by Beth Bolles | Sep 8, 2017
Trees are a valuable resource. They add beauty to our community, serve as food and shelter for animals, filter the air, and cool urban environments. Trees can also be a liability when poorly maintained, damaged, or diseased. There are often times when an arborist is needed to help determine the best course of action for the tree.
There are many individuals who are involved in the tree care and removal business. Not all of these people are certified in the care of trees. Arborists are people who receiving training in the planting, care, and maintenance of trees.

Professional arborists have specialized training to create safe, structurally sound trees, even when damaged by storms. Photo by Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension Escambia County
Certified arborists go through a voluntary certification process with the International Society of Arboriculture which means that they have at least three years experience and have passed a comprehensive examination developed by tree experts. A certified arborist maintains certification by attending regular training courses.
An arborist may also be a member of another organization which helps professionals stay up-to-date on tree care techniques and information. These include the National Arborist Association and the American Society of Consulting Arborists.
Hiring an arborist to work on your trees is important for several reasons. An arborist can evaluate the tree and determine the steps necessary to create a healthy specimen. In regards to pruning, the professional will determine what type of pruning is necessary and remove branches properly.
Professionals will also perform tree care practices that are recommended by University research. A few practices that the arborist would not perform include topping trees, using climbing spikes on trees which are not being removed, and making flush cuts against the trunk.

Flush cuts are damaging to trees and can create a future hazard in your landscape. Photo by Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension Escambia County
Finally arborists have the skills and equipment to safely and efficiently prune or remove trees. This includes personal and property damage insurance and workers compensation insurance.
Next time you need tree work or advice, hire a professional for the job. It will definitely be worth the investment.
by Sheila Dunning | May 25, 2017
 As oak trees are now fully leafing out and people start hanging out in the shade of the canopy, many of you are noticing strange growths on the branches. They look like potatoes, spiky cones and fuzz balls on the leaves and stems. Don’t worry. It’s just a harmless wasp that chose that tree to create a nursery for her young.
As oak trees are now fully leafing out and people start hanging out in the shade of the canopy, many of you are noticing strange growths on the branches. They look like potatoes, spiky cones and fuzz balls on the leaves and stems. Don’t worry. It’s just a harmless wasp that chose that tree to create a nursery for her young.
Galls are abnormal plant growth or swellings comprised of plant tissue. Galls are usually found on foliage or twigs. These unusual deformities are caused by plant growth-regulating chemicals produced by tiny wasps. The chemicals produced by these insects interfere with normal plant cell growth.
The life cycles of the various gall-forming wasps are highly variable. Two or more years are required for gall wasps that develop in woody twig galls to reach maturity. Gall-forming wasps usually overwinter as adults in protected places away from the host tree. As the buds break in the spring and the leaves begin to expand, these small wasps start to lay their eggs in expanding plant tissue. During the egg-laying process or early larval-feeding period, specialized body glands secrete growth-regulating chemicals that interact with certain plant chemicals to produce these abnormal growths.
After a brief period of cell growth, gall development stops completely. Once these galls are formed, they do not continue to use nutrients from the host plant. The insect is confined within “its house” and feeds only on gall tissue during the remainder of its development. The galls provide shelter, protection, and food for the immature wasps. Inside a gall, the larvae are surrounded by tissues rich in nutrients
 There are a variety of gall-forming species of small wasps that commonly infest oak, Quercus spp ., trees. Galls generally are aesthetically objectionable to homeowners who find them unattractive and fear that galls will cause damage to the health of their oak trees. Most leaf galls on oak cause little or no harm to the health of a tree. However, twig or branch galls may cause injury by distorting branch development in a heavily infested tree.
There are a variety of gall-forming species of small wasps that commonly infest oak, Quercus spp ., trees. Galls generally are aesthetically objectionable to homeowners who find them unattractive and fear that galls will cause damage to the health of their oak trees. Most leaf galls on oak cause little or no harm to the health of a tree. However, twig or branch galls may cause injury by distorting branch development in a heavily infested tree.
Chemical control is seldom suggested for management of leaf galls on oak. Cultural methods of control may be effective in reducing the impact of these insects. Some fallen leaves may harbor various life stages of gall-producing pests. Therefore, it may be useful to collect and destroy all infested leaves. Some of these pests overwinter in twigs and branches of oak. Where such woody galls are detected, prune and destroy the infested plant material when the galls are small and have just started to develop. But, remember every bug needs a home!
All photos by Eileen Buss, UF Entomologist
by Julie McConnell | Apr 7, 2017
It’s really tempting to buy a tree and plant it in the middle of your lawn or directly in front of your picture window, but instead take some time to choose the best spot first. Several considerations such as maintenance and mature size should be taken into account before the site is selected.

Mowing close to the trunk of this Pindo palm has caused repeated injury to the trunk. Photo: JMcConnell, UF/IFAS
Placing a tree in a lawn area without creating a bed can lead to maintenance issues for both the tree and the turfgrass. It is easy to simply cut out a small patch of turf the size of the rootball and install a tree, however, as the grass grows up towards the trunk over time maintaining that grass will become difficult. It is common to see mechanical injuries to tree trunks because weed eaters or mowers have chipped away at the bark when trying to cut the grass. Other potential problems are irrigation zones calibrated for turf delivering the wrong amount of water to trees and herbicides used on grass that may cause injury to trees.
Over time, as the tree canopy grows, it will create shade and any grass trying to grow in that area will thin and be more susceptible to disease and insect pressure. By creating a large ornamental bed for your tree, you will prevent some pitfalls associated with placing the tree in the lawn.
Another common mistake is planting a tree too close to a house or other structure. It can be difficult to imagine how large a tree will grow at maturity because it is not a quick process. Trees placed close to houses may grow into eaves and shed leaves onto roofs and into gutters. This adds to maintenance and can provide mosquito breeding grounds. Also, some tree roots may interfere with walkways or septic systems and should be sited far enough away to avoid these issues.

These Japanese Maples are planted in a bed separate from the lawn making care for both plant types easier. Photo: JMcConnell, UF/IFAS
Be sure to research any tree you plan to install to find out ideal growing conditions and mature size. If you plan ahead and use good maintenance practices, a tree can become an valuable part of your home landscape to be enjoyed for years to come.
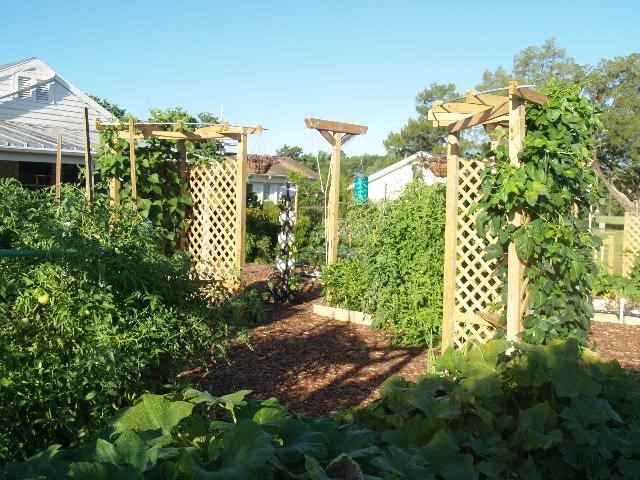

by Ray Bodrey | Mar 20, 2017

Figure 1: Edible Landscaping.
Credit: Dr. Gail Hansen, Environmental Horticulture-UF/IFAS
Edible landscaping has become a trend for many gardening enthusiasts. A combination of edible plants along with traditional ornamentals can create an artful presentation. There are some challenges when designing such a landscape, but in those challenges opportunities’ may be found. One of the most difficult challenges is making sure your garden or landscape is healthy and vibrant year-round since many edibles are short-lived annuals. These include plants such as eggplant, pepper, lettuce, artichoke and some annual herbs. There is a solution to this concern. First, know your edible plant’s propagation and maturity months. This way you can offset plantings to ensure color in your landscape. Another key measure is to mix some evergreen ornamentals in with short season edibles and long season edibles. Examples of long season edibles include berry shrubs, fruit trees and biennial or perennial herbs.
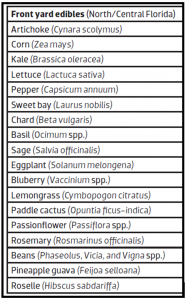
Table 1: North/Central Florida Front Yard Edibles.
Credit: Dr. Gail Hansen, Environmental Horticulture-UF/IFAS.
When designing your edible landscape, think about style and theme to help guide you through the process. A formal design has more straight edges and geometric shapes, whereas the more natural approach has meandering edges and irregular shapes. A color scheme in harmony is very important. Remember, an edible landscape should not just be a production food garden but a visual treat. The goal is not to grow a high yield garden, but only to produce supplemental edibles to make the endeavor worthwhile.
Dr. Gail Hansen, Associate Professor of Environmental Horticulture at the University of Florida, has developed twelve ideas when creating an edible landscape:
- Combine reliable, low-maintenance ornamental with edible plants. Use evergreen ornamentals to maintain enough green structure, so that potential cool season bare spots are not visual.
- Use support structures for an artistic effect and to assist in growth of some plants. Trellises, arbors and even tomato cages are some examples that can be used.
- Use containers in areas to keep the landscape more organized. Planters will also help in maintenance, as plants will be easier to reach and the soil will be easier to manage.
- Create some hard edges in your landscape. Raised beds, garden walls and borders will give defining lines to the landscape and promote a clean appearance.
- A pathway through the landscape will both provide an access to plants and give an inviting appeal. Brick pavers, gravel and mulch are good examples of pathway material.
- Remember color is key. Create a visually pleasing combination of plant color, form, texture and sizes.
- Always start by keeping it simple. So, start small and simple. Then, you can begin filling in the landscape.
- Look for one unique feature to create an added interest to you landscape and provide growth to plants. This could be a shade house for ferns and other hanging baskets or a hay bale, where lettuce, tomatoes or peppers could grow upon.
- Select appealing and easy to grow plants that you want to eat!
- Let plants reach maturity before taking them out of the landscape. For example, rainbow chard will grow larger, if allowed to continue to grow after seed has been produced.
- Use the Florida-Friendly Landscaping principle, “Right Plant, Right Place”, when adding edibles to your landscape. Match the growing needs with the most suitable location.
- Consider your location and layout for irrigation. All plants need some degree of water. An above ground drip irrigation system is usually the most flexible and adjustable irrigation method in regards to overall plant watering needs in a landscape.
Following Dr. Hansen’s ideas will help you create the edible landscape of your dreams. For more information on edible landscaping, please contact your local county extension office for more details.
Supporting information for this article can be found in the UF/IFAS EDIS Publications, “Landscape Design with Edibles” by Dr. Gail Hansen: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/EP/EP47500.pdf
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Mary Salinas | Mar 9, 2017

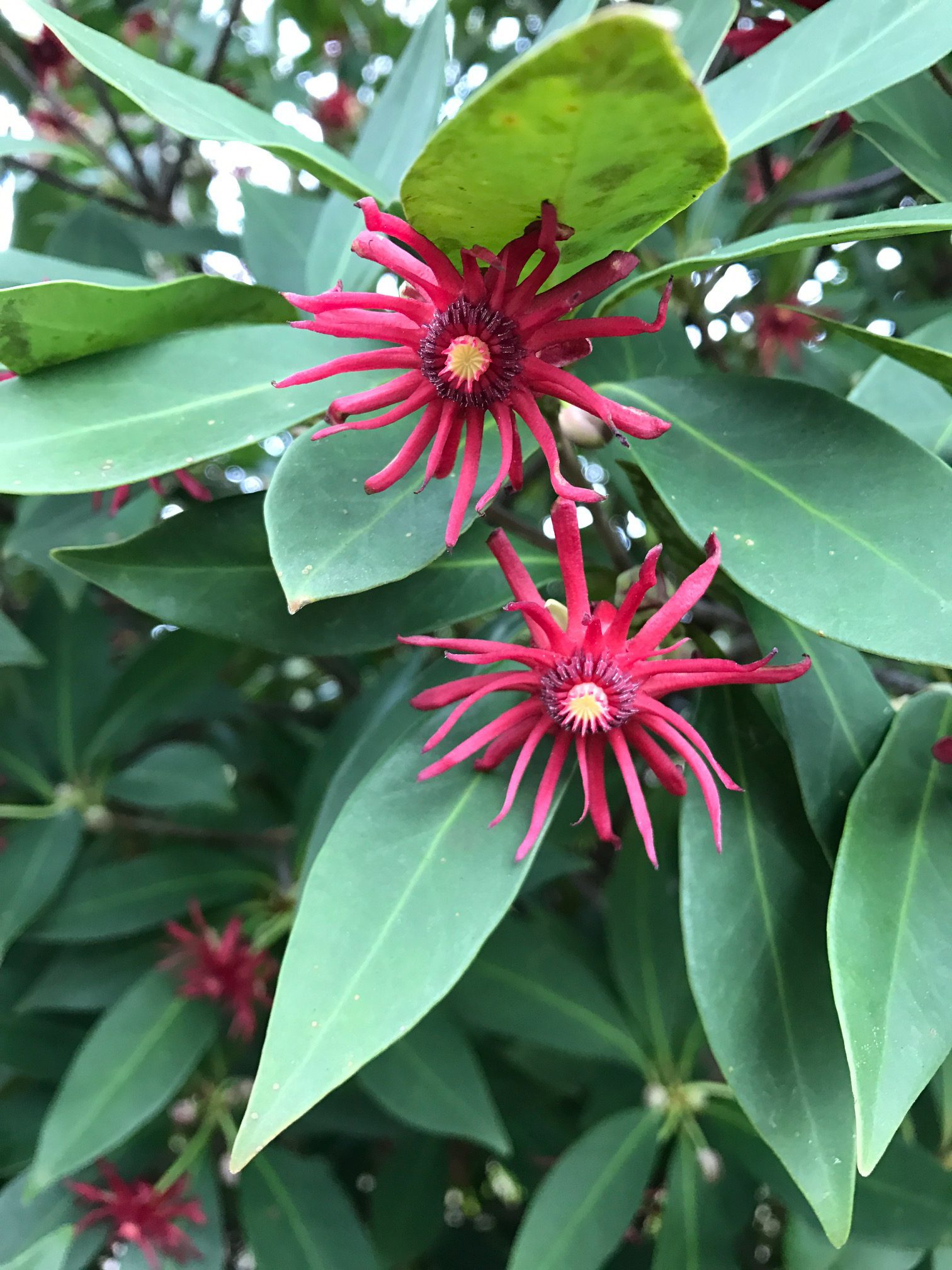
Dark red flowers of Florida red anise arrive in the springtime. Photo credit: Mary Derrick, UF/IFAS Extension.
Springtime brings small but very pretty red blooms on an outstanding native shrub/small tree, Florida red anise (Illicium floridanum). It occurs naturally in the wild in the central and western panhandle of Florida and west along the gulf coast into Louisiana. Its natural environment is in the understory along streams and in rich, wooded areas.
This is a great shrub for a part shade to shady and moist area in your landscape. The dense foliage, dark green leaves and the fact that it is evergreen all year makes it a great choice for an informal hedge. Plan for it to grow to a maximum height of 12 to 15 feet.

Dense growth habit of Florida red anise. Photo credit: Mary Derrick, UF/IFAS Extension.
The leaves have a licorice-like aroma when crushed but this is NOT the species that gives us the edible culinary anise. Maybe it is that aroma that makes this a relatively pest-free plant!
Yellow anise (Illicium parviflorum) is a very similar native shrub but has small yellow flowers and adapts better to a drier environment. The native range of the yellow anise is north central Florida.














