
by Pat Williams | Aug 11, 2021
The lawn is a source of pride for most and anything out of the ordinary causes alarm. Now image finding something that looks like lumpy green jelly in your turfgrass and it doesn’t go away. You try raking it, spraying it, covering it, and it still comes back time and time again. One of the things we see in late spring/early summer turf is a reemergence of cyanobacteria (Nostoc), sometimes confused with algae because of green coloring and this remains all summer long.

Dehydrated cyanobacteria in a centipedegrass lawn.
Unlike normal bacteria that needs a food source, cyanobacteria contains chlorophyll and produces its own food source through photosynthesis which allows it to grow on bare sandy soils, fabric mats, concrete sidewalks, plastic, and yes even your lawn. Besides the green pigment, it also produces a blue pigment and is why we call it cyanobacteria which means blue-green bacteria. In addition to photosynthesis, cyanobacteria can also fix nitrogen, and are believed to produce cyanotoxins and allelopathic compounds which can affect plant growth around them.
Cyanobacteria are considered one of earth’s oldest organism and they have tremendous survival capabilities. They can dry out completely, be flat, flaky, black-green dried particles in your lawn and once rehydrated, spring back to life. If you happen to notice it spreading throughout your yard, remember that pieces of the organism can stick to your wet shoes or lawnmower tires and be transported unintentionally.
The question then becomes how to control the cyanobacteria and reclaim your turfgrass. The first solution is to have a healthy lawn. Cyanobacteria likes poorly-drained compacted soils. This same condition is unfavorable to turf growth and why you end up with bare spots and establishment. Reduce soil compaction by using a core aerator, and then adding organic matter. This will increase drainage, gas exchange, and encourage microorganism populations which I like to call soil pets. Spike aerators only push the soil particles aside and don’t really loosen as well. Try to reduce low lying areas in the lawn where water sits after rainfall and irrigation. You might have to till and reestablish those areas of the yard.

The same cyanobacteria pictured above 24 hours after being rehydrated in a petri dish of standing water.
Controlling the amount of water Mother Nature gives us and humidity levels during summer is not possible, but you can control your irrigation whether it be automatic (sprinkler system) or hand-watered. During the rainy season, you should be able to get by with only rainfall and shut off your system. If needed during extended dry weeks, it is easy enough to turn the system back on. It is thought that cyanobacteria likes phosphorus which is another reason to use little to no phosphorus in your lawn fertilizers.
As you begin to rid your lawn of cyanobacteria, remember when fully hydrated it forms a slippery surface so be careful walking on it. Cultural practices will be more effective in controlling the spread versus using chemical methods. Cultural solutions are safer for your lawn, yard and all of the wildlife that visits. If you need help with your cyanobacteria, please contact your local Extension office and we are always happy to assist.
A special thanks to Dr. Bryan Unruh, UF/IFAS for his assistance in identifying the cyanobacteria.
For additional information, please read the sources listed below.
Biology and Management of Nostoc (Cyanobacteria) in Nurseries and Greenhouses. H. Dail Laughinghouse IV, David E. Berthold, Chris Marble, and Debalina Saha
Rain, Overwatering Can Cause Slippery Algae to Pop Up in Turfgrass. C. Waltz
Nostoc. N.J. Franklin

by Mark Tancig | Jul 29, 2021
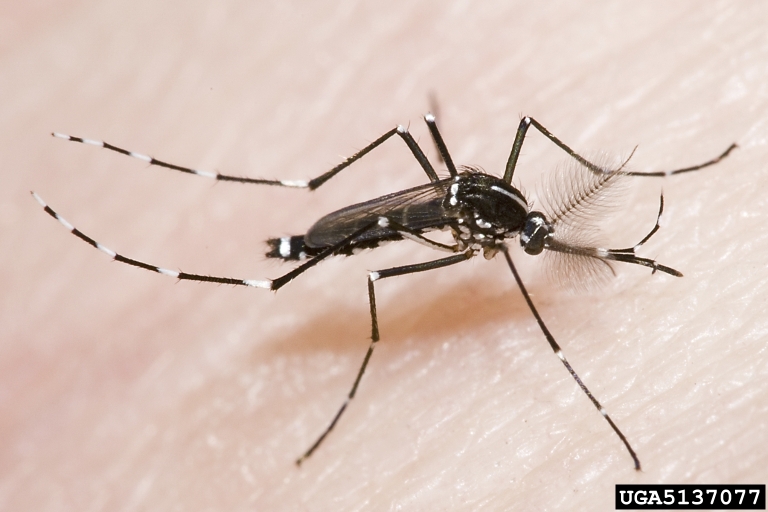
Now that we’re getting plenty of rain and the temperatures are nice and toasty, our nemesis to enjoying the outdoors is back in full force. Yes, I’m talking mosquitoes, the reason for inventing window screens! If you’re gardening outside these days, you’ve probably been annoyed by one of the many mosquito species that occur in our area. Many of these mosquitoes are native species that play an important role in the food chain, feeding many aquatic and terrestrial wildlife, but some of them, like the daytime biting Asian tiger mosquito, are invasive species that were accidentally introduced. While mosquitoes are an important food source to more charismatic critters, they are annoying and can spread disease, and so we can benefit by reducing their presence.

The Asian tiger mosquito, another annoying invasive species. Photo credit: Susan Ellis, Bugwood.org.
In addition to the age-old advice of draining any standing water, there are other control methods that can be very effective at reducing the mosquito population. One of the most effective and least-toxic options is the use of Bti products. These products come in granular or “donut” forms with the smaller granules being best for various uses around the home and the dunks/donuts for larger areas of standing water like ponds. These Bti products are considered a type of biological control since it is a species of bacteria, Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis to be precise, that causes mosquito, blackfly, and fungus gnat larvae to perish as they wiggle around and grow into their pupal stage. Because it only affects a narrow range of species, it is considered a selective pesticide that does not cause harm to non-target species, such as bees, birds, butterflies, frogs, lizards, and other desirable garden visitors. Bti can be sprinkled into rain barrels, bird baths, bromeliads, gutters, and other places where water may stand more than 5-7 days, the amount of time needed for mosquito eggs to develop into adults.

Bti granules prevent mosquito larvae from becoming biting adults. Photo by: Mark Tancig, UF/IFAS.
If considering other methods of mosquito control, such as the use of foggers, keep in mind that many of the pesticides used to control adult mosquitoes are not selective products and can kill the pollinators you may be trying to invite to your garden. Additionally, planting citronella plants, eating copious amounts of garlic, wearing repellent bracelets, or using ultra-sonic devices or cell phone apps has not been shown to repel mosquitoes so stick to what is known to work.
For a more enjoyable mosquito season, keep the window screens tight, wear long pants and sleeves and use appropriate repellents when outdoors, and do your best to minimize standing areas of water. If you have questions about mosquitoes and their control, visit the UF/IFAS Florida Medical Entomology Lab website (https://fmel.ifas.ufl.edu/) and browse the many resources available.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Jul 22, 2021
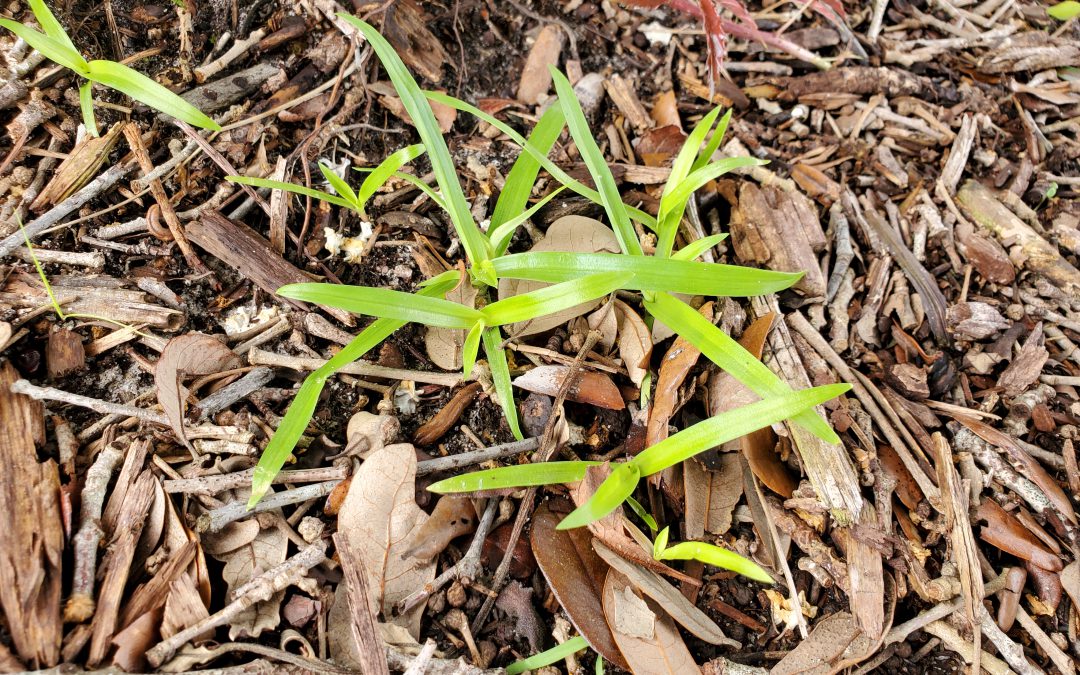
If you’ve taken care of your yard properly from spring green-up to now (mid-July), you might think you can comfortably coast into the cool temperatures of fall without any problems. You would be mostly right, save for one extraordinarily tough weed that waits until the depths of summer to rear its troublesome head: Doveweed (Murdania nudiflora).

Doveweed seedlings just emerged on July 9, 2021. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
Doveweed is an insidious invader of Panhandle lawns. In the Panhandle, Doveweed germinates (sprouts) long after most other summer annual weeds, from late May-June when soil temperatures reach ~70°F. This allows it to sneakily avoid spring pre-emergent herbicide applications and even early summer post-emergent applications that target common weeds like Florida Pusley, Spurge species, and others. Doveweed also looks an awful lot like many of our common lawn turfgrasses, especially Centipede and St. Augustine Grass. It possesses thick, shiny, grass-like foliage and even grows in a spreading, low to the ground fashion. This mimicry causes many homeowners to not realize there is a problem until it’s too late. Once Doveweed is mature and displaying its characteristic purple flowers, it is very difficult to control. Finally, Doveweed is extremely tough and aggressive, particularly thriving in moist areas of the lawn. In these areas, Doveweed can easily outcompete the desirable turfgrass and, without intervention by you, will soon have the whole lawn to itself.
Controlling Doveweed is no easy task and requires a combination of practices to keep it out of your lawn. The first line of defense against any weed, Doveweed included, is through proper cultural practices. In turfgrass lawns, this means ensuring that you mow your lawn regularly and at the proper height (2.5” or so for Centipedegrass), keeping the lawn irrigated during droughty periods, fertilizing based on a soil test, etc. Being diligent in the above tasks will go a long way to ensuring that your turfgrass is healthy and better able to ward off a Doveweed invasion. However, even when homeowners maintain their turf perfectly, chemical herbicides are usually required to keep Doveweed at bay.

Doveweed patch in St. Augustine Sod.
While many commonly used homeowner herbicides are not effective on Doveweed, there are several quality options at your disposal.
- Doveweed is most easily controlled with preemergent herbicides, specifically one of the following: Atrazine, Pennant Magnum (S-metolachlor), Tower (dimethenamid), and Specticle (indaziflam). The issue with pre-emergents is that most folks shelve them after spring application in February or March. Since these products lose their efficacy after 4-6 weeks, Doveweed’s emergence in May is undeterred. To obtain control on Doveweed with these products, split the spring application and apply once in late Feb/early March and again in mid-late April.
- Doveweed can also be controlled by post-emergent herbicides after it is up and growing, though multiple applications may be required. The most effective formulations contain a combination of 2,4-D or Dicamba and other herbicides. While most of these products have at least fair efficacy on Doveweed, stronger, more expensive products like Celsius, Tribute Total and others provide better results.
- If Doveweed has already displaced turfgrass in large areas of your lawn, you may unfortunately be better off to make an application of a non-selective herbicide like glyphosate (Roundup), kill out the entire area of infestation and start over by resodding.
While Doveweed is a major problem in Panhandle lawns, it doesn’t have to be in yours! By keeping your turf healthy with proper cultural practices and making timely applications with effective herbicides, your lawn can be a Doveweed free zone! For assistance in Doveweed identification in your lawn, help choosing herbicides and calculating application rates, or any other horticultural information, contact us at the UF/IFAS Calhoun County Extension office! Happy Gardening!

by Larry Williams | Mar 25, 2021
As a boy in a small town in Georgia we had a St. Augustinegrass lawn. My dad started the lawn before I was born. That lawn was still doing fine when I left for college at age seventeen. I don’t remember weeds in the lawn during summer months. I do fondly remember winter “weeds” in that lawn.
To see clumps of winter annuals in our yard and in neighbors’ yards was a natural part of the transition from winter to spring. They added interest to what

Blue Easter egg hidden in chickweed. Photo credit: Larry Williams
would have been a plain palette of green. It was expected to see henbit with its square stiff stems holding up a display of small pinkish purple flowers in late winter and early spring. A clump of henbit was a great place to hide an Easter egg, especially a pink or purple one.
Wild geranium, another common winter annual, offered another good hiding place for Easter eggs with its pink to purple flowers. Large clumps of annual chickweed would nicely hide whole eggs. Green colored eggs would blend with chickweed’s green leaves.

Pink Easter egg hidden in crimson clover & hop clover mix. Photo credit: Larry Williams
Crimson clover with its reddish flowers, hop clover and black medic with their bright yellow flowers were good hiding places for Easter eggs. Plus clovers add nitrogen back to our soils.
I never remember my dad using any weed killer, he rarely watered. The lawn was healthy and thick enough to be a deterrent to summer weeds. But during fall and winter as the lawn would naturally thin and go dormant, winter annual weeds would run their course.
I’ve heard that the sense of smell provides our strongest memories. I remember the first mowing of the season with the clean smell of chlorophyll in the spring air. It was refreshing. Once mowed and as the heat took its toll, by late April or mid-May, these winter annual weeds were gone. What was left was a green lawn to help cool the landscape as the weather warmed. The lawn was mowed high as St. Augustine should be, played on and typically not worried with.
Most people have winter weeds in their lawns that let us know spring is near. Perhaps we worry too much with these seasonal, temporary plants that may have wrongly been labeled as weeds. Besides, how long have we been doing battle with these weeds and they are still here. Most lawns have countless numbers of winter annual seeds awaiting the cooler temperatures and shorter days of early winter to begin yet another generation. By May they are gone.

by Matthew Orwat | Mar 25, 2021
Stinkbugs and their relatives are not always problematic in the flower or vegetable garden, but when they become so, they can suck the life out of our fruits and vegetables, create ugly abrasions, and destroy flowers such as roses.

Over-wintering adult leaffooted bug emerging from hibernation . Image Credit Matthew Orwat, UF / IFAS Extension
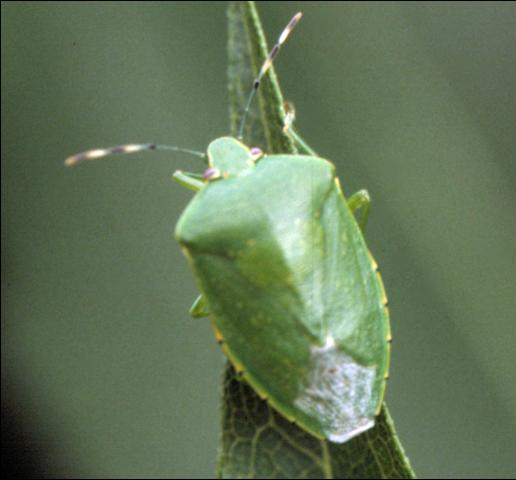

The green stink bug Acrosternum hilare (Say). Image and caption credit EDIS, Dr. Russ Mizell
What is a Stink Bug?
The stink bug (Pentatomidae family) is a major garden pest of a variety of fruits and vegetables including squash, peppers, tomatoes, peaches, plums, pecans and a variety of other edibles. They are known as a “piercing and sucking” insect because that’s the way they feed, by using their mouth, or proboscis, just like a needle to pierce the fruit and suck out the juices. This feeding leaves a damaged area of the fruit which may develop discoloration, rot or fungal disease and render the fruit unsaleable or inedible.
Who are “their relatives”
The leaf footed bug, Leptoglossus phyllopus (L), is a relative of the stinkbug and feeds in the same way, has a similar lifecycle and causes similar damage. They are usually slightly larger and have “leaf like” appendages on their legs which are their namesake.
What is their lifecycle?
In Florida, overwintering adult stink bugs will place a clutch, or tight group of eggs, on a host plant early in the growing season. If their preferred plant is not available, they use a variety of weeds and grasses to lay eggs upon and provide food for their young. After eggs hatch, they go through several nymph stages before they finally reach the adult stage. Stink bugs have multiple generations in a year, often four to five. They readily move to find preferable food sources and might appear in a garden without warning to feed and cause destruction.

Nymph of the leaffooted bug, Leptoglossus phyllopus (L.). Photograph by Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida.
How are they best controlled?
First of all, many stink bugs use weeds as host plants to gather and feed upon, so controlling weedy plants around vegetable and fruit gardens might limit their numbers. If stink bugs are a major problem, planting trap crops, such as sunflowers, is beneficial. Stink bugs prefer to feed on sunflowers more than some other vegetables. This situation can be used to the gardener’s advantage by mechanically killing or spraying stink bugs on trap crops while avoiding treating food crops with pesticides. More information on trap cropping can be found here.
Additionally, stink bug traps are available. These mechanically trap stink bugs, thus reducing their numbers in the garden, but need to be monitored and serviced regularly. Several species of parasitic Tachinid flies are also predators of stink bugs. These flies lay their eggs on adult stink bugs. The fly larva use the bug as a buffet, slowly killing the bug.
Stink bugs are difficult to control with insecticides, but some measure of control can be achieved at their nymph stage with various approved fruit and vegetable insecticides containing pyrethrins. These products are readily available at local garden centers and feed & seed stores.
For more information, please check out the following resources:
by Pat Williams | Oct 21, 2020
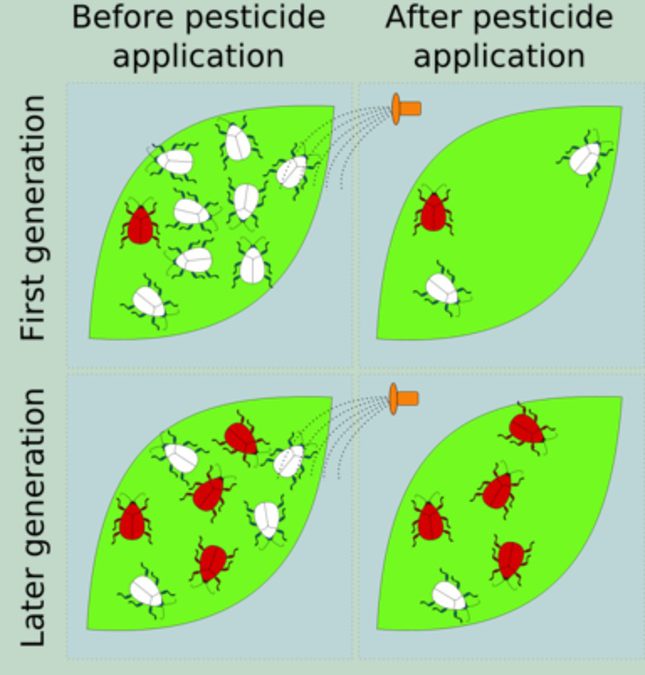
Normally, you will have one of four answers: “yes”, “no”, “I don’t know” or “what are super bugs?” The answer to the last one is an insect or other pest that has become resistant to chemical treatments through either natural selection (genetics) or an adaptive behavioral trait.
The next question is do you treat insect or pest problems at home with a purchased EPA registered chemical (one purchased from the nursery or other retailer)? If you answered yes, then the next question is how many times in a row do you apply the same chemical? If you only use one chemical until the product is used up, then you might be creating super bugs. Do you ever alternate chemicals and if you answer yes, do you understand chemical Modes of Action (how the pesticide kills the pest)? If you do not, then chances are the rotating chemicals might act in the same way. Thus, you are creating super bugs because in essence you are applying the same chemical with different labels.
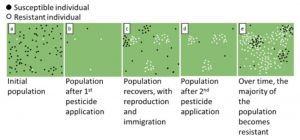
Click on image for a larger view. Taken from https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in714.
One of the first ways to reduce creating super bugs is to practice Integrated Pest Management (IPM). The very last step of an IPM philosophy is chemical control. You should choose the least toxic (chemical strength is categorized by signal words on the label: caution, warning, and danger) and most selective product. A chemical label advertising it kills many pests is an example of a non-selective chemical. You want to choose a chemical that kills your pest or only a few others. In Extension education, you will always hear the phrase “The label is the law.” To correctly purchase a chemical, you must first correctly identify the pest and secondly the plant you want to treat. If you need help from Extension for either of these, please contact us. Before purchasing the chemical, always read the whole label. You can find the label information online in larger print versus reading the small print on the container.

IRAC phone app.
You now have the correct chemical to treat your pest. Wear the recommended personal protective equipment (PPE) and apply according to directions. If your situation is normal, the problem is not completely solved after one treatment. You might apply a second or third time and yet you still have a pest problem. The diagram explains why you still have pests or more accurately super bugs.
Now the last question is how do we really solve the problem given that chemicals are still the only treatment option? A bit more work will greatly help the situation. You need to download the Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) guide and find the active ingredient on your chemical label (http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi121 or https://irac-online.org/modes-of-action/ and select the pdf). If you are like me, you can just download the IRAC MoA smartphone app and type in the active ingredient; otherwise, Appendix 5 in the pdf has a quick reference guide. Either way, you will know the Group and/or Subgroup. A lot of commonly purchased residential chemicals fall within 1A, 1B or 3. The successful treatment option is to select chemicals from different group numbers and use them in rotation. If you start practicing this simple strategy, your treatment should be more successful. Then when someone asks if you are creating super bugs, your answer will be no.
If you have any questions about rotating your chemical Modes of Action, please contact me or your local county Extension agent. For more resources on this topic, please read Managing Insecticide and Miticide Resistance in Florida Landscapes by Dr. Nicole Benda and Dr. Adam Dale (https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in714).


















