
by Erik Lovestrand | Jun 28, 2024
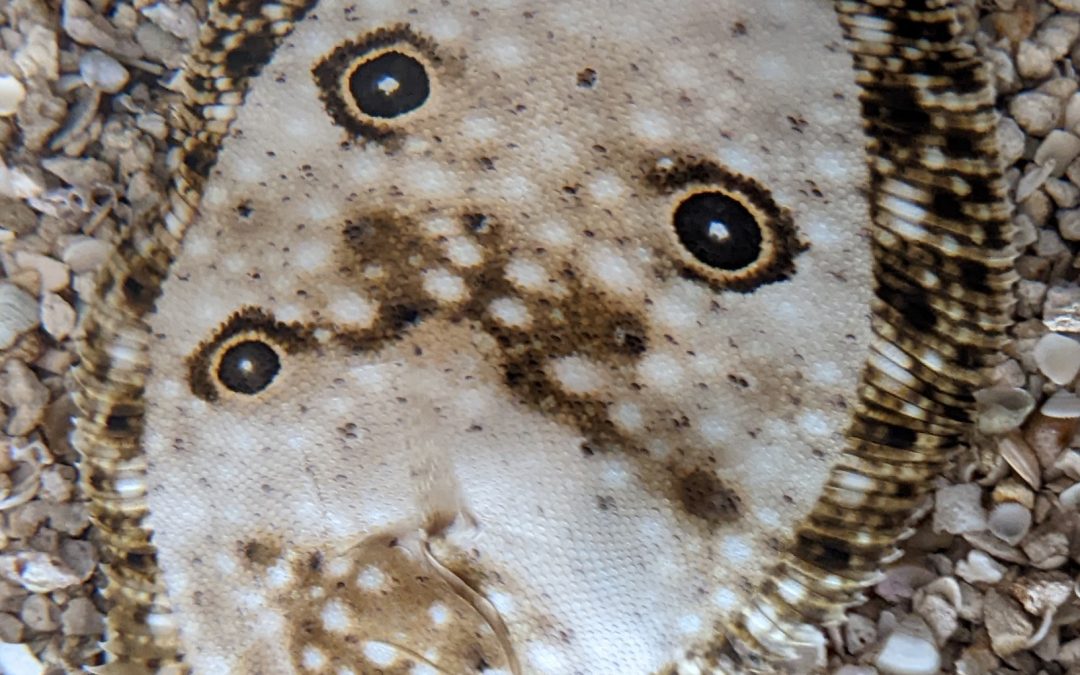
One of several “flatfish” inhabiting our Panhandle coastal waters, the ocellated flounder (Ancylopsetta ommata) is one of the more striking species, in my opinion. From the four distinctive eye spots (ocelli) to its incredible variability in background patterns, I must just say that it is a beautiful creature. Flounders are unique among fish, in that early during larval development one eye will migrate over to join the other and the fish will orient to lay on its side when at rest. Only the top side will have coloration and the bottom side will be white. While the eyes end up on the same side, the pectoral and pelvic fins remain in their traditional positions, although the bottom-side pectoral fin is reduced in size.
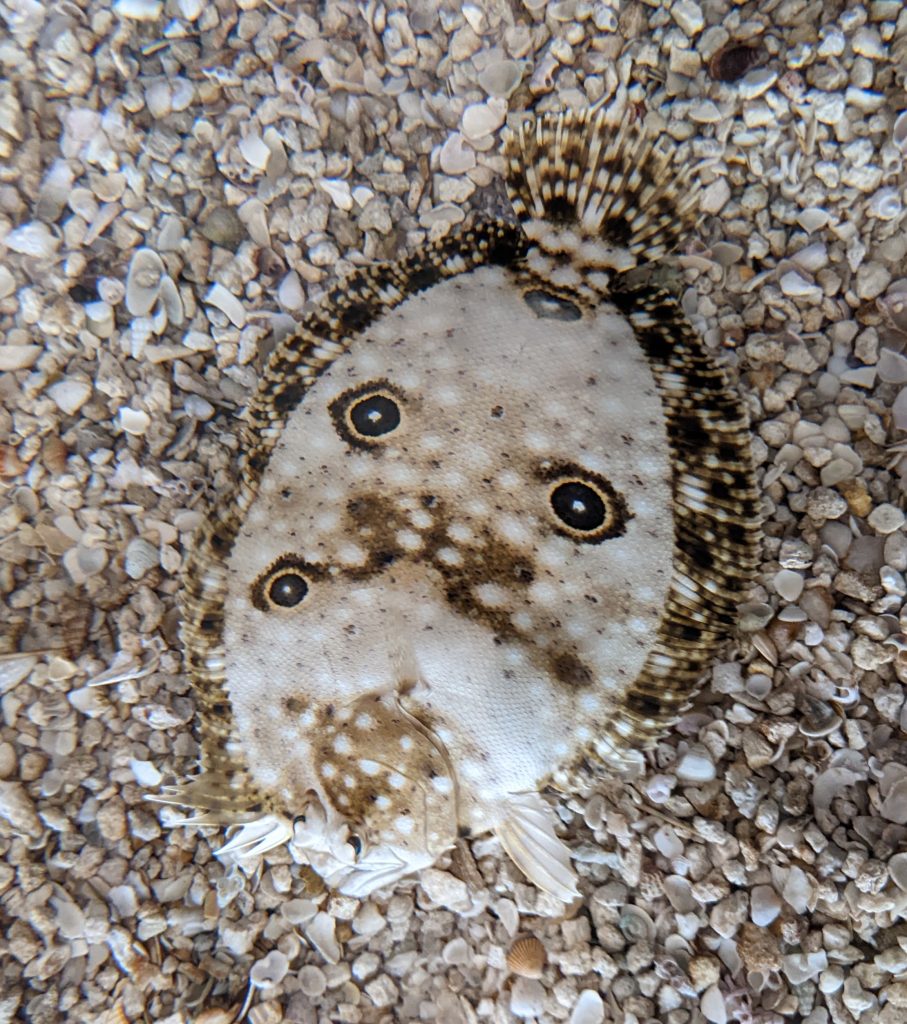

Not the Biggest but Definitely one of the Coolest Flounder Species Around
Ocellated flounders are always left-eyed, meaning if you stood them up vertically with their pelvic fins down, the left side of the body has the eyes. When laying on the ocean floor, their independently moving eyes can keep a lookout in all directions. However, flounders tend to remain immobile when approached, depending on an awesome ability to camouflage themselves from predators. They can flip sand or gravel onto their top side which hides their outline and their ability to match the color and texture of the surrounding substrate is phenomenal.
This species is a fairly small fish, reaching lengths of about ten inches. However, they are by no means the smallest flatfish around. We also have hogchokers (a member of the sole family, 6-8 in.) and blackcheek tonguefish (to 9 in.). These are dwarfed by the larger Gulf flounder and Southern flounder which are highly prized table fare by fishers along our coasts and can reach sizes that earn them the nickname of “doormat” flounders. Regardless of the species of flounder you observe, it is unquestionably one of the super cool animals we have the privilege of living with here along the North Florida Gulf Coast.

by Rick O'Connor | Jun 21, 2024
Today’s society is more educated about sharks and shark behavior than our forefathers. In the 18th, 19th, and much of the 20th century we thought of sharks as mindless eating machines – consuming anything available. Whalers would witness sharks consuming carcasses, as did many other fishermen. Sailors noted sharks following the smaller boats across the ocean, always present when bad situations occurred.
During World War II the U.S. Navy was moving across the Pacific and a deeper understanding of sharks was needed to keep servicemen safe. The sinking of the USS Indianapolis pushed the Navy into a larger research program to determine how to repel sharks and better understand what made them tick. After the war funding for such research continued. One of the leading researchers was Dr. Eugene Clark, who eventually founded the Mote Marine Laboratory in Sarasota with the intention of developing a better understanding of shark behavior. Dr. Clark frequently appeared on the Undersea World of Jacques Cousteau educating the public about how sharks function and respond to their environment. All with the idea of how to better reduce negative shark encounters.

Pregnant Bull Shark (Carcharhinus leucas) cruses sandy seafloor. Credit Florida Sea Grant Stock Photo
In the 1970s Peter Benchley wrote Jaws but included a marine biologist as one of the key characters who would provide science insight into how sharks work. The film was a cultural phenomenon. I remember standing in a line that wrapped the cinema twice to get in. This was followed by more funding for shark research and a better understanding of how they work. This was then followed by a popular summer series known as “Shark Week”, which remains popular to this day. Many of the old tales of shark behavior were disproved or explained. The idea of a mindless eating machine was replaced with a fish that actually thinks and responds to certain cues. People began to realize that shark attacks are quite rare and could be explained if we understood what happened leading up to the attack.
We now understand that sharks are fish, in a class where the members have cartilaginous skeletons (they lack true bone). They are one of the most perceptive creatures in the ocean, using their senses to detect potential prey and that there are signals that can “turn them on”. On the side of their bodies there is a line of small gelatinous cells that can detect slight vibrations in the ocean – from up to a mile away. The ocean is a noisy place, and it appears that sharks respond to different frequencies. I like to use the analogy of yourself being in a large student cafeteria. Everyone is talking and it is very noisy. Then someone calls your name. Somehow, amongst all the background clatter, you hear this and respond to it. Studies suggest that sharks do the same. With all of the noise moving though the ocean, sharks hear things that catch their attention and then move towards the source.
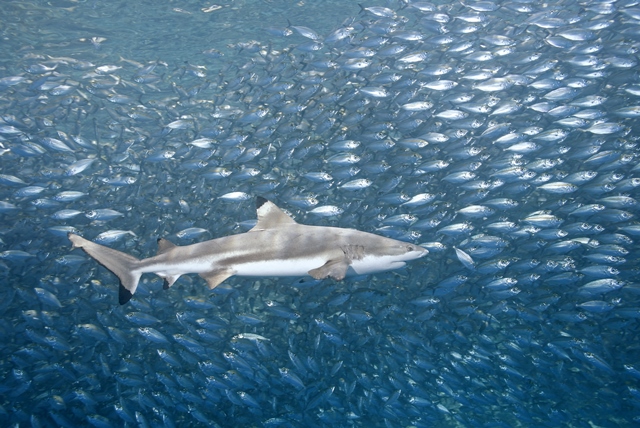

Blacktip sharks are one of the smaller sharks in our area reaching a length of 59 inches. They are known to leap from the water. Photo: Florida Sea Grant
As they get closer their sense of smell kicks in. Everyone has heard that sharks can detect small amounts of blood in large amounts of seawater – remember “Bruce” from Finding Nemo? It is true, but they do have to be down current to pick up the scent and they will now focus their search to find the source. Some studies suggest other “odors”, such as the urine of seals, might produce the same reaction that blood does. All may lead to shark to think a possible meal is nearby.
Eyesight is not great with any creature in the sea. Light does not travel well in water – but sharks do have eyes and they do see well (one of the old tales science disproved – that sharks are basically “blind”). However, because of the low light, they do have to be close to the target to get a visual. Some studies suggest that sharks are detecting shadows or shapes they may confuse as a potential prey, bite it, and then release when they discover it was not what they thought it was. This idea is supported by the fact that many who are bitten experience what is called “bite and release” – and they turn and swim away. It is also known that sharks have structures in the back of their retinas that act as mirrors, collecting what light is available, reflecting it within the eye, and illuminating their world. They believe they see pretty well at night – better than us for sure. The image they see may appear to be a prey item and may be what is producing the vibrations and odors that they detected.

The Scalloped Hammerhead is one of five species of hammerheads in the Gulf. It is commonly found in the bays. Photo: Florida Sea Grant
And they have one more “sixth sense” – the ability to detect weak electric fields. The shark’s mouth is not in position to attack prey as they move forward. It is on the bottom of their head and, one of the old tales, was that sharks must swim over their prey to bite it. Video taken during the filming for Jaws showed that the shape of the shark’s head changes at the last moment of an attack. The entire head becomes distorted to get the mouth in the correct position for the bite. The “eyes roll back” – as the old fishermen used to say – and the jaws move up and forward. At this point the shark can no longer use its eyes to zero in on the target. However, they have small cells around their snout called the Ampullae of Lorenzini that can detect the small electric fields produced by muscle movement – even the prey’s heartbeat – and know where they are. But – they must be very close to the prey to detect this.
Understanding all of this gives scientists, and the public, a better idea of how sharks work. What “turns them on” and how/when they will select prey. One thing that has come from all of this is that we do not seem to be high on their target list.
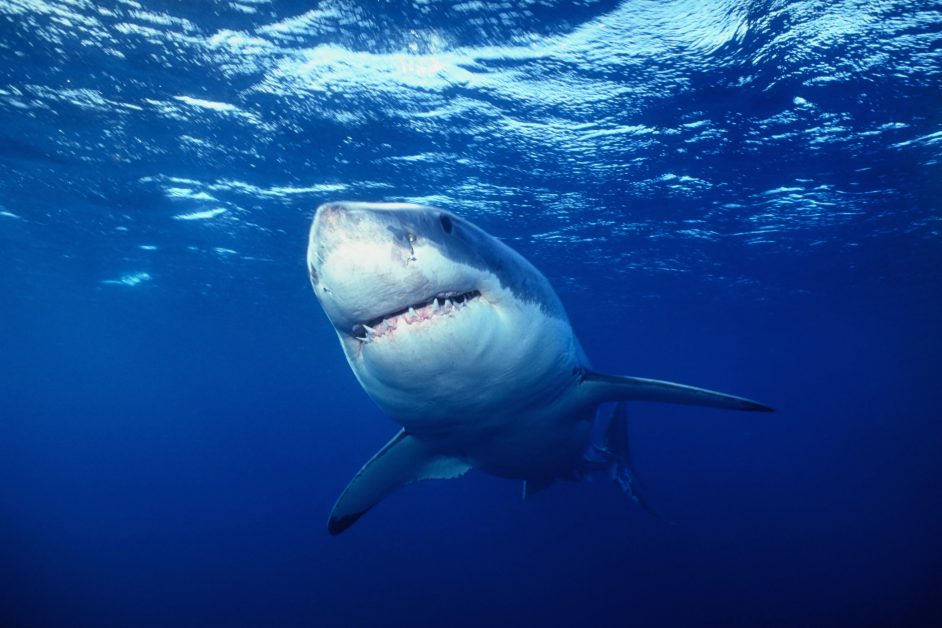

The Great White shark.
Photo: UF IFAS
The International Shark Attack File is kept at the Florida Museum of Natural History in Gainesville. It has cataloged shark attacks from around the world dating back to 1580. The File only catalogs UNPROVOKED attacks. With provoked attacks – those occurring while people are grabbing them, or fishing for them, or in some way provoked an attack – we understand why the shark bit the human. It is the unprovoked attacks that are of more interest. Those where the person was not doing anything intentionally to invite a shark bite, but it happened.
One thing we can tell from this data is that unprovoked attacks are not common. Since 1580, they have logged 3,403 unprovoked shark attacks worldwide. Considering how many people have swum in the ocean since 1580, this is a very small number. Note, the File is only as good as the reports it gets. In the past, many unprovoked attacks were not reported. But in our modern age of communication, it is rare that such an attack does not make the headlines today.

The Bull Shark is considered one of the more dangerous sharks in the Gulf. This fish can enter freshwater but rarely swims far upstream. Photo: Florida Sea Grant
Of these attacks 1,640 (48%) have occurred in the United States, followed by 706 in Australia. Many have explained this by the large levels of water activities people in both countries participate in. In the US Florida leads the way with 928 unprovoked attacks (57%), most of these (351 – 34%) are from Volusia County. This may be due to breakthrough emergency communications with Volusia County and thus more reports. Many of the reports are minor, small bites from small sharks such as blacktips, but unprovoked none the less. There are 26 unprovoked attacks logged from the Florida panhandle – 3% of the state total – and most of these (n=9) were from Bay County.
When looking at what people were doing when attacked, most were at the surface and participating in some surface water activity such as surfing, skiing, boogie boarding, etc. This is followed by surface swimming or snorkeling.
This brings us to the attacks this summer in the panhandle. There have been a lot of questions as to what may have caused them. They are still assessing the situation before and during these attacks to try and determine why they happened. As we have mentioned, we have learned a lot about sharks and shark behaviors over the last 50 years and several hypotheses are open for discussion. We will see what the investigators learn. Until then, the International Shark Attack File does offer a page on how you can reduce your risk. There is “Advice to Swimmers”, “Advice to Divers”, “Color of Apparel”, “Menstruation and Sharks”, “Quick Tips”, “Advice to Spearfishers”, and “How to Avoid a Shark Attack”. Read more on these tips at https://www.floridamuseum.ufl.edu/shark-attacks/reduce-risk/.

by Thomas Derbes II | Jun 21, 2024
In Part 1 of The Estuary’s Natural Filtration System article, we discussed the major contributors to natural filtration inside of the estuary. These examples included oysters, marsh plants, and seagrasses. In Part 2, we will discuss the smaller filter-feeding organisms including tunicates, barnacles, clams, and anemones.
Tunicates
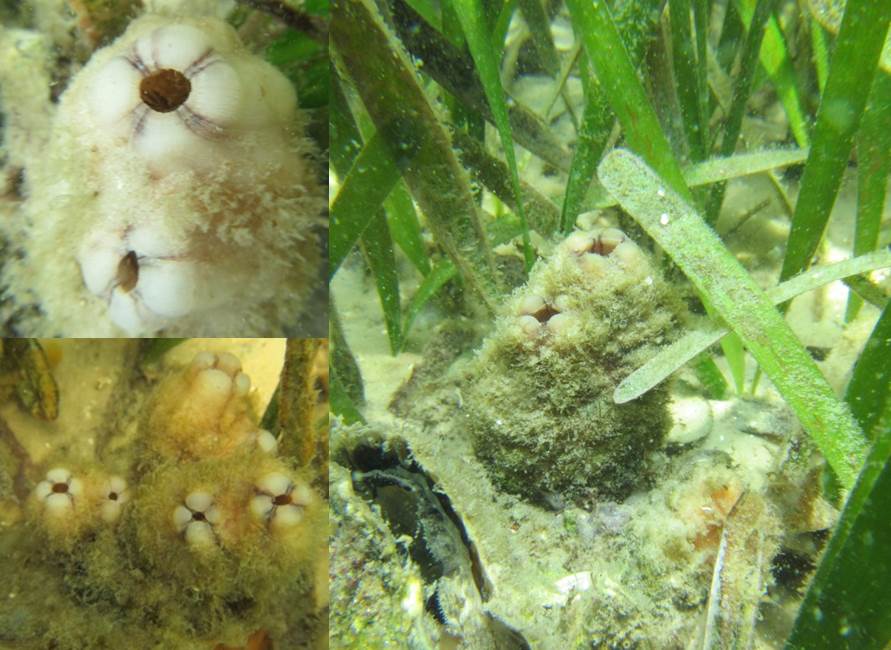

Pleated Sea Squirt – Photo Credit: Don Levitan, PH.D. FSU
Tunicates, also known as sea squirts, are very interesting marine invertebrates and can be easily confused for a sponge. There are many different types of tunicates in the estuaries and can be either solitary or colonial. You might’ve seen these at an aquarium attached to different substrates, and when removed from the water, their name sea squirt comes into play. Tunicates have a defense mechanism to shoot out the water inside their body in hopes of being released by any predator.
Tunicates are filter feeders and intake water through their inhalant siphons and expel waste and filtered water through their exhalant siphons. Tunicates can filter out phytoplankton, algae, detritus, and other suspended nutrients. The tunicate produces a mucus that catches these nutrients as it passes through, and the mucus is then conveyed to the intestine where it is digested and absorbed.
An invader to the Gulf of Mexico, the Pleated Sea Squirt (Styela plicata), hitched rides on the hulls of ships and found the Gulf of Mexico waters very favorable. You can sometimes spot these organisms on ropes that have been submerged for a long period of time in salty waters. Even though they are non-native, these sea squirts can filter, on average, 19 gallons of water per day.
Barnacles

Barnacles along the seashore is a common site for many.
Photo: NOAA
One organism that seems ubiquitous worldwide is the barnacle (Genus Semibalanus and Genus Lepas). The Genus Semibalanus contains the common encrusting barnacle we are accustomed to seeing in our waterways along pilings, submerged rocks, and even other animals (turtles, whales, crabs, and oysters). The Genus Lepas contains Gooseneck Barnacles and can be seen attached to flotsam, floating organic debris, and other hard surfaces and have a stalk that attaches them to their substrate. Interesting fact, certain gooseneck barnacle species are eaten in different parts of the world.
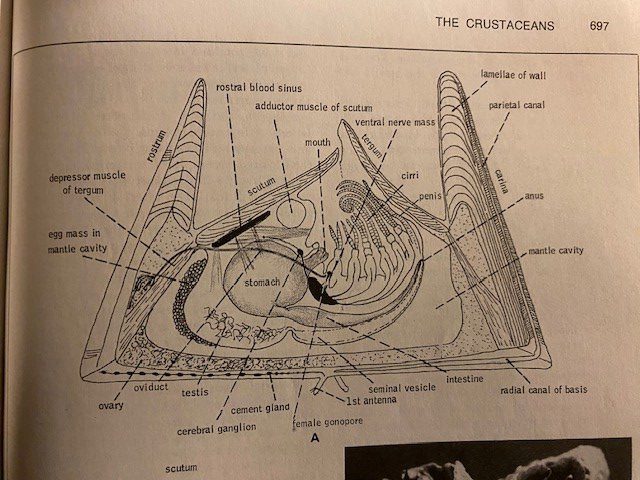
This image from a textbook shows the internal structure of a barnacle. Notice the shrimplike animal on its back with extendable appendages (cirri) for feeding.
Image: Robert Barnes Invertebrate Zoology.
Barnacles have over 2,100 species, are closely related to crabs and lobsters, and are a part of the subphylum Crustacea. At first glance, you might not think a barnacle is closely related to crabs, but when you remove the hard plates surrounding it, the body looks very similar to a crab. Barnacles also have life cycle stages that are similar to crabs; the nauplius and cyprid developmental stages. Inside of the hard plates is an organism with large feather-like appendages called cirri. When covered by water, the barnacles will extend their cirri into the water and trap microscopic particles like detritus, algae, and zooplankton. Barnacles are at the mercy of tides and currents, which makes quantifying their filtering ability difficult.
Hard Clams

Clams of North Florida – UF/IFAS Shellfish
Even though not as abundant in the Florida Panhandle as they were in the 1970’s – 1980’s, hard clams (Mercenaria mercenaria and M. campechiensis) can still be found in the sand along the shoreline and near seagrass beds. These clams are also known as Quahogs and are in the family Veneridae, commonly known as the Venus clam family, and contain over 500 living species. Most of the clams in the family Veneridae are edible and Quahogs are the types of clams you would see in a clam chowder or clam bake.
Being the only bivalve on this list does not make it any less important than the oyster or scallop on Part 1’s list. In fact, a full-grown adult Southern Quahog clam can filter upwards of 20 gallons of water per day and have a lifespan of up to 30 years. Clams also live a much different lifestyle than their oyster and scallop cousins. Clams spend the majority of their life under the sand. Their movement under the sand helps aerate and mix the soil, which can sometimes stimulate seagrass growth.
Right outside the Florida Panhandle and in the Big Bend area, Quahog clams are commercially farmed in Cedar Key. Southern Quahog clams are also being used for restoration work in South Florida. Clams are being bred in a hatchery and their “seed” are being released into Sarasota Bay to help tackle the Red Tide (Karenia brevis) issue. According to the project’s website, they have added over 2 million clams since 2016, and the clams are filtering over 20 million gallons of seawater daily.
Anemones
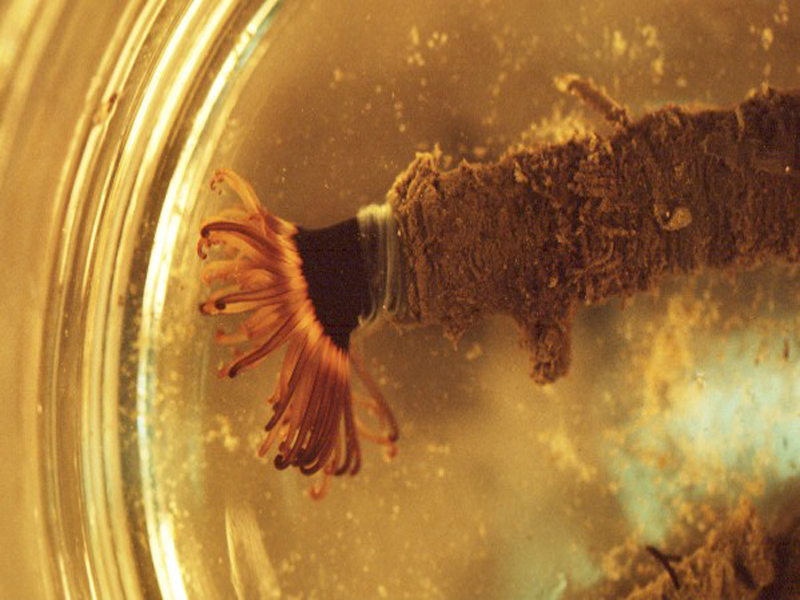

Tube-Dwelling Anemone Under Dissection Scope – UF/IFAS Shellfish
Anemones are beautiful Cnidarians resembling an upside-down, attached jellyfish, which couldn’t be closer to the truth. The phylum Cnidaria contains over 11,000 species of aquatic animals including corals, hydroids, sea anemones, and, you guessed it, jellyfish. Anemones come in many different shapes and sizes, but the common estuary anemones include the tube-dwelling anemone (Ceriantheopsis americana) and the tricolor anemone (Calliactis tricolor), also known as the hitchhiking anemone. If you have ever owned a saltwater aquarium, you might have run into the pest anemone Aiptasia (Aiptasia sp.).
Anemones filter feed with their tentacles by catching plankton, detritus, and other nutrients as the tide and current flows. The tentacles of the anemone are lined with cnidocytes that contain small amounts of poison that will stun or paralyze the prey. The cnidae are triggered to release when an organism touches the tentacles. If the anemone is successful in immobilizing the prey, the anemone will guide the prey to their mouth with the tentacles. Just like the barnacle, anemones are at the mercy of the tides and currents, and filtration rates are hard to calculate. However, if you ever see an anemone with food around, they move those tentacles to and from their mouths quickly and constantly!
In Parting
As you can see, there are many different natural filters in our estuary. Healthy, efficiently filtering estuaries are very important for the local community and the quality of the waters we love and enjoy. For more information on our watersheds and estuaries and how to protect them, visit Sea Grant’s Guide To Estuary-Friendly Living.

by Ray Bodrey | Jun 3, 2024
The University of Florida/IFAS Extension & Florida Sea Grant faculty are reintroducing their acclaimed “Panhandle Outdoors LIVE!” series on St. Joseph Bay. This ecosystem is home to some of the richest concentrations of flora and fauna on the Northern Gulf Coast. This area supports an amazing diversity of fish, aquatic invertebrates, turtles and other species of the marsh and pine flatwoods. Come learn about the important roles of ecosystem!

Registration fee is $40. You must pre-register to attend.
Registration link: https://www.eventbrite.com/e/panhandle-outdoors-live-st-joseph-bay-by-land-sea-tickets-906983109897
or use the QR code:
Meals: Lunch, drinks & snacks provided (you may bring your own)
Attire: outdoor wear, water shoes, bug spray and sunscreen
*If afternoon rain is in forecast, outdoor activities may be switched to the morning schedule
Held at the St. Joseph Bay State Buffer Preserve Lodge: 3915 State Road 30-A, Port St. Joe
| 8:30 – 8:35 Welcome & Introduction – Ray Bodrey, Gulf County Extension (5 min) |
| 8:35 – 9:20 Diamondback Terrapin Ecology – Rick O’Connor, Escambia County Extension |
| 9:20 – 10:05 Exploring Snakes, Lizards & the Cuban Tree Frog – Erik Lovestrand, Franklin County Extension |
| 10:05 – 10:15 Break |
| 10:15 – 11:00 The Bay Scallop & Habitat – Ray Bodrey, Gulf County Extension |
| 11:00 – 11:45 The Hard Structures: Artificial Reefs & Derelict Vessel Program – Scott Jackson, Bay County Extension |
| 11:45 – Noon Question & Answer Session – All Agents |
| Noon – 1:00 Pizza & Salad! |
| 1:00 – 1:20 Introduction to the Buffer & History – Buffer Preserve Staff |
| 1:20 – 2:20 Tram Tour – Buffer Preserve Staff |
| 2:20 – 2:30 Break |
| 2:30 – 3:00 A Walk in the Mangroves – All Agents |
| 3:00 – 3:15 Wrap up & Adjourn – All |

by Rick O'Connor | May 17, 2024
Recently I participated in a local festival to educate the public about the Rice’s Whale – the newly described species in the Gulf of Mexico that is now listed as critically endangered, possibly the most endangered whale in the world’s oceans. I honestly did not know enough about it to provide much education and chose to do terrapin conservation at my table instead (something I know more about) but have since learned much about this new member of the Gulf community.
One of the more frequent comments I heard during the event was “I did not know we even had whales in the Gulf”. This is understandable since we rarely see them – most of us have never seen one. When we think of whales we think of colder climates like Alaska, New England, and the colder waters off California. But many large whales must give birth to their smaller calves in warmer waters – so, they make the trek to tropical locations like Hawaii and Florida to do so. But there are also resident whales in the tropical seas.
You first must understand that the term “whale” does not only mean the large creatures of whale hunting fame, but any member of the mammalian order Cetacea. Cetaceans include both the large baleen whales – like the blue, gray, and right whales – but also the toothed whales – like the sperm, orca, and even the dolphins.
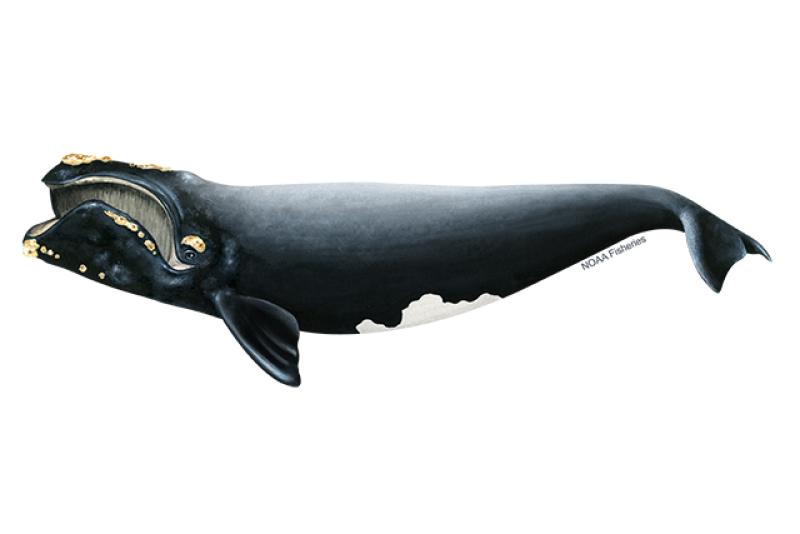

The Right whale is another critically endangered whale found in the Gulf of Mexico. Image: NOAA.
There are 28 cetaceans that have been reported from the Gulf, 21 of those routinely inhabit here. Most exist at and beyond the continental shelf – hence we do not see them. Only two frequent the waters over the shelf – the Atlantic Bottlenose Dolphin and the Atlantic Spotted Dolphin, and only one is routinely seen near shore – the Atlantic Bottlenose Dolphin.
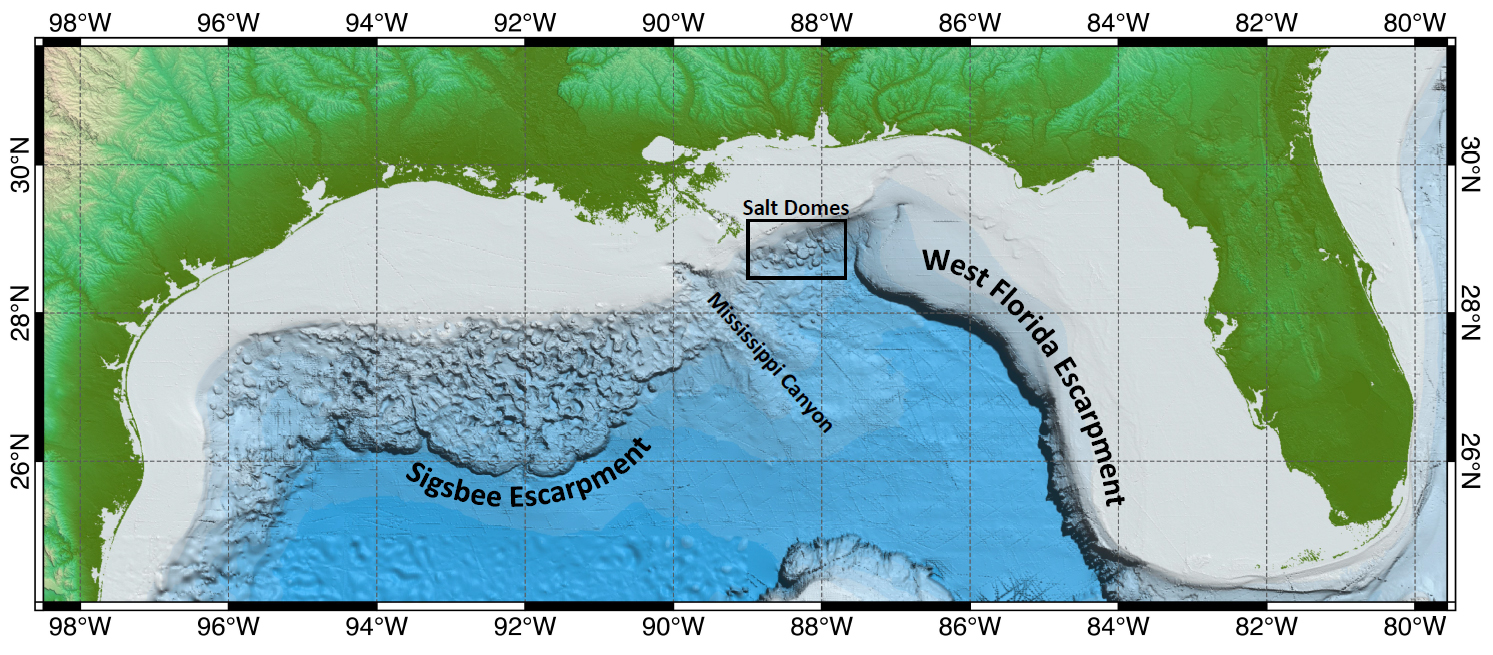
This image shows the location of the continental shelf and thus the location of most of the whales found in the Gulf of Mexico. Image: NOAA.
But offshore, out at the edge of the continental shelf, exists several species of large and small cetaceans. The endangered Sperm, Sei, Fin, Blue, Humpback, and Northern Right whales have been seen. Of those only sperm whales are common. Others include several beaked whales (which resemble dolphins but are much larger), large pods of other species of dolphins, pygmy and dwarf sperm whales, pygmy and false killer whales (as well as the killer whale itself), and other baleen whales such as the Minke and Bryde’s whale.
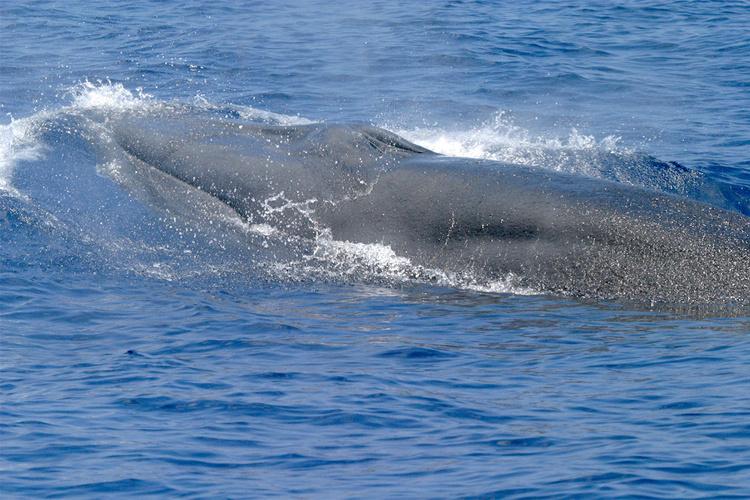
The Bryde’s whale is one of interest to this story.
The Bryde’s whale (pronounced “brood-duss” – Balaenoptera edeni) is a medium sized baleen whale, reaching lengths of about 50 feet and weighing 30 tons. It is often confused with the larger sei whale. They are found in tropical oceans across the planet and are not thought to make the large migrations of many whales due to the fact it is already here in the tropics for birth, and its food source is here as well. They reside in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico extending from the DeSoto Canyon, off the coast of Pensacola, to the shelf edge near Tampa. They appear to travel alone or in small groups of 2-5 animals. They feed on small schooling fish, such as pilchards, anchovies, sardines, and herring. Their reproductive cycle in the Gulf is not well understood.

The Bryde’s whale was thought to be the only resident baleen whale in the Gulf of Mexico. Photo: NOAA.
Strandings have occurred – as of 2009, 33 have been logged. There are no records of mortality due to commercial fishing line entanglement, but vessel strikes have occurred. Due to their large population across the planet, they were not considered for listing under the Endangered Species Act, but that may change in the Gulf region due to human caused mortality. Between 2006-2010 it was estimated that 0.2 Bryde’s whales died annually due the vessel strikes.
In the 1960s Dr. Dale Rice described the Gulf of Mexico population as a possible subspecies. It is the only baleen whale that regularly inhabits the Gulf of Mexico. And ever since that time scientists examining stranded animals thought they may be dealing with a different species.
In the 1990s Dr. Keith Mullin began examining skull differentiation and genetic uniqueness from stranded animals of the Gulf population. Dr. Patricia Rosel and Lynsey Wilcox picked up the torch in 2008. In 2009 a stranded whale, that had died from a vessel strike, was found in Tampa Bay and provided Dr. Rosel more information. In 2019 a stranded whale, that had died from hard plastic in gut in the Everglades, was examined by Dr. Rosel and her team and, with data from this skull, along with past data, determined that it was in fact a different species. The new designation became official in 2019.

The newly described Rice’s whale only exists in the Gulf of Mexico. Photo: NOAA.
The new whale was named the Rice’s whale (Balaenoptera ricei) after Dr. Dale Rice who had first describe it as a subspecies in the 1960s. With this new designation everything changed for this whale. This new species only lives in the Gulf of Mexico, and it was believed there were only about 50 individuals left. Being a marine mammal, it was already protected by the Marine Mammal Protection Act, but with this small population it was listed as critically endangered and protected by the Endangered Species Act.
New reviews and publications began to come out about the biology and ecology of this new whale. Rice’s whales do exist alone or in small groups and currently move between the 100m and 400m depth line along the continental shelf from Pensacola to Tampa. Diet studies suggest that it may feed near the seafloor, unlike their Bryde’s whale cousins. They may have lived all across the Gulf of Mexico at the 100-400m line at one time. They prefer warmer waters and do not seem to conduct long migrations.

The area where the Rice’s whale currently exists. Image: NOAA.
Being listed under the Endangered Species Act, NOAA National Marine Fisheries (NMFS) was required to develop a recovery plan for the whale. NMFS conducted a series of five virtual workshops between October 18 and November 18 in 2021. Workshop participants included marine scientists, experts, stakeholders, and the public. There were challenges identified from the beginning. Much of the natural history of this new whale was not well understood. Current and historic abundance, current and historic distribution, population structure and dynamics, calving intervals and seasonality, diet and prey species, foraging behavior, essential habitat features, factors effecting health, and human mortality rates all needed more research.
At the end of the workshop the needs and recommendations fell into several categories.
Management recommendations
- Create a protected area
- Restrict commercial and recreational fishing in such – require ropeless gear
- Require VMS system on all commercial and recreational vessels
- Require reporting of lost gear and removal of ghost gear
- Risk assessment for aquaculture, renewable energy, ship traffic, etc.
- Prohibit aquaculture in core area and suspected areas
- Reduce burning of fossil fuels
- Prohibit wind farms in core area
- Renewable energy mitigation – reduce sound, night travel, passive acoustic
- Develop spatial tool for energy development and whale habitat use
- Require aquaculture to monitor effluent release
- Develop rapid response focused on water quality issues
- Develop rapid response to stranding events
- Reduce/cease new oil/gas leases
- Reduce microplastics and stormwater waste discharge
- Work with industry to use technologies to reduce noise
- Reduce shipping and seismic sound within the core area
- Restrict speed of vessels
- Maintain 500m distance – require lookouts/observers while in core
- Consider “areas to be avoided”
Monitoring recommendations
- Long-term spatial monitoring
- Long-term prey monitoring
- Electronic monitoring of commercial fishing operations
- Necropsies for pollution and contaminants
Outreach and Engagement are needed
Top Threats to Rice’s Whale from the workshop Include:
- Small population size – vessel collisons
- Noise
- Environmental pollutants
- Prey – Climate change – marine debris
- Entanglement – disease – health
- Offshore renewable energy development
The Endangered Species Act (ESA) requires the designation of critical habitat for listed species. In July 2023 NOAA proposed the area along the U.S. continental shelf between 100-400 meters depth as critical habitat. Comments on this designation were accepted through October 6, 2023.

The proposed protection zone for the Rice’s whale including the core area. Image: NOAA.
Vessel strikes are a top concern. It is understood that the most effective method of reducing them is to keep vessels and whales apart and reduce vessel speeds within the approved critical habitat.
On May 11, 2021, NOAA Fisheries received a petition submitted by five nongovernmental agencies and one public aquarium to establish a year-round 10-knot vessel speed limit in order the protect the Rice’s whale from vessel collisions. The petition included other vessel mitigation measures. On April 7, 2023, NOAA published a formal notice in the Federal Register initiating a 90-day comment period on this petition request. The comment period closed on July 6, 2023, and they received approximately 75,500 comments. After evaluating comments, and other information submitted, NOAA denied the petition on October 27, 2023.
NOAA concluded that fundamental conservation tasks, including finalizing the critical habitat designation, drafting a species recovery plan, and conducting a quantitative vessel risk assessment, are all needed before we consider vessel regulations. NOAA does support an education and outreach effort that would encourage voluntary protection measures before regulatory ones are developed.
On that note, the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) did issue voluntary precautionary measures the industry could adopt to help protect the Rice’s whale. These include:
- Training observers to reduce vessel collisions.
- Documenting and recording all transits for a three-year period.
- All vessels engaged in oil and gas, regardless of size, maintain no more than 10 knots and avoid the core area after dusk and before dawn.
- Maintain 500m (1700 feet) distance from all Rice’s whales.
- Use automatic identification system on all vessels 65’ or larger engaged in oil and gas.
- These suggestions would not apply if the crew/vessel are at safety risk.
So…
This is where the story is at the moment…
This is what is up with the Rice’s whale in the Gulf of Mexico.
We will provide updates as we hear about them.
References
1 An Overview of Protected Species in the Gulf of Mexico. NOAA Fisheries Service, Southeast Regional Office, Protected Resources Division. 2012. https://www.boem.gov/sites/default/files/oil-and-gas-energy-program/GOMR/NMFS-Protected-Species-In-GOM-Feb2012.pdf.
2 Rosel, P.E., Mullin, K.D. Cetacean Species in the Gulf of Mexico. DWH NRDA Marine Mammal Technical Working Group Report. National Marine Fisheries Service. Southeast Fisheries Science Center.
https://www.fws.gov/doiddata/dwh-ar-documents/876/DWH-AR0106040.pdf.
3 A New Species of Baleen Whale in the Gulf of Mexico. 2024. NOAA Fisheries News.
https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/feature-story/new-species-baleen-whale-gulf-mexico.
4 Rice’s Whale. NOAA Fisheries Species Directory.
https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/rices-whale.
5 Rice’s Whale. Marine Mammal Commission.
https://www.mmc.gov/priority-topics/species-of-concern/rices-whale/.
6 Rice’s Whale: Conservation & Management. NOAA Species Directory. 2024.
https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/rices-whale/conservation-management.
7 BOEM Issues Voluntary Precautionary Measures for Rice’s Whale in the Gulf of Mexico. 2023. U.S. Department of Interior. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management.
https://www.boem.gov/newsroom/notes-stakeholders/boem-issues-voluntary-precautionary-measures-rices-whale-gulf-mexico.
8 NOAA Fisheries Denies Petition to Establish a Mandatory Speed Limit and Other Vessel Mitigation Measures to Protect Endangered Rice’s Whales in the Gulf of Mexico. NOAA Fisheries News. FB23-079. Gulf of Mexico Fishery Bulletin. October 27, 2023.
https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/bulletin/noaa-fisheries-denies-petition-establish-mandatory-speed-limit-and-other-vessel-0#:~:text=NOAA%20Fisheries%20denied%20a%20petition,with%20rulemaking%20at%20this%20time..
9 Petition to Establish Vessel Speed Measures to Protect Rice’s Whale. NOAA Fisheries. Protected Resources and Actions.
https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/action/petition-establish-vessel-speed-measures-protect-rices-whale.
10 Denial of Gulf Protections Could Lead to the “Permanent Loss” of Rice’s Whale. Jim Turner. WUSF News. October 31, 2023.
https://www.wusf.org/environment/2023-10-31/denial-of-gulf-protections-could-lead-to-the-permanent-loss-of-rices-whales.

by Thomas Derbes II | May 3, 2024
I might shock a few people when I say this, but I’d rather be out in the bay somewhere rather than the beach. I just feel like I always bring a gallon of sand back on me even after washing down before getting in the car. However, there is one activity that will always get me out on the beach, and it just so happens to be the right time of the year for it. Florida Pompano (Trachinotus carolinus), aka Pompa-Yes, have started to cruise the white, sandy beaches in search of food as they migrate west to their breeding grounds. While out on a fishing trip this past weekend, the Pompano (and every other fish) eluded me, but I was blessed with an amazing array of wildlife.
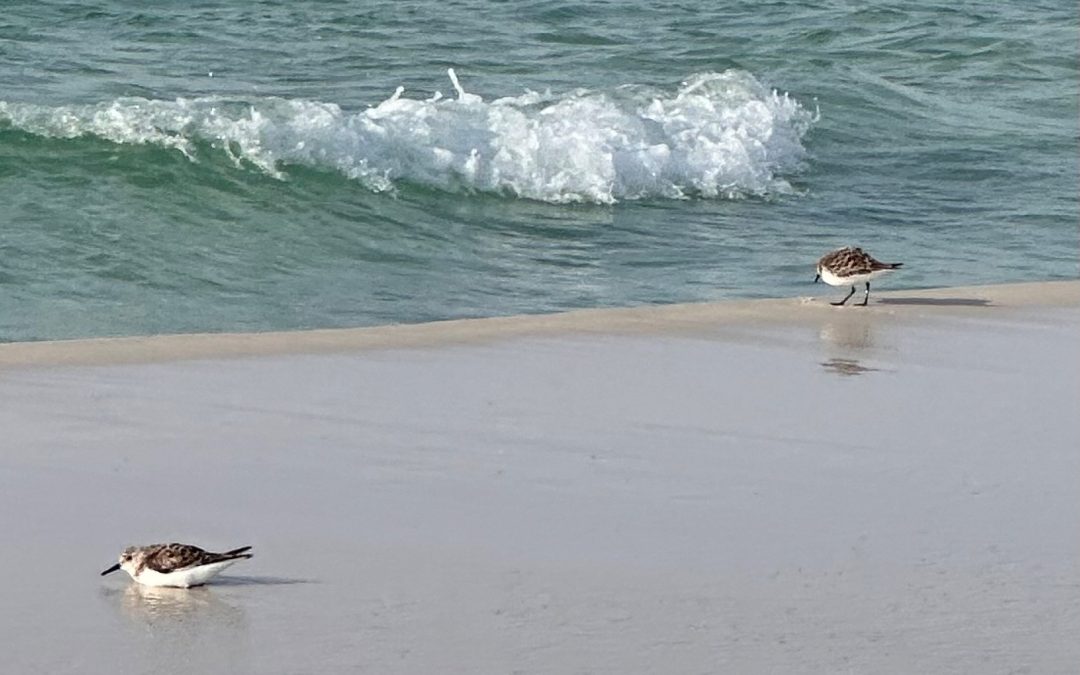
When I first arrived at my spot just to the east of Portofino Towers, I was greeted with a pair of Sanderlings (Calidris alba) playing the “water is lava” game while taking breaks between waves to argue with each other and probe the sand with their beaks from marine invertebrates. When I was doing more research on sanderlings, one comment I saw was that they ran like wind-up toys, and that’s the truth! They were pretty brave too, not a single footprint of mine in the wet sand didn’t go un-probed. Sanderlings are “extremely long-distance” migratory birds that breed on the arctic tundra close to the North Pole and winter on most of the sandy beaches in the Gulf of Mexico and around the world. Non-breeding sanderlings will often stay on sandy beaches throughout the summer to save energy. They were great entertainment for the whole fishing trip.
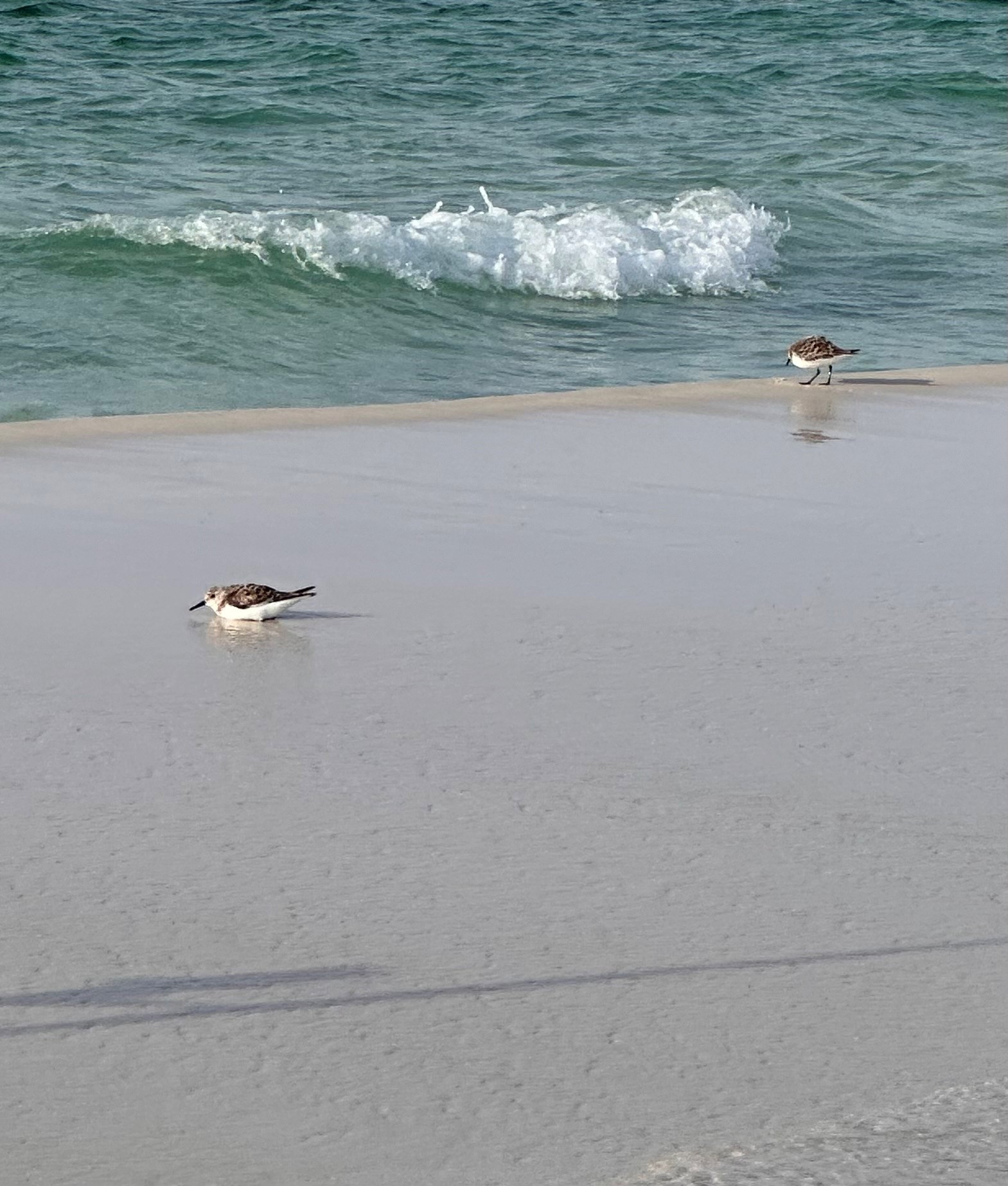

Sanderlings in the Tide Pool – Thomas Derbes II
Brown Pelicans (Pelecanus occidentalis) were out in numbers that day. I am not the best photographer, but I was very proud to capture a Pelican mid-flight. These birds are residents of the Florida Panhandle year-round. If you’ve ever been to Pensacola, you might have bumped into one of the many Pelican Statues around the area, and they’re pretty much the unofficial mascot of the area. I am always amazed at how these seemingly big, clumsy birds can effortlessly glide over the waves and water as if they are the Blue Angels doing a low-pass. Pelicans were almost wiped out by pesticide pollution in the 1960’s, but they have made an incredible comeback.
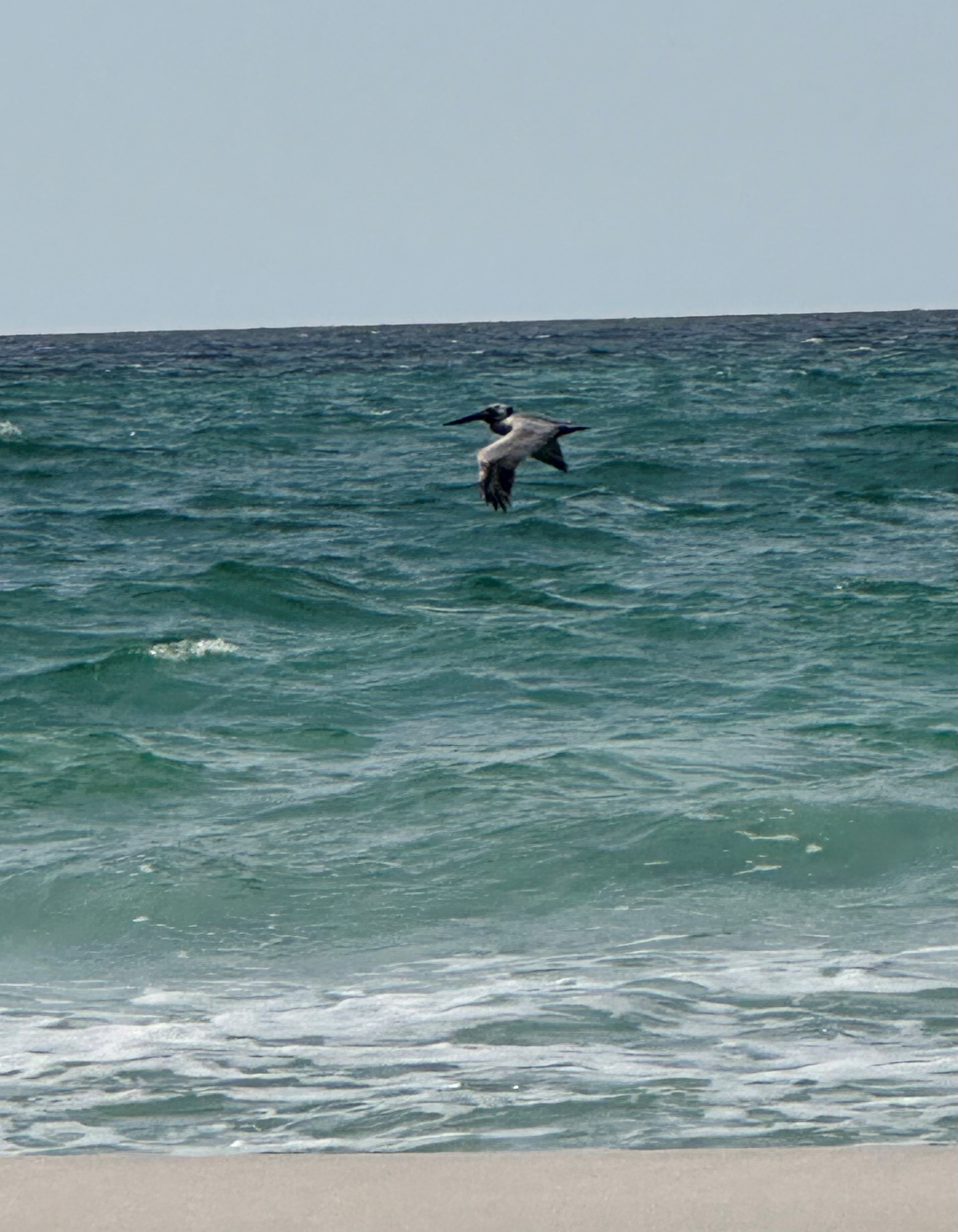

Brown Pelican – Thomas Derbes II
While I was waiting for a Pompano to bite, I had a visit from a small Atlantic Stingray (Dasyatis sabina) that was caught in the tidepool that was running along the beach. He didn’t seem injured or sick, so I quickly grabbed a glove and released him into the gulf. Stingrays are pretty incredible creatures and can get to massive sizes, but they do contain a large, venomous spine on their tail that poses a threat to beach goers. They are not aggressive however, and a simple remedy to make sure you don’t get hit is to do the “Stingray Shuffle” by shuffling your feet while you move in the water to scare up the stingrays.
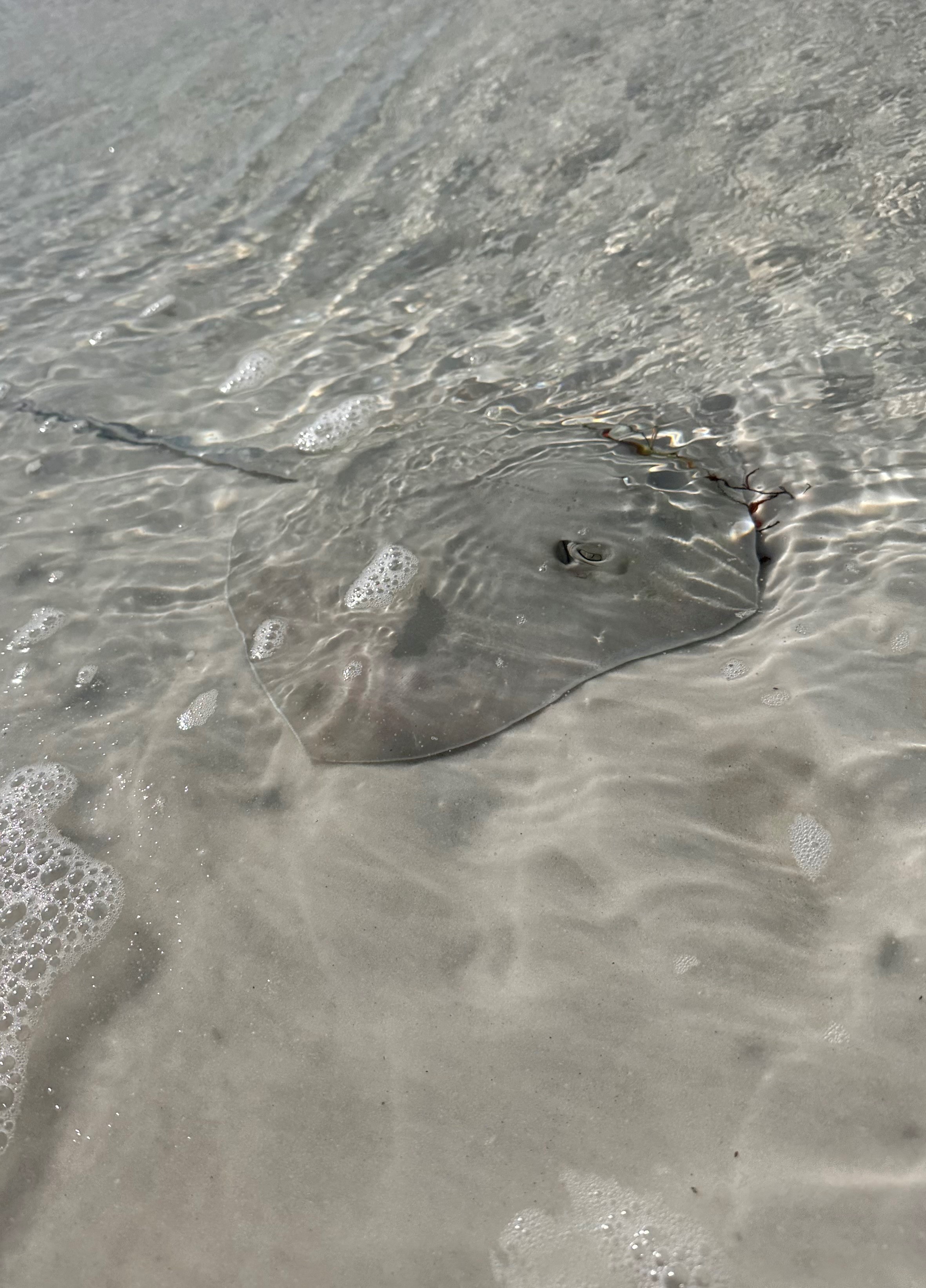

Atlantic Stingray Cruising the Tide Pool- Thomas Derbes II
As I was getting ready to pack up, I noticed a new shorebird flying in to investigate the seaweed that had washed up on shore. I had a hard time identifying this bird, but once I was able to see it in flight with its white stripe down the back, I realized it was a Ruddy Turnstone (Arenaria interpres). Turnstones get their name from their foraging behavior of turning over stones and pebbles to find food. Even though we do not have pebbles, the turnstone was looking through the seaweed for any insects or crustaceans that might be an easy meal. Turnstones are also “extremely long-distance” migratory birds breeding in the arctic tundra with non-breeding populations typically staying on sandy beaches during the summer. The turnstone made sure to stay away from me, but I was able to get a good photo of it as it ran from seaweed clump to clump.
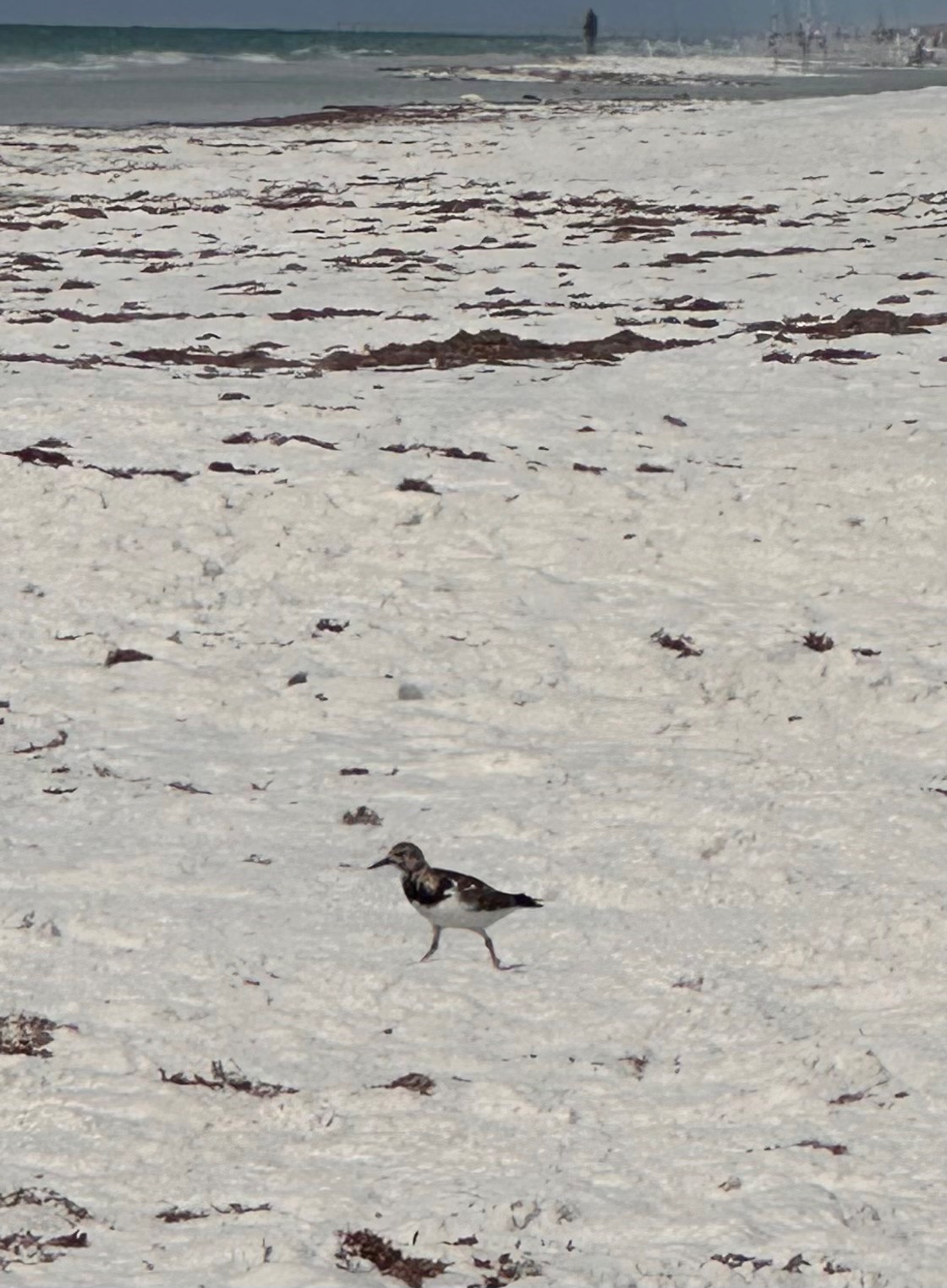

Ruddy Turnstone – Thomas Derbes II
While I didn’t catch anything to bring home for dinner, I did get to enjoy the beautiful day and playful wildlife that I wouldn’t have experienced sitting on a couch. You can turn any bad fishing day into an enjoyable day if you pay attention to the wildlife around you!



























