In Part 1 of The Estuary’s Natural Filtration System article, we discussed the major contributors to natural filtration inside of the estuary. These examples included oysters, marsh plants, and seagrasses. In Part 2, we will discuss the smaller filter-feeding organisms including tunicates, barnacles, clams, and anemones.
Tunicates
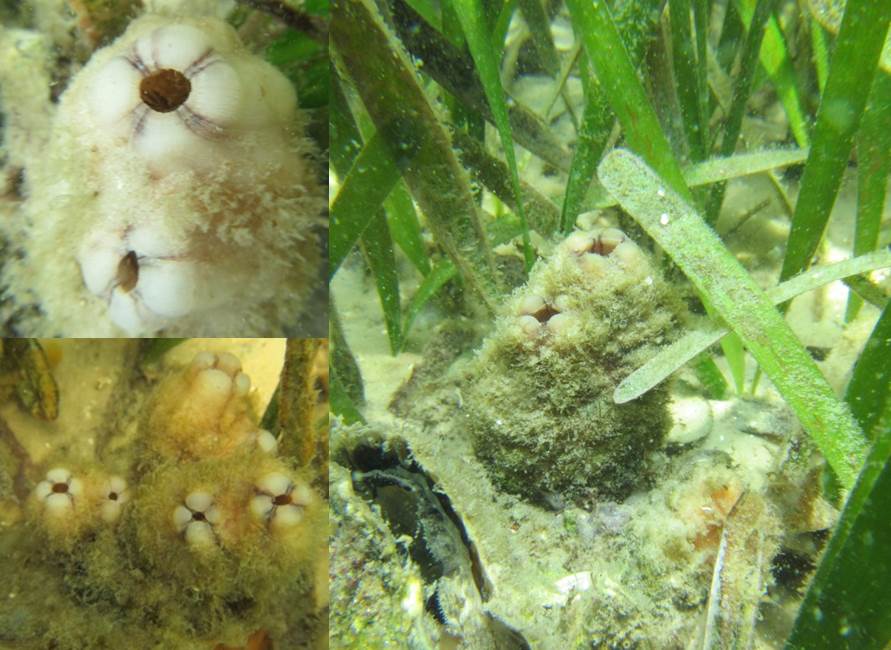
Tunicates, also known as sea squirts, are very interesting marine invertebrates and can be easily confused for a sponge. There are many different types of tunicates in the estuaries and can be either solitary or colonial. You might’ve seen these at an aquarium attached to different substrates, and when removed from the water, their name sea squirt comes into play. Tunicates have a defense mechanism to shoot out the water inside their body in hopes of being released by any predator.
Tunicates are filter feeders and intake water through their inhalant siphons and expel waste and filtered water through their exhalant siphons. Tunicates can filter out phytoplankton, algae, detritus, and other suspended nutrients. The tunicate produces a mucus that catches these nutrients as it passes through, and the mucus is then conveyed to the intestine where it is digested and absorbed.
An invader to the Gulf of Mexico, the Pleated Sea Squirt (Styela plicata), hitched rides on the hulls of ships and found the Gulf of Mexico waters very favorable. You can sometimes spot these organisms on ropes that have been submerged for a long period of time in salty waters. Even though they are non-native, these sea squirts can filter, on average, 19 gallons of water per day.
Barnacles
One organism that seems ubiquitous worldwide is the barnacle (Genus Semibalanus and Genus Lepas). The Genus Semibalanus contains the common encrusting barnacle we are accustomed to seeing in our waterways along pilings, submerged rocks, and even other animals (turtles, whales, crabs, and oysters). The Genus Lepas contains Gooseneck Barnacles and can be seen attached to flotsam, floating organic debris, and other hard surfaces and have a stalk that attaches them to their substrate. Interesting fact, certain gooseneck barnacle species are eaten in different parts of the world.
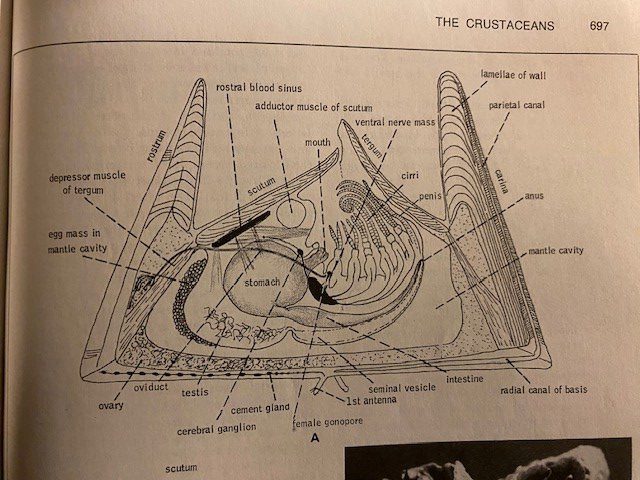
This image from a textbook shows the internal structure of a barnacle. Notice the shrimplike animal on its back with extendable appendages (cirri) for feeding.
Image: Robert Barnes Invertebrate Zoology.
Barnacles have over 2,100 species, are closely related to crabs and lobsters, and are a part of the subphylum Crustacea. At first glance, you might not think a barnacle is closely related to crabs, but when you remove the hard plates surrounding it, the body looks very similar to a crab. Barnacles also have life cycle stages that are similar to crabs; the nauplius and cyprid developmental stages. Inside of the hard plates is an organism with large feather-like appendages called cirri. When covered by water, the barnacles will extend their cirri into the water and trap microscopic particles like detritus, algae, and zooplankton. Barnacles are at the mercy of tides and currents, which makes quantifying their filtering ability difficult.
Hard Clams
Even though not as abundant in the Florida Panhandle as they were in the 1970’s – 1980’s, hard clams (Mercenaria mercenaria and M. campechiensis) can still be found in the sand along the shoreline and near seagrass beds. These clams are also known as Quahogs and are in the family Veneridae, commonly known as the Venus clam family, and contain over 500 living species. Most of the clams in the family Veneridae are edible and Quahogs are the types of clams you would see in a clam chowder or clam bake.
Being the only bivalve on this list does not make it any less important than the oyster or scallop on Part 1’s list. In fact, a full-grown adult Southern Quahog clam can filter upwards of 20 gallons of water per day and have a lifespan of up to 30 years. Clams also live a much different lifestyle than their oyster and scallop cousins. Clams spend the majority of their life under the sand. Their movement under the sand helps aerate and mix the soil, which can sometimes stimulate seagrass growth.
Right outside the Florida Panhandle and in the Big Bend area, Quahog clams are commercially farmed in Cedar Key. Southern Quahog clams are also being used for restoration work in South Florida. Clams are being bred in a hatchery and their “seed” are being released into Sarasota Bay to help tackle the Red Tide (Karenia brevis) issue. According to the project’s website, they have added over 2 million clams since 2016, and the clams are filtering over 20 million gallons of seawater daily.
Anemones
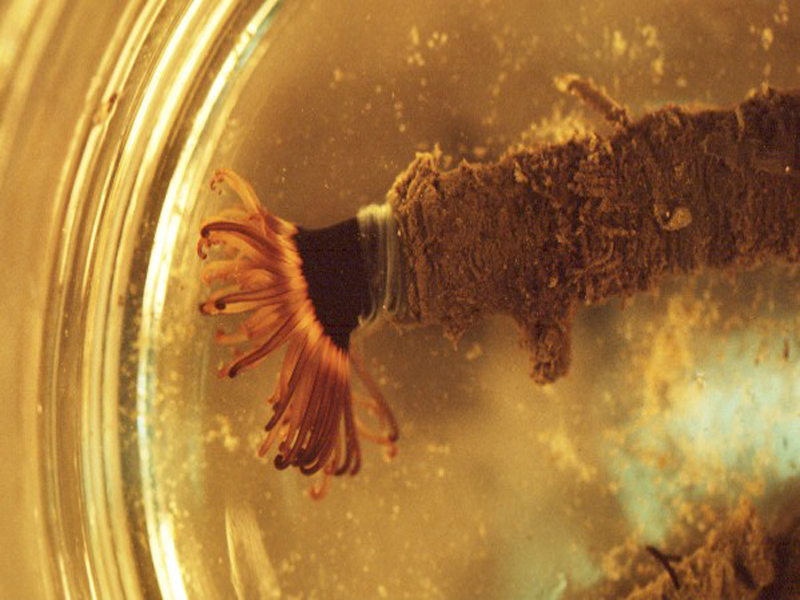
Anemones are beautiful Cnidarians resembling an upside-down, attached jellyfish, which couldn’t be closer to the truth. The phylum Cnidaria contains over 11,000 species of aquatic animals including corals, hydroids, sea anemones, and, you guessed it, jellyfish. Anemones come in many different shapes and sizes, but the common estuary anemones include the tube-dwelling anemone (Ceriantheopsis americana) and the tricolor anemone (Calliactis tricolor), also known as the hitchhiking anemone. If you have ever owned a saltwater aquarium, you might have run into the pest anemone Aiptasia (Aiptasia sp.).
Anemones filter feed with their tentacles by catching plankton, detritus, and other nutrients as the tide and current flows. The tentacles of the anemone are lined with cnidocytes that contain small amounts of poison that will stun or paralyze the prey. The cnidae are triggered to release when an organism touches the tentacles. If the anemone is successful in immobilizing the prey, the anemone will guide the prey to their mouth with the tentacles. Just like the barnacle, anemones are at the mercy of the tides and currents, and filtration rates are hard to calculate. However, if you ever see an anemone with food around, they move those tentacles to and from their mouths quickly and constantly!
In Parting
As you can see, there are many different natural filters in our estuary. Healthy, efficiently filtering estuaries are very important for the local community and the quality of the waters we love and enjoy. For more information on our watersheds and estuaries and how to protect them, visit Sea Grant’s Guide To Estuary-Friendly Living.
- Bring Some Wild Game To Your Holiday Dinner - December 15, 2025
- Aquaculture in the Southern United States: Part 5 – North and South Carolina - December 8, 2025
- Aquaculture in the Southern United States: Part 4-Louisiana & Mississippi - October 29, 2025




