
by Matthew Orwat | Oct 10, 2017

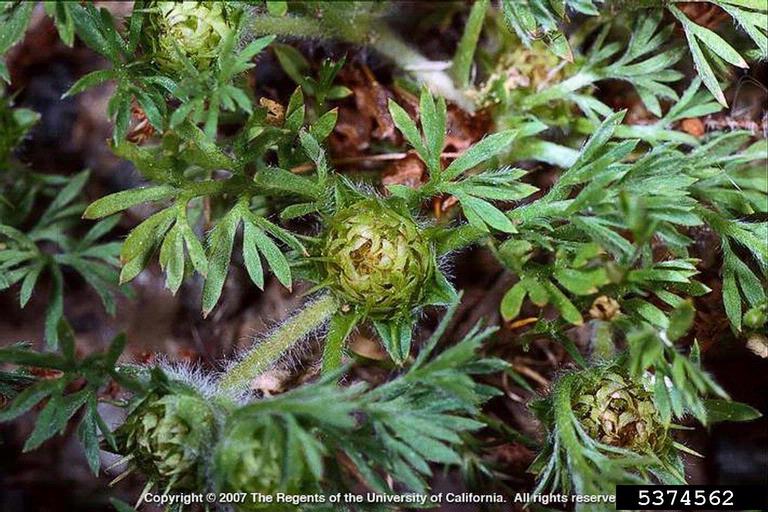
Burweed, Soliva Sessilis. – Image Credit: Joseph M. DiTomaso, University of California – Davis, Bugwood.org. Creative Commons License
On the top of my list of lawn related annoyances is stepping into a patch of burweed, Soliva sessilis, which is in the sunflower family and is also known as spurweed. The leaves are opposite along the stem and sometimes resemble parsley. The main ways in which burweed can irk the casual gardener are sticking to socks, sneaking in with the dog, or littering flower beds with its nuisance. It can also hide in the house and reappear when shoes are removed. This causes pain in both the foot and the ear.
Lawn burweed has been an especially noticeable problem in lawns. Over the years, extension offices throughout Northwest Florida have been fielding many questions and finding solutions to lawn burweed infestations!
Maintaining a healthy vigorous lawn will prevent weeds from taking over. If your lawn is reasonably healthy and only a few instances of this weed exist, try to mechanically remove them and encourage the lawn to outgrow them.
If an infestation of burweed occurred last year on a specific patch of turf, take note. The best time to apply pre-emergent herbicides to control burweed is in October, when nighttime temperatures drop to between 55-60 degrees F for a few consecutive nights. A widely used pre-emergence product for burweed control is isoxaben, which is sold under the brand name of Gallery as well as others. It prevents the weed from emerging from the ground when it germinates and can be used on St. Augustine, centipede, bahia and zoysia lawns, as well as in ornamental shrub beds. In northwest Florida, this herbicide needs to be applied in October for best results. A second application later in the season might be warranted. For more information about control, please consult this excellent article on lawn burweed management.
Now is the time to control burweed before it gets started. As temperatures cool burweed seed will germinate, as it is a winter annual. In cases where it is already coming up, control with post-emergent herbicide may be warranted.
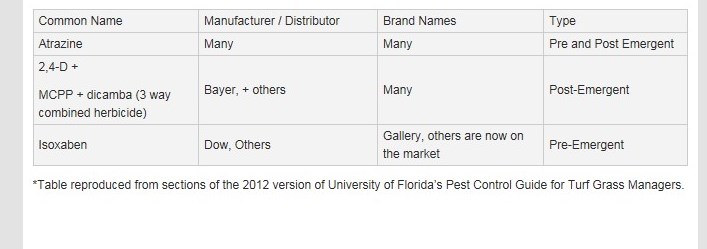
The active ingredients mentioned above are present in a variety of ‘trade name’ products* available from your local garden center, farm supply or co-op. Be sure to read label instructions carefully and contact your local extension office for any assistance. I hope all the northwest Florida lawn managers prevent burweed this fall so that lawns will be burweed free next spring.
Happy Gardening!

by Sheila Dunning | Aug 17, 2017
If you are one of the many that have taken advantage of the frequent rain in order to establish a new lawn, keep an eye open for “grass worms”. Though truly caterpillars, not worms, these destructive, chewing insects can wreak havoc on new sod.

Sod Webworm Photo by: Lyle Buss UF
Tropical sod webworm larvae are destructive pests of warm season turfgrasses in the southeastern U.S. especially on newly established sod. Larval feeding damage reduces turfgrass aesthetics, vigor, photosynthesis and density, which is very evident on finer-bladed grasses such as bermudagrass and zoysiagrass. Adults, a dull brown colored moth about ¾ inch long, rest in sheltered and shrubby areas during the day and are active at dusk. Females deposit clusters of 10-35 eggs on the upper surface of grass blades. The eggs hatch in 3-4 days and develop from a 1 mm long caterpillar to one over 11 mm long through six instars within 21 to 47 days, depending on temperature. Larval feeding occurs at night, leaving the grass looking ragged, shortened and missing.
Control should be against damaging larvae, not the flying moths. However, insecticidal soap applications to moth harboring areas can reduce re-population frequency if such areas are located. Soil-drenching soap flushes can be used to find the caterpillars, especially in dry and hot grass areas. Bacterial-based insecticides will control sod webworm caterpillars without impacting beneficial species as long as they are applied with each flush of grass growth.
Excessive fertilizing will lead to caterpillar outbreaks in lawns. Newly installed sod is usually rich in nutrients and rapid growing, which makes it very attractive to sod webworms. Grass installation over the summer months should be immediately followed by sod webworm treatment.

Fall Armyworm Photo by: Lyle Buss UF
Fall armyworms are also attracted to newly installed sod. They feed any time of the day or night, but are most active early in the morning or late in the evening. The 1 ½ inch long gray and white moth lays about 1,000 eggs in multiple masses on any vegetation. Two to 10 days later, the small caterpillar hatches and begins to grow to nearly 2 inches long over a two week period. The fall armyworm is easily recognized by its dark head marked with a distinct pale-colored inverted Y and the long black stripe running along each side of its body. These aggressive feeders “march” rapidly across grassed areas consuming every above-ground plant part. While bacterial-based insecticides will reduce the numbers, control of armyworms usually requires synthetic insecticides. Diligent inspection and early pesticide application is critical to establishment of new sod installed during the summer months.
by Mark Tancig | Aug 1, 2017
Florida’s panhandle has received quite a bit of rain this summer. In the last three months, depending on the location, approximately 15 to 35 inches of rain have come down, with the western panhandle on the higher end of that range. In addition to the rain, we all know how hot it has been with heat index values in the triple digits. And who can forget the humidity?! Well, these weather conditions are just the right environmental factors for many types of fungi, some harmful to landscape plants, most not.
In the classification of living things, fungi are divided into their own Kingdom, separate from plants, animals, and bacteria. They are actually more closely related to animals than plants. They play an important role on the Earth by recycling nutrients through the breakdown of dead or dying organisms. Many are consumed as food by humans, others provide medicines, such as penicillin, while some (yeasts) provide what’s needed for bread and beer. However, there are fungi that also give gardeners and homeowners headaches. Plant diseases caused by various fungi go by the names rusts, smuts, or a variety of leaf, root, and stem rots. Fungal pathogens gardeners may be experiencing during this weather include:
- Gray leaf spot – This fungus can often show up in St. Augustine grass lawns. Signs of this fungus include gray spots on the leaf (very descriptive name!). This disease can cause thin areas of lawn and slow growth of the grass.

Gray leaf spot on St. Augustine grass. Credit: Phil Harmon/UF/IFAS.
- Take-all root rot – This fungus can attack all our warm-season turfgrasses, and may start as yellow leaf blades and develop into small to large areas of thin grass or bare patches. The roots and stolons of affected grasses will be short and black.

Signs of take all root rot. Credit: UF/IFAS.
Powdery mildew – This fungus can be found on many plants, from roses to cucumbers. It looks like white powder on the leaves and can lead to plant decline.
- Armillaria root rot – This fungus can infect a variety of landscape plants, including oaks, hickories, viburnums, and azaleas. Symptoms can include yellowing of leaves and branch dieback, usually in adjacent plants. Old hardwood stumps can harbor this fungus and lead to the infection of nearby ornamentals.
Because fungi are naturally abundant in the environment, the use of fungicides can temporarily suppress, but not eliminate, most fungal diseases. Therefore, fungicides are best used during favorable conditions for the particular pathogen, as a preventative tool.
Proper management practices – mowing height, fertilization, irrigation, etc. – that reduce plant stress go a long way in preventing fungal diseases. Remember that even the use of broadleaf specific herbicides can stress a lawn and exacerbate disease problems if done incorrectly. Since rain has been abundant, irrigation schedules should be adjusted to reduce leaf and soil moisture. Minimizing injury to the leaves, stems, and roots prevents stress and potential entry points for fungi on the move.
If you think your landscape plants are suffering from a fungal disease, contact your local Extension Office and/or visit the University of Florida’s EDIS website at http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu for more information.

by Blake Thaxton | Jul 21, 2017
Northwest Florida has experienced an enormous amount of rain this summer. The western panhandle has received over 29 inches of rain since the beginning of May according to the Florida Automated Weather Network station at the West Florida Research and Education Center in Jay, Florida. That is 44% of average annual rainfall in less than two months. All of this rain has probably thrown off the normal lawn mowing routine. It is hard to get out and mow the lawn when its pouring buckets or the lawn resembles a swamp. With all of this in mind, there are a couple of mowing pointers that would be useful to implement to address the out of control lawn growth and the challenges posed by not being able to stick to normal mowing schedule.
- Always attempt to mow at the IFAS recommended height for your species of turfgrass. The recommended heights are determined by how quickly the species grow in our climate. The chart below shows the best heights at which to mow your lawn. The fine textured zoysiagrasses are not listed but should be mowed at 0.5 to 1.5 inches. Check the lawn mowers mowing height by measuring the distance from the ground to the bottom of the mowing deck on a flat surface.
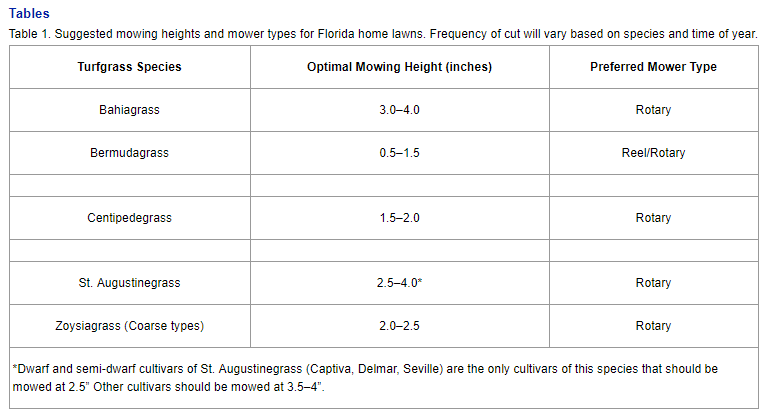
From Mowing Your Florida Lawn: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/LH/LH02800.pdf
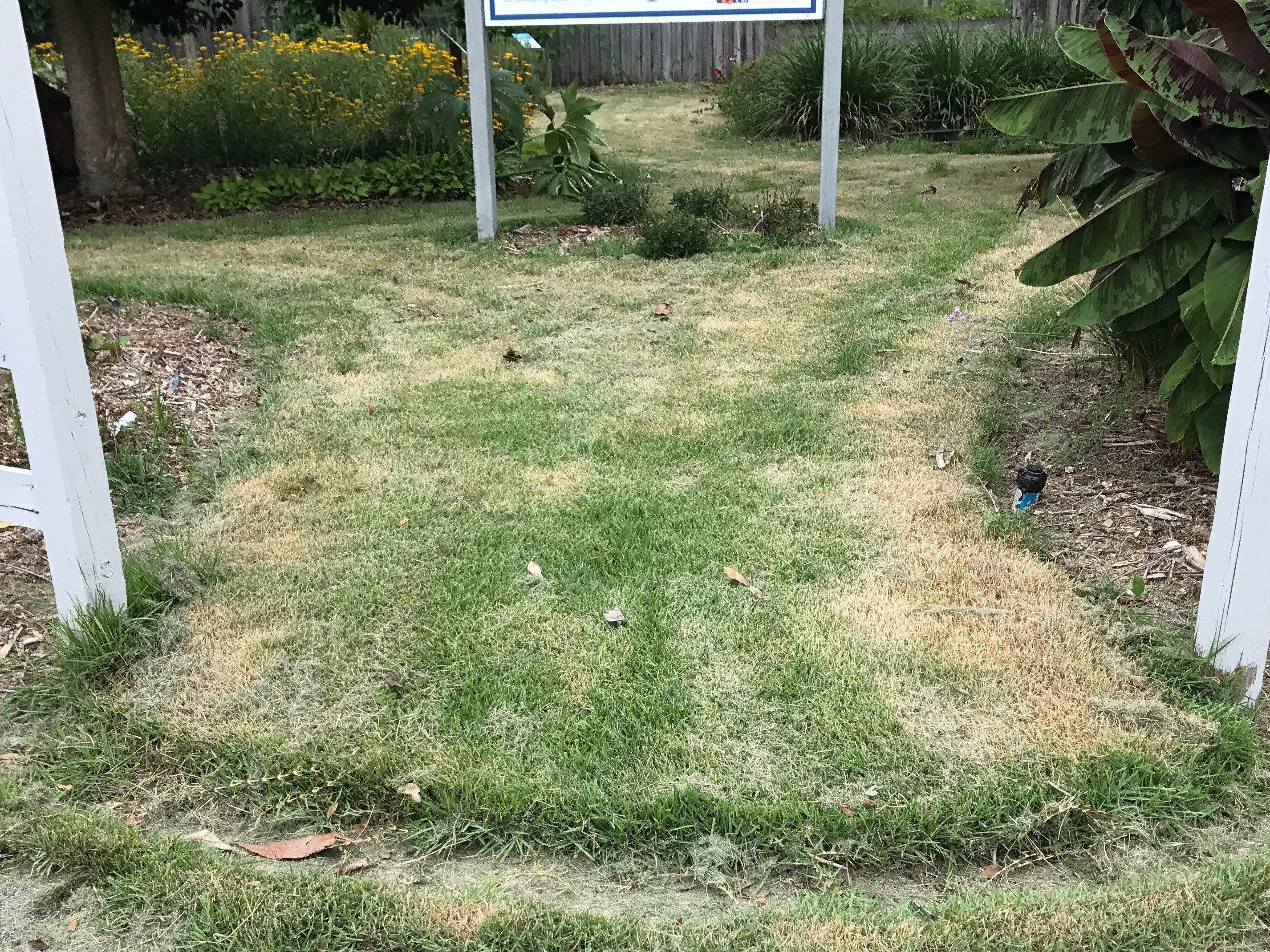
- When you do get out to mow, never remove more than 1/3 of the leaf blade. If you cut to short you will “scalp” the turf and cause a brown look on the lawn. This can be damaging to the turf and allow for weeds to get established by exposing the soil to the sunlight. What is taking place more in northwest Florida is not mowing frequently enough and cutting off excess growth due to the rain. This also can cause scalping so it is very important to mow frequently enough to only remove 1/3 of the leaf blade.
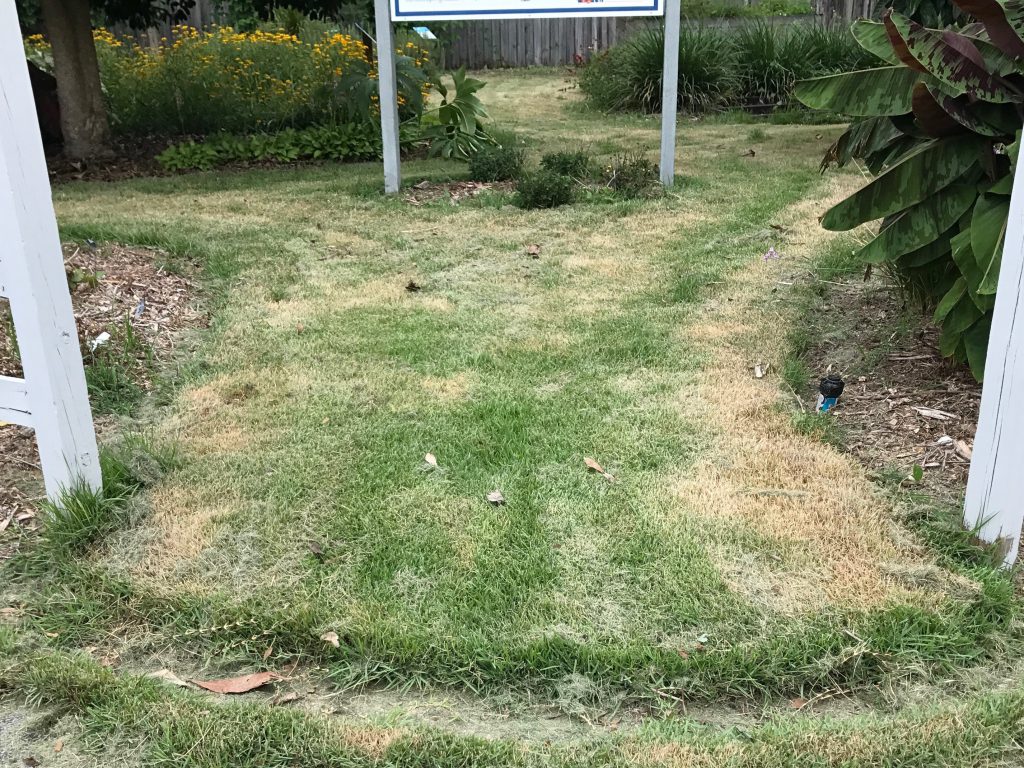

A zoysia lawn that has been “scalped” after excess growth and infrequent mowing. (Photo Credit: Blake Thaxton)
Other practices such as keeping your mower blade sharp, mowing in different directions, and leaving clippings on the ground will help keep a healthy Florida lawn. Please see more information about mowing correctly in Florida in the University of Florida/IFAS Extension publication: Mowing Your Florida Lawn

by Matthew Orwat | Jun 16, 2017

Slime Mold Sporangia. Image Courtesy Matthew Orwat
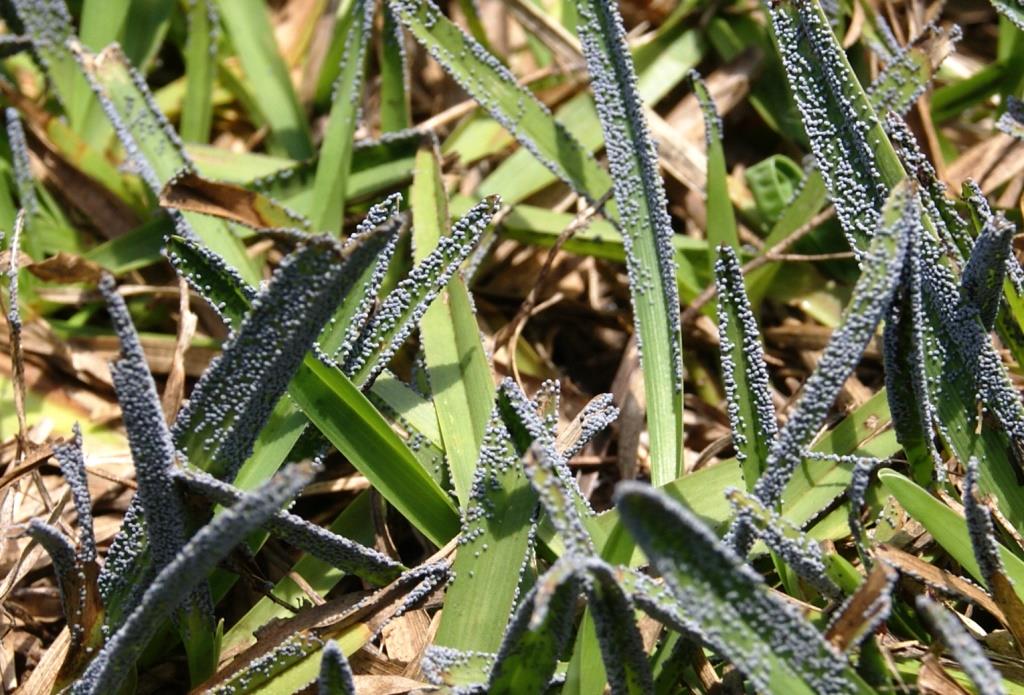
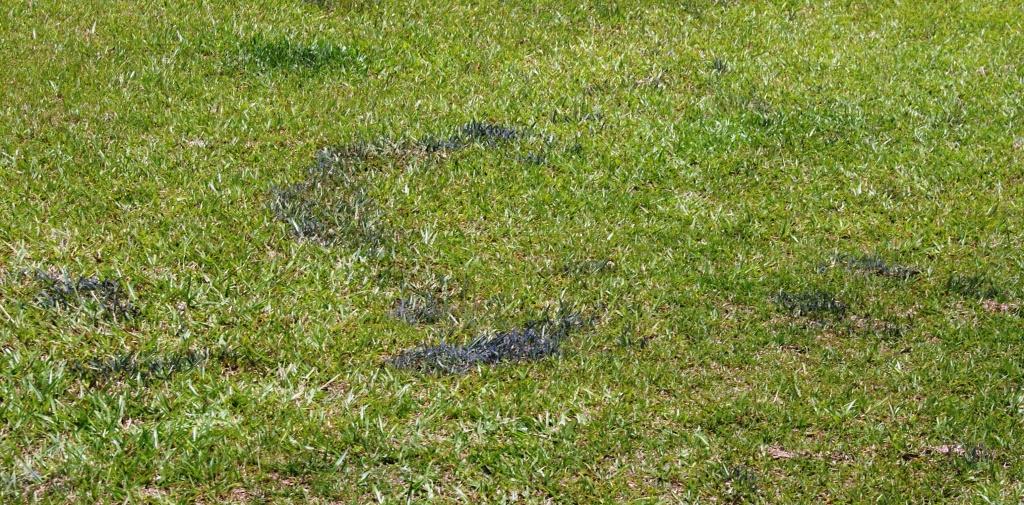
Although black or white streaks are shocking when they appear on an otherwise healthy lawn, slime molds are rarely harmful.
Slime mold is actually caused by the reproductive structures of an array of different organisms, classified as plasmodia or Protista, which are regularly present in the soil. They are often mistaken for fungi. The different types are referred to as myxomycetes or dictyosteliomycetes. They usually appear on warm humid days in late spring or early summer after extended periods of rain. This extended period of heat and humidity, as is currently being experienced in the Florida Panhandle, initiates the perfect climate for slime mold development.
While regularly present in the soil, they usually make a visual appearance on warm humid days in late spring or early summer after extended periods of rain. This extended period of heat and humidity, currently being experienced in the Florida Panhandle, initiates the perfect climate for slime mold development.
As depicted in the picture, slime mold makes the lawn look like it was just spray-painted with black or grey paint. They can sometimes be pink, white, yellow or brown as well. The round fruiting bodies, called sporangia, carry the spores which will give rise to the next generation of the mold. After a few days the sporangia will shrivel up, release the spores and leave no noticeable trace on the lawn.
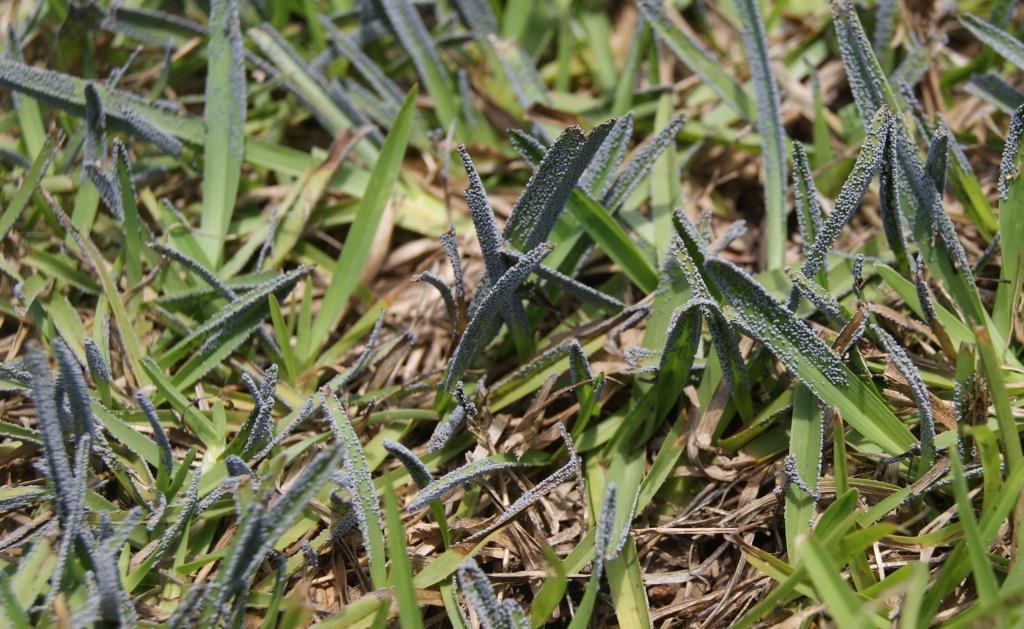

Closeup: Slime Mold in Centipedegrass. Image courtesy Matthew Orwat
Currently, no fungicide exists to control slime mold because chemical control is not necessary. An excellent method to speed up the dissipation of slime mold is to mow or rake the lawn lightly. This will disturb the spores and hasten their departure. Another effective removal method is to spray the lawn with a forceful stream of water. This process washes off the slime mold sporangia and restores the lawn to its former dark green beauty.
Excessive thatch accumulation also increases the probability of slime mold occurrence.
For more information consult your local county extension agent consult the UF / IFAS Slime Mold Fact Sheet, or read the Alabama Cooperative Extension publication Slime Mold on Home Lawns.

Slime Mold in Centipedegrass. Image Courtesy Matthew Orwat

by Les Harrison | Jun 15, 2017

Fertilizer spreader use is in full swing throughout the Florida panhandle
Fertilizing a lawn properly in the summer can enhance the landscape without inducing disease or harming the environment .
One universal activity is seasonal lawn and landscape maintenance. While some consider it a chore, many view it as a means to enhancing their personal environment.
The list of tasks are, for the most part, standard with few surprises. Raking leaves and pine straw, replacing shrubs which did not make it through the winter, and fertilizing the lawn and landscape.
While a routine undertaking, applying fertilizer requires thought and consideration to be effective without negative consequences. It should be a deliberate and well-planned accomplishment which is science based.
The proper selection of a fertilizer should be based on a soil test. Every UF/IFAS Extension Office has supplies for pulling and submitting a soil sample for evaluation.
The results, which can come via mail or e-mail, will tell the homeowner what nutritional deficiencies exist in their lawn and landscape. Based on the type of grass or shrubs, the report will deliver the information on the fertilizer analysis needed for optimum plant performance.
With this information in hand, the homeowner can visit a local retailer who can provide the product which meets the needs of the landscape without wasting excess nutrients. Excess soil nutrients can easily be relocated to bodies of water when storm water washes it downstream.
Homeowners have several types of fertilize from which to choose for use on their lawn. Each has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Dry blend fertilizer is usually the least expensive and is easy to find in the market place. It is a mixture of minerals and compounds which are combined to produce a particular analysis, such as 10-10-10.
This analysis is ten percent nitrogen, ten percent phosphorus, and ten percent potassium with the remaining 70 percent being micronutrients and inert carrier. Applied correctly, it can be effective at delivering the needed nutrients.
It is most effective when applied several times throughout the growing season. The grass and shrubs will then have a continuous supply of the needed nutrients over time.

Soil test kit available from your local Extension office. Photo: Mary Derrick, UF/IFAS.
One potential problem with dry blend fertilizer is the particle size of the different nutrients. If irregular, they can separate during transportation to the retailer.
This can be easily corrected by the homeowner. Just pour the contents of the bag into a container and mix using a can or shovel.
Dry slow-release fertilizers are gaining popularity, but they are more expensive. They have a sulfur or polymer coating on the particles which allows for the slow release of the nutrients.
A single application can last for up to six months which frees the homeowner to pursue other activities. The most common use of this product is with shrubs and potted plants.
Liquid fertilizer concentrates are available, but the convenience comes at a high cost. It is easily diluted for use, but uniform application over a large area can be challenging.
No matter which form is used, proper application will grow good results. A healthy and well maintained lawn and landscape leave more time for other springtime pursuits.
To learn more about the fertilizer for your landscape, contact your county agent and refer to this section on our website devoted to lawn fertilization.


















