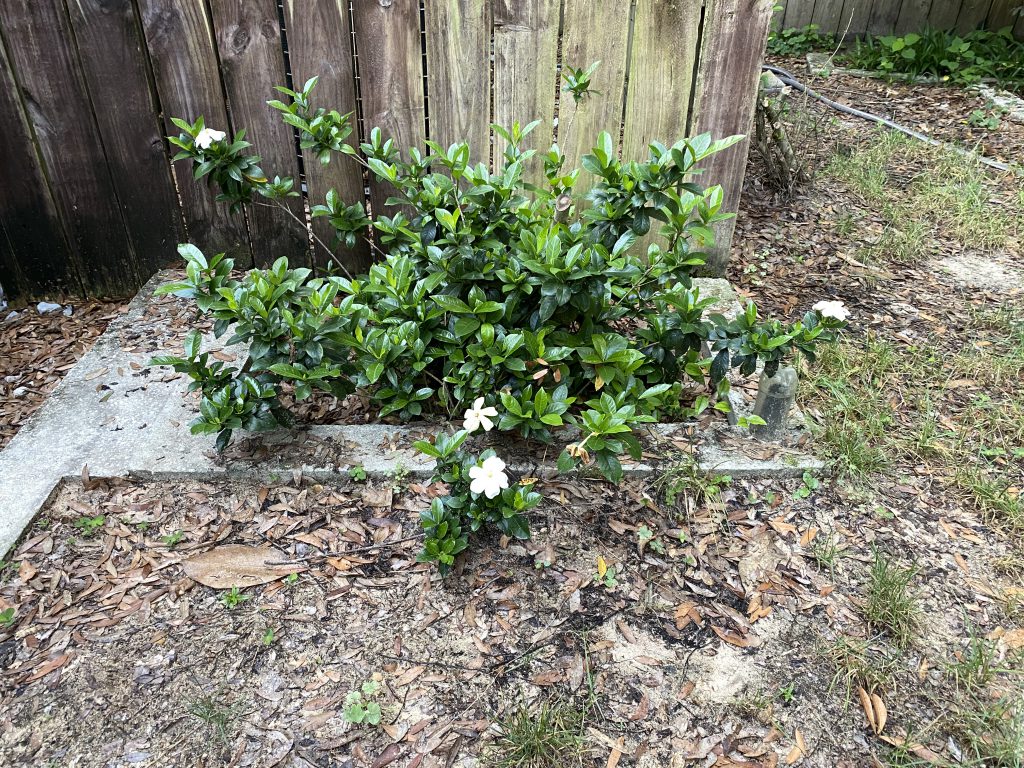

A gardenia shrub six weeks after renewal pruning. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
Six weeks after being pruned, this shrub is flowering for a second time. In a matter of short time it will be providing much needed shade for the HVAC units again. (That is..if I remember to selectively prune throughout the year.) For more information on how to prune and what to prune, please visit the UF/IFAS Gardening Solutions page on pruning.

by Matt Lollar | Mar 20, 2020
It’s always fun to add new plant to the landscape. And it’s even more fun to propagate your own plant material. The question is, what plant propagation method is best? The answer depends on a number of factors such as:
- How much time and money is available?
- Is a uniform crop desired or is trait variation preferred?
- What is the plant species being propagated?
Plants can be propagated either by seed (sexual propagation) or by segments of vegetative material (asexual propagation). Sexual propagation takes far less time and effort because new plants are being started from the seeds (offspring) of parent plants. This type of propagation promotes genetic diversity because offspring may not have the exact characteristics of the parent plants. Sexual propagation increases the possibility of hybrid vigor, which is the improved quality of plant material to that of parent plants. Asexual propagation usually takes more time, but generally ensures that propagated plants will maintain the same characteristics as the parent plant. For some species it may be the only way to pass on desired traits to subsequent generations and it may be the only way to propagate certain species. A plant produced vegetatively can become larger than a plant produced by see in the same amount of time.
Tips for Successful Sexual Propagation
- Seed Collection – Seeds should be collected when fruit is ripe, just before they fall to the ground. In general, seeds should be cleaned, dried, and stored at 40 degrees Fahrenheit (in a refrigerator). However, palm seeds should be planted immediately after harvesting and cleaning.
- Seed Dormancy – Some seeds have thick seed coats the inhibit germination. Some seeds need to be scarified (breaking of the seed coat) and/or stratified (stored in a specific environment) in order to germinate.
- Seed Sowing – Seeds can be germinated in flats or other suitable containers in a seed starting media. Seeds should be planted at a depth of two to three times their diameter, but no deeper than 3 inches. Cycad seeds should be planted just below the medium surface.

Seeds stored in an envelope. Photo Credit: University of Florida/IFAS
Tips for Successful Asexual Propagation – In general, asexual propagation is the propagation of plant material from cuttings of stems, leaves, and/or roots.
- Rooting Hormones – Increase rooting percentage, hasten root initiation, increase the number of roots per cutting, and increase root uniformity. Auxin based rooting hormones (Indolebutyric acid (IBA) and Naphthalenacetic acid (NAA)) are available in dry or liquid forms. It is important to use the correct concentration for the particular plant species because over application can cause damage to cutting base.
- Sticking Cuttings – Cuttings should be stuck in the medium only deep enough to support the cuttings and hold them upright (1/2″ to 1″ deep).
- Post-Rooting Care – Fertilization should be applied as soon as roots emerge from the cuttings. However, overfetilization can increase soluble salts and burn roots.
Examples of Asexual Propagation
- Softwood Cuttings – Taken from woody plants usually three to four weeks after a new flush of growth. Commonly propagated species using this method include: crape myrtle; magnolia; oleander; azalea; jasmine; and boxwood.
- Semihardwood Cuttings – Similar to softwood cuttings, but the lower portion of the cutting has become lignified (woody). Usually taken from new shoots six to nine weeks after a flush of growth. Commonly propagated species using this method include: camellia; pittosporum; junipers; and some hollies.
- Hardwood Cuttings – Taken from the previous season’s growth, just before or during the dormant period. Commonly propagated species using this method include narrow-leaved evergreens and deciduous species during the dormant season after leaves have dropped.
- Leaf Cuttings – Comprised of only the leaf blade or the leaf blade and petiole (leaf stalk). Cuttings are stuck upright in the propagation medium with the basal end (petiole end) of the leaf inserted into the propagation medium. Commonly propagated species using this method include begonias and peperomias.
- Root Cuttings – Taken in late winter or early spring from two to three-year-old plant material. Plants propagated by root cuttings may not reproduce true to type if they are budded or grafted. Commonly propagated species using this method include: plumbago; bayberry; oakleaf hydrangea; and yucca.

Plants being propagated by leaf cuttings. Photo Credit: University of Florida/IFAS
This article provides only a brief overview of propagation methods and techniques. For more information on plant propagation please visit University of Florida Plant Propagation Glossary or Plant Propagation Techniques for the Florida Gardener. Please be advised that some plant material is patented and it is illegal to propagate patented material without written authorization or licensing of the patent holder. If it is patented, a notation of patent number will be on the tag.

by Sheila Dunning | Jan 13, 2020
 No previous experience or accreditation it required to be a landscaper in the state of Florida. So when homeowners are searching for service providers, it is important that they question potential companies about their skills. One good measure is completion of voluntary certifications such as the Florida Nursery, Growers and Landscape Association (FNGLA) Certified Horticulture Professional (FCHP). The FCHP program has been the industry’s standard for measuring horticulture and landscape knowledge since 1984. The training is also useful for property managers, homeowner associations and retail garden center employees, or anyone that wants to know more about Florida’s plants and their care.
No previous experience or accreditation it required to be a landscaper in the state of Florida. So when homeowners are searching for service providers, it is important that they question potential companies about their skills. One good measure is completion of voluntary certifications such as the Florida Nursery, Growers and Landscape Association (FNGLA) Certified Horticulture Professional (FCHP). The FCHP program has been the industry’s standard for measuring horticulture and landscape knowledge since 1984. The training is also useful for property managers, homeowner associations and retail garden center employees, or anyone that wants to know more about Florida’s plants and their care.
Plants are complex and variable living things that range from microscopic to the largest of living organisms. With steady population growth in the state of Florida, environmental damage risks created by the use of improper products and practices has continually risen. State and federal natural resource protection agencies have restricted certain horticultural practices, as well as, fertilizer and pesticide application. It takes scientific knowledge to maintain lawns and landscapes, not just a “green thumb” in order to keep plants healthy while reducing contamination to the soil, air and water that we all need.
The Florida Certified Horticulture Professional training covers 16 areas, including identification, fertilization, irrigation, pest management, safety and business practices. Lecture and hands-on activities are utilized at each session. The 70-hour course will enhance anyone’s knowledge and will provide the basis for professionals to deliver a skilled service to clientele.
If you are a green industry worker or a concerned citizen interested in attending a FCHP preparatory course, there is an opportunity here in Crestview. Beginning Thursday, January 16, 2020 and continuing for 10 weeks to March 19, 2020, the Okaloosa County Extension office will be providing training for $175, which included the newest hard copy manual. Contact Sheila Dunning, 850-689-5850, sdunning@ufl.edu for more information.

by Matt Lollar | Jan 13, 2020
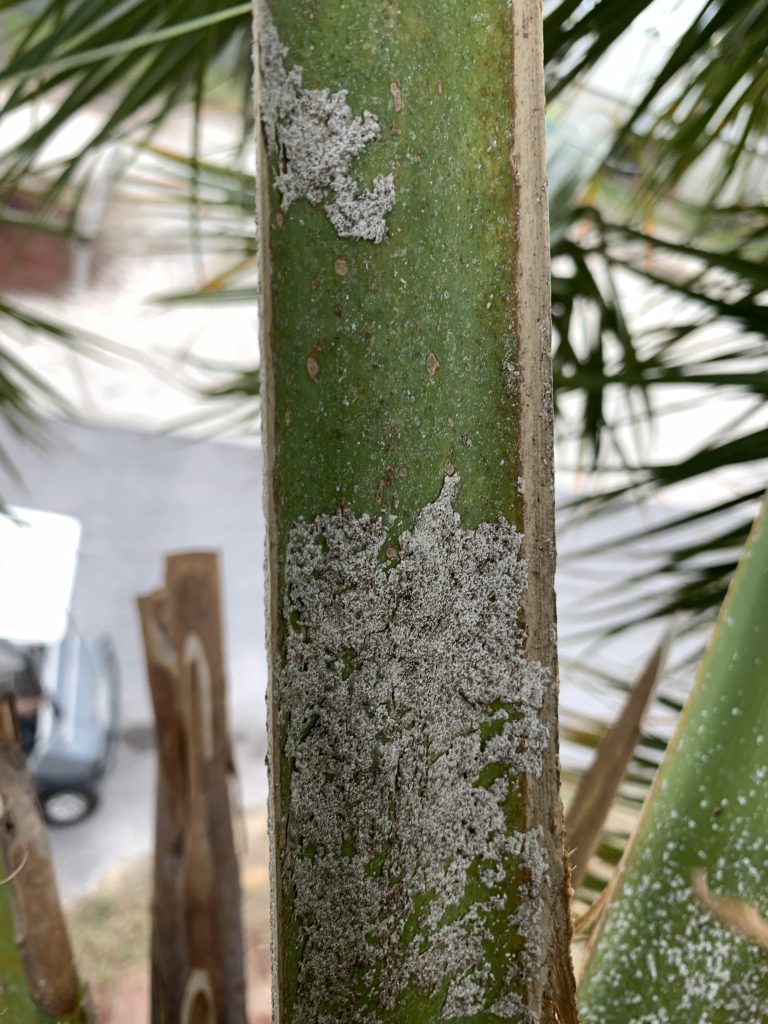

Scale insects on a cabbage palm (Sabal palmetto). Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
This week I was on a couple site visits to look on some cabbage palms (Sabal palmetto) and some banana shrubs (Michelia figo). The palms had a white, waxy substance on their frond petioles and the banana shrubs had white specs on the tops of their leaves. Upon further investigation, I realized the waxy substance and specs were both different species of scales. Scale insects are serious pests of a number of ornamental plants. Here in Florida there are 13 different families of scales with the most common being armored scales, soft scales, and mealybugs. Scales have piercing-sucking mouthparts which they use to siphon fluids from the leaves, stems, and sometimes roots of many ornamental plants. Heavy infestations cause extensive leaf yellowing, premature leaf drop, branch dieback, and eventually plant death.
Scale Biology
The life cycle of a scale begins with eggs being laid beneath wax coverings or beneath the adult female. Eggs typically hatch in 1 to 3 weeks. The newly hatched nymphs, called crawlers, move around a plant until they find a spot to feed. Once a feeding site is located, their piercing sucking mouthparts are inserted into the plant and the crawlers begin to feed and grow. The males of many scale species develop wings as adults and fly to other plants to reproduce.
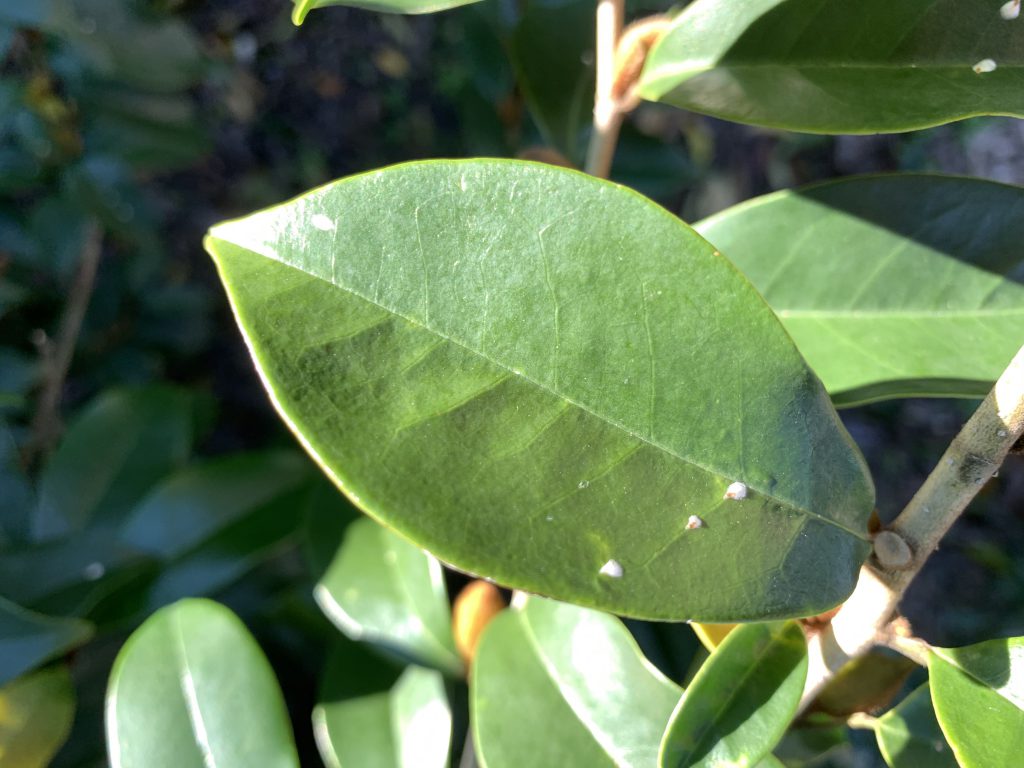

Magnolia white scales on a banana shrub (Michelia figo). Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
Armored Scales
Armored scales get their armor by secreting a waxy covering over their bodies that is not attached. The scale lives under this covering and uses it as a protection to feed under. Armored scales can be almost any color or shape and range anywhere from 1/16 to 1/8 inch in diameter. For females, these shapes range from circular to oval to long and slender. The males typically have coverings that are more elongate and smaller than the females. As adults, the males are tiny, winged, gnat-like insects and are rarely seen.
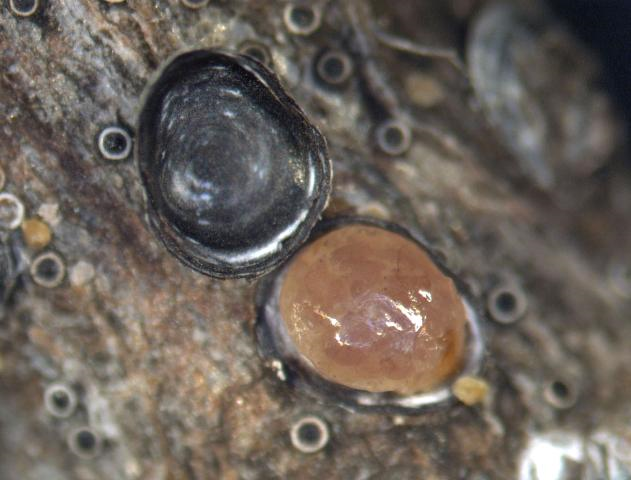

Gloomy scale (Melanaspis tenebricosa) with armored covering removed. Photo Credit: A. G. Dale, University of Florida/IFAS
Soft Scales
Similar to armored scales, soft scales secrete a waxy covering, but it is attached to their bodies. Soft scales can be a number of colors, shapes, and sizes and range anywhere from 1/8 to 1/2 inch in diameter. Their shapes vary from spherical to nearly flat.

Population of adult and immature tuttle mealybugs (Brevennia rehi) on a blade of zoysiagrass. Photo Credit: Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida/IFAS
Mealybugs
Mealybugs are soft-bodied insects that possess a covering of flocculent, white, waxy filaments. They are about 1/8 inch in length and usually pinkish or yellowish in color. Mealybugs have piercing-sucking mouthparts which they use to siphon fluids from the leaves, stems, and sometimes roots of many ornamental plants. Mealybug damage produces discolored, wilted, and deformed leaves.
Scale and Mealybug Management
- Cultural Control – Plant inspection prior to purchase or installation is the first line of defense against a scale or mealybug population. Make sure to inspect the undersides of leaves and plant stems. Infested sections of plants can be pruned and plant material should be cleaned from the planting area and discarded. Also, you can increase air flow and decrease humidity by proper installation and pruning. Over-fertilizing can also increase pest populations.

Larva of a brown lacewing. Credits: Lyle Buss, University of Florida.
- Biological Control – Predators, such as ladybugs and green lacewings, are usually present in large enough numbers to suppress scales and mealybugs to a desirable threshold. However, broad-spectrum insecticides and bad weather can reduce predator numbers. Look for signs of predation by inspecting dead scales for jagged holes in their waxy coatings. If predation signs are present, use more selective chemical controls and oils as opposed to broad-spectrum products.
- Chemical Control – Timing is everything when it comes to managing scale and mealybug insects. Crawler activity is more pronounced with the flush of new plant growth in the spring. Before application, prune infested plant parts off first to promote greater penetration of insecticides into the foliage. Dormant Oils are often used in the winter to smother scale insects. These are good choices to implement because they don’t harm non-target or beneficial insects. Care must be taken to read the label and use them at the correct temperature, since use in hot weather may burn foliage. Contact products (acephate, bifenthrin, carbaryl, etc.) must be applied to inhibit the crawler stages of these insects and systemic products (acetamiprid, imidacloprid, thiamethoxam, etc.) can be used on the sessile growth stage. Plants should be sprayed thoroughly to the point of drip or “run off” from leaves, twigs, and stems. Repeated applications may still be necessary even if the timing is right, as crawler populations are often large and crawlers like to hide under old waxy scales. Systemic drenches are also a viable option. With good spray coverage, horticultural oils can kill scales at all stages of growth. Refer to the product label for phytotoxicity and temperature guidelines. Even after successful treatment, the outer coatings of the scales may remain on the plant material for weeks, which can be unsightly. The best way to determine if scales are dead is to squeeze them. They will be dry when squeezed if they are dead and they will ooze liquids if they are living (they were at least alive to the point of being squashed).
For insect identification and additional information on scale control, please see:
A Guide to Scale Insect Identification
UF/IFAS Featured Creatures
Your County Extension Office

by Matt Lollar | Aug 1, 2019
Large patch Rhizoctonia solani (known as brown patch in cool season grasses) is a common disease of many turfgrass species. It usually occurs during the cooler months from October through May when temperatures are below 80 degrees Fahrenheit. However, signs and symptoms of large patch and other Rhizoctonia diseases can be observed throughout the summer. Less common Rhizoctonia species that occur during the summer months are Rhizoctoni zeae and Rhizoctonia oryzae. Extended periods of turf wetness from excessive rainfall or overwatering provide ideal conditions for the disease to develop and spread.
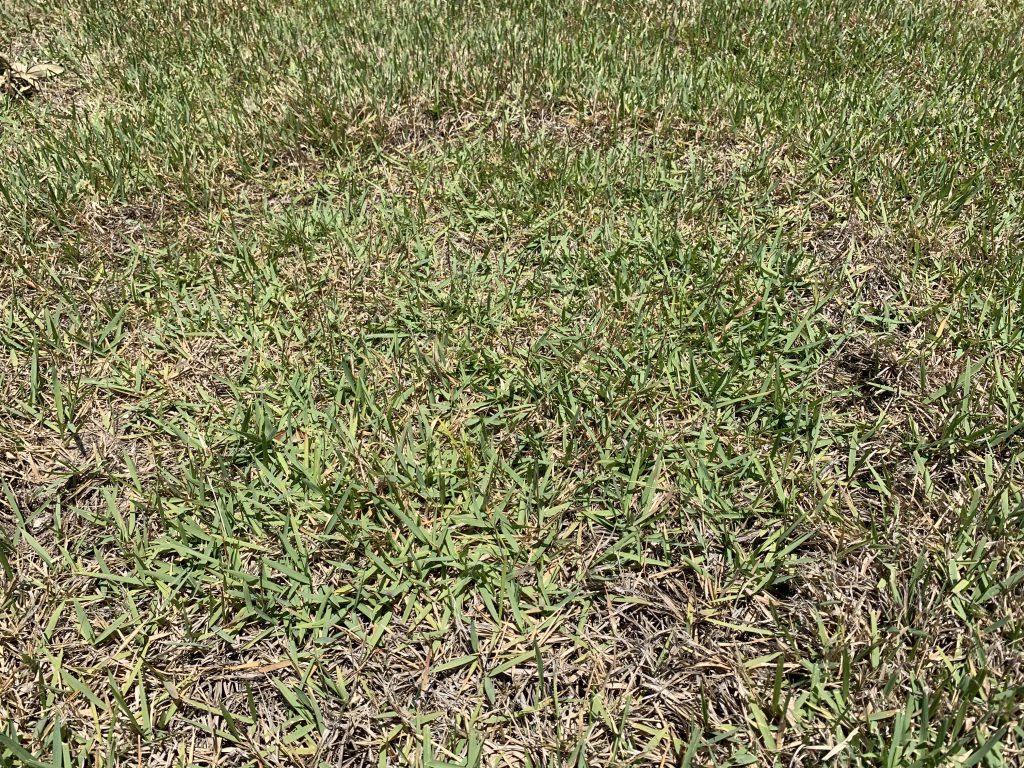

Rhizoctonia in a zoysiagrass lawn. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
This summer in Santa Rosa County, Rhizoctonia has been positively diagnosed in both St. Augustinegrass and zoysiagrass lawns and suspected in a number of centipedegrass lawns. The disease usually starts as small, yellow patches (about a foot in diameter) that turn reddish brown, brown, or straw colored as the leaves start to die. Patches often expand to several feet in diameter. It is common to see rings of yellow or brown turf with otherwise healthy turf in the center. The fungus infects portions of the blades closest to the soil, eventually killing the entire leaf. Grass blades can easily be pulled off their stems, but roots are not affected by the disease.
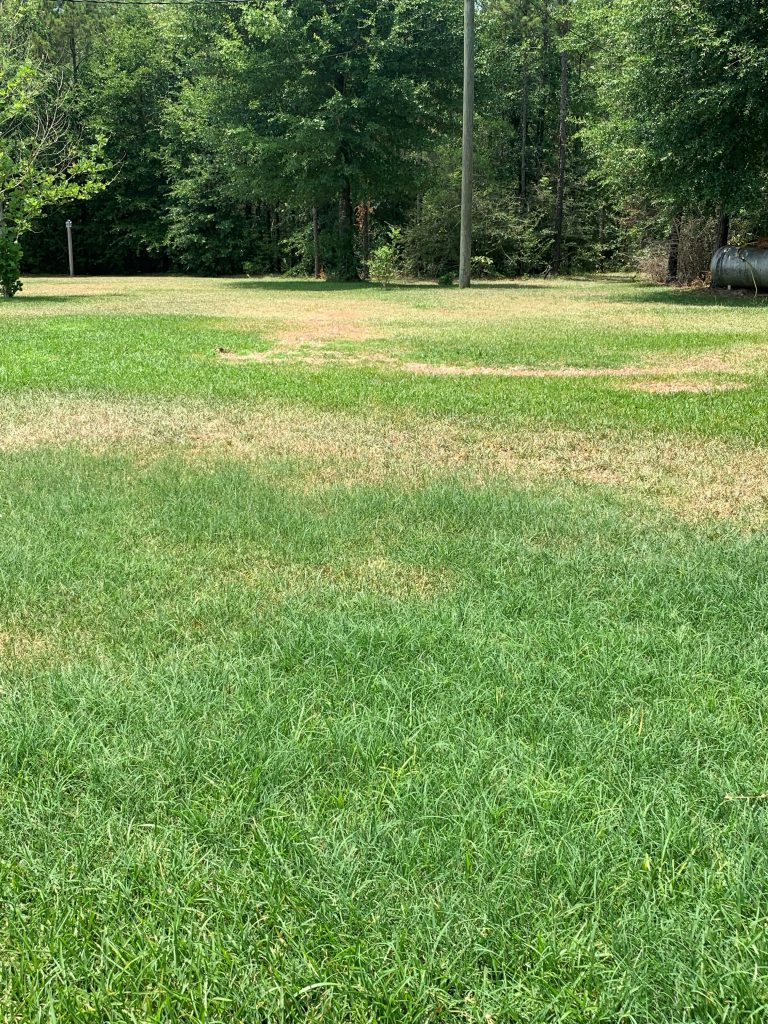

Rhizoctonia in a St. Augustinegrass lawn. Photo Credit: John Atkins, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
Overwatering and excessive fertilization can both contribute to the development of Rhizoctonia disease. Improper timing of fertilizer application can also promote disease development. In the Florida Panhandle, turfgrass is actively growing from April to October. Slow-release fertilizers are recommended to allow for a more even distribution of nutrients over the course of multiple months. Recommended fertilizer rates are based on turfgrass species, geographical location, and fertilizer analysis. Please refer to the UF/IFAS Publication: “Urban Turf Fertilizer Rule for Home Lawn Fertilization” for rate recommendations.
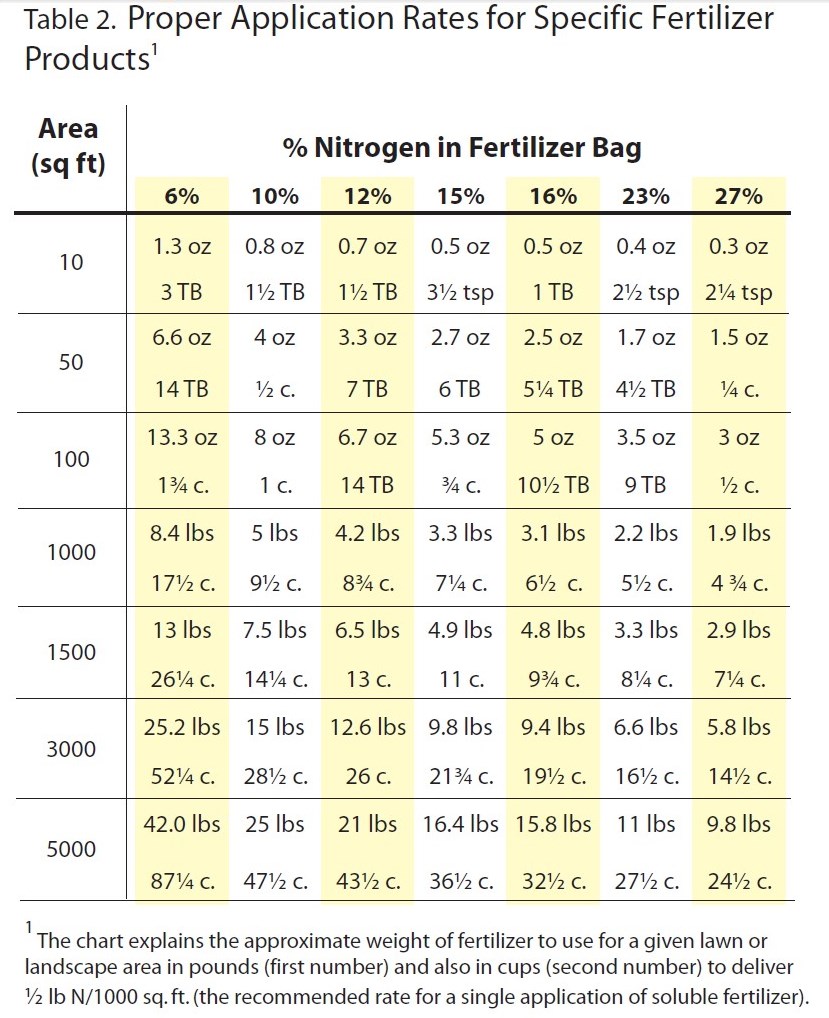
Chart excerpted from Florida-Friendly Landscaping publication.
If large patch or another Rhizoctonia disease is confirmed in your lawn, then chemical controls are necessary to keep the disease from spreading. Fungicide products containing the active ingredients azoxystrobin, chlorothalonil, fludioxonil, flutolanil, iprodione, mancozeb, metconazole, myclobutanil, polyoxin D, propiconazole, thiophanate-methyl, thiram, triadimefon, trifloxystrobin, or triticonazole are viable options for keeping the disease from spreading. For best results, follow the fungicide label for application instructions. It’s important to not only treat the affected areas, but also the healthy turf surrounding these areas in order to keep the diseased spots from growing in size.
Unfortunately, turf diseases are often not noticed until large patches of declining and dead turf are noticed. In these cases when large dead patches exist in the lawn, it is usually necessary to resod these areas. As with most problems that arise in the landscape, good cultural practices are the most proactive way to mitigate the chances with turfgrass diseases. The UF/IFAS Florida Friendly Website provides up-to-date solutions and recommendations for caring for Florida landscapes.
by Sheila Dunning | Jul 11, 2019
The Irrigation Association (IA) kicks off the official start of this year’s campaign on Tuesday, July 9, 2019. The initiative promotes the social, economic and environmental benefits of efficient irrigation technologies, products and services in landscape, turf and agricultural irrigation.
Irrigation (agricultural and turf/landscape) accounts for 65-70% of total freshwater use in the United States. According to the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) WaterSense program, the average American family household uses more than 300 gallons of water per day; roughly 30% of this occurs outdoors. Efficient landscape irrigation systems and practices dramatically reduce water being lost or wasted.
The starting point for improving the efficiency of a home landscape sprinkler system is to calibrate each zone (http://ufdc.ufl.edu/IR00003389/00001) and make adjustments and repairs. That includes the rain shut-off device.
Florida is one of the few states with a rain sensor law. The most recent version of the statute (2010) states the following: “Any person who operates an automatic landscape irrigation system shall properly install, maintain, and operate technology that inhibits or interrupts operation of the system during periods of sufficient moisture.” (Florida Statute 373.62). Regardless of the water source or age of the system, all in-ground irrigation systems must be connected to a functioning rain sensor of some kind.
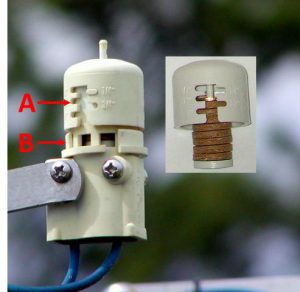
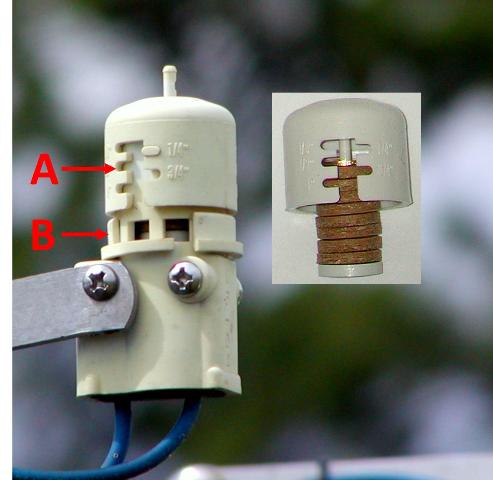
Expanding disk Rain Sensor
Expanded disk devices are the most popular rain sensor due to their low cost, ease of installation, and low maintenance. Traditionally, they are wired into the controller, but a wireless version allows for quicker installation and mounting up to 300 feet from the controller. These “mini-click” sensors contain disks made of cork that absorb rainfall and expand, triggering a pressure switch. The disk cover is rotated to adjust for the predetermined amount of rainfall required to trigger the switch. It should be set on ½ – ¾ inch, depending on soil type and rooting depth of irrigated plants. The switch continues to interrupt the scheduled controller as long as the disks are swollen. When the rain stops, the disks begin to dry out. Once they have contracted, the switch closes and the regularly scheduled irrigation cycle begins where it left off before the interruption. These small cork disks wear out in Florida’s heat and need to be replaced. By checking and repairing the sensor parts, the sprinkler system will operate much more efficiently. We have all seen irrigation systems running in pouring rain. Keep yours maintained to avoid this needless waste of water.
So, join the kids this summer. Go outside and play in the water. Turn on the sprinkler system and check it out. July is Smart Irrigation Month. Let’s see how efficient you can make your system and reduce the water waste in Florida.





















