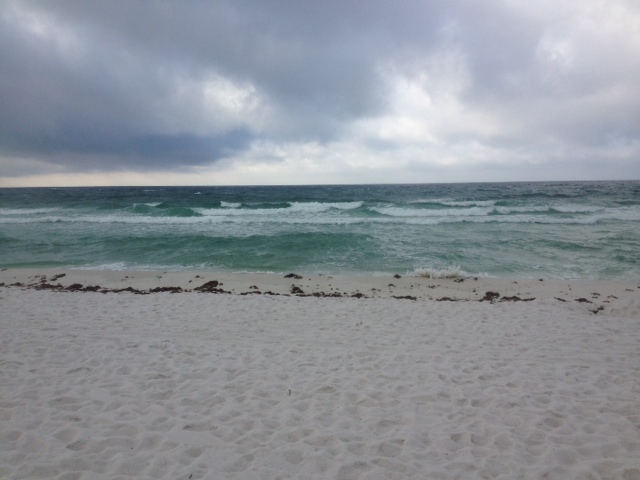

by Rick O'Connor | Apr 17, 2015
As we left the winter months and headed into spring I was expecting a lot of new blooms, new animal tracks, and more live encounters with wildlife… and then the rain began. I do not know if the entire panhandle has been getting what Pensacola has but the rain has been nonstop for over a week now. I track rain days for a water quality project and for the first three months of 2015 the number of days during a month where it rained was between 23-30%. We are about half way through April and so far it has rained 61% of the days. WELL… rain or shine we will make this hike and see what is happening on our barrier island.

Hole left by a sand castle architect. These can be problems for wildlife and rescue vehicles. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The first thing I noticed when I began the trip along the Gulf was this large hole left by a sand castle architect. These can be problematic for some forms of wildlife, including sea turtles, but they can also be a problem for rescue and turtle watch vehicles. Please enjoy the beach and make awesome sand castles, but when you are finished please fill the hole.

Sargassum is floating form of brown algae. Notice the “air bladders” (pneumatocyst) Photo: Rick O’Connor

A tropical seed commonly referred to as a sea bean. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The line of seaweed and debris along the surf zone is called wrack. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The line of seaweed and debris that washes ashore during storms is called the wrack. For the most part it is natural material and provides the nutrients needed for many of the high energy shoreline plants to grow. Many of the beach animals found in the berm and primary dune depend on this wrack as well. Many locals and visitors find this material and eye sore and, at times, producing an unpleasant odor. But this material is an important part of the beach ecology. Sargassum is a drifting member of the brown algae, sometimes called “gulfweed”. It possess small air bladder structures called pneumatocysts that allow it to remain at the surface of the open Gulf where the sunlight is. These large offshore mats of Sargassum have been targets for local fishermen for decades. Many small invertebrates live in these drifting mats and these are targets for small fish, which in turn are targets for even larger sport fish. They are also the hideaway for sea turtle hatchlings. When the little guys head for the Gulf after hatching this is where they are heading. Large ocean currents, including the Gulf Stream, push Sargassum into large mats in the middle of the open ocean. The area within the Atlantic where this happens in known as the Sargasso Sea. If you get a chance this summer, grab a small hand net and mask when the Sargassum is just offshore. Collecting you may find a lot of cool interesting creatures. Sea Beans is a generic word for a variety of tropical seeds that wash ashore in the northern Gulf. Some of these may sprout, including mangroves, but most will not make it through our winters.
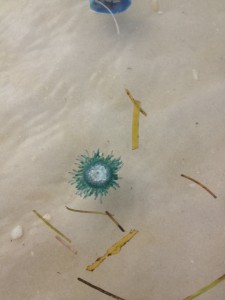
The Blue Button Jellyfish is a tropical cousin of the Portuguese man-of-war. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The Portuguese Man-of-War is one of the more venomous jellyfish in Florida waters. Photo: Rick O’Connor.

A variety of shorebirds utilize the wrack. Photo: Rick O’Connor
One of the more venomous jellyfish in Florida waters is now making its way onto our shores. The Portuguese man-of-war, named for the many “guns” this animal possess, is well known by locals but not so much by some of our visitors. The man-of-war is actually not one animal but a colony of sedentary polyp jellyfish that produce an inflated bag which floats at the surface carrying them across the sea. The dark blue tentacles hang down into the water column where passing fish are stung and consumed. Each of the polyps have connecting stomachs which helps move the food around to the whole colony. The sting of this jellyfish is quite painful and should be avoided. When they arrive life guards will usually fly a purple flag.
Their close cousins, the Blue Button Jelly, is very similar to the man-of-war albeit they are much smaller and the venom is not as potent. They are more tropical and not common along the northern Gulf but in recent years more have been washing ashore; they are here now.

A variety of plastics ends up in the Gulf. Each is a potential problem for marine life. Photo: Rick O’Connor

Pieces of plastic ribbon resemble jellyfish tentacles and are frequently consumed by sea turtles. Photo: Rick O’Connor
One of the bigger issues are oceans are facing are discarded plastics. These materials takes years to decompose and are found in all oceans and seas. Even some distant isolated islands have huge piles of this form of marine debris. Plastics can entangle marine organisms or they may actually swallow it, plugging their digestive system and eventually starving them. We encourage locals and visitors alike to help with this problem by taking your trash with you and discarding it in a location where it will not reach the Gulf.

This ephemeral pond formed around a small dune which becomes a temporary island. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The Chinese tallow is an invasive species the entire state is dealing with. Photo: Rick O’Connor
With the heavy rains of the last week ephemeral ponds have formed on parts of the island. These small pockets of freshwater can be “manna from heaven” for many island residents, particularly the amphibians. I have been hiking this section of Pensacola beach for years, leading field trips for all sorts of groups. I have never seen this Chinese Tallow until today. Also known as the “popcorn tree” due to its unique looking fruit, this plant is listed as an invasive in the state of Florida and is very aggressive. I did not see any others and will seek permission to remove it before it spreads to other dunes and out competes the native plants.

One of the few plants blooming in April, the Spiderwort is a common weed in many lawns. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The blossoms of Conradina first appeared in February. They are all but gone this time of year. Photo: Rick O’Connor
I was actually expecting more flowers to be in bloom this month but there were few. The Conradina, which have been in bloom since February, have lost most of its blossoms. The “new kids on the block” are the Spiderwort, the Primrose, the Sandhill Milkweed, and the Devil’s Joint Cactus.

There are a variety of primrose that grow on our barrier islands. They are beginning to bloom now. Photo: Rick O’Connor

New growth on a pine tree. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The Sandhill Milkweed. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The Sandhill Milkweed is one of the plants used by the monarch butterfly to gain fuel for their great flight across the Gulf to Mexico. The milky toxic sap of this plant is consumed by the monarch caterpillar but it does not harm it. The chemical toxins therefore become a defense for the monarch and the butterfly has earned the respect of many birds; though it may be a trial and error learning experience.

A decomposing log is a microhabitat for many organisms. Photo: Rick O’Connor

New growth on a live oak. Photo: Rick O’Connor
Most environmental centers, state and federal parks, leave fallen trees where they lie. The tree is actually a storage house of nutrients and full of cavities that can be used by a lot of organisms within the beach community.

The mysterious “drags” we have seen the last three months were not to be found in April. Photo: Rick O’Connor.

The beautiful yellow bloom of the Devil-Joint cactus. Photo: Rick O’Connor
This month the weather was warm enough for me to venture into the Salt Marsh. Salt marshes are wetlands but differ from swamps in that the dominate plants are grasses, not trees. Our local salt marsh is dominated by two species of grass, the Smooth Cordgrass, and the Black Needlerush. There are many other plants that exist here but these are the most common. This particular marsh is dominated by Black Needlerush. Salt marshes are one of the most productive systems on the planet, producing tons of organic material annually. 90% of the commercially valuable marine species spend part or all of their lives here. There are many unique species to this system as well. Today the water was crystal clear but I saw few fish. I expect as it gets warmer we will see more. It is very possible that with the heavy rains that they have moved to deeper, saltier spots in the Sound.

It’s warm enough to enter the salt marsh. Photo: Rick O’Connor

The marsh periwinkle is one of the more common mollusk found in our salt marsh. Photo: Rick O’Connor
The Marsh Periwinkle is an interesting guy. This snail will crawl up the stalks of marsh plants during high tide to avoid predators like blue crab and diamondback terrapins. Both of these predators appear to be on the decline and it will be interesting to see how this impacts the ecology of the marsh. At low tide the periwinkles descend and feed on the organic leaf litter on the muddy bottom.

This dewberry has flowered and the dark fruit will be ready next month. Photo: Rick O’Connor

Gracilaria is a common epiphytic red algae growing in our seagrass beds. Photo: Rick O’Connor

Black Needlerush is one of the two dominant plants of our salt marshes. Photo: Rick O’Connor
Though it has a white appearance, Gracilaria is a member of the red algae group. This algae grows on seagrasses as Spanish moss grows on oaks. The plant is usually kept in check by herbivorous grazers, such as green sea turtles, but in recent decades the number of predators have declined and the amount of nutrient runoff has increased. This has sparked a increase in the growth of this algae and, in some cases, to the determent of the seagrass itself.

This eroded pine tree gives evidence of the ever changing shorelines of our barrier islands. Photo: Rick O’Connor

This submerged mound of peat is the remnants of a salt marsh which is now below sea level. Photo: Rick O’Connor
These photos of peat and the eroded tree are indications of a changing shoreline. Due to storms, boat wake, and time, the shoreline of Santa Rosa Island, like all barrier islands, is changing. Peat is actually the remnants of an old salt marsh that has now pass the high tide line and is within the Sound.

Trash left behind by those enjoying the beach. Photo: Rick O’Connor

We encourage those who pack it in… to pack it out. Photo: Rick O’Connor
As the weather has warmed and spring break has fallen upon us I have noticed an increase in the amount of trash on this hike, both the Gulf of Sound sides. We encourage locals to take their trash with them and encourage visitors to do the same. Let’s try to keep our waste out of our waters.
I am expecting some animal nesting in May. We will see what we find. Until then.

by Rick O'Connor | Apr 10, 2015
The American Alligator is an icon in the state of Florida. Viewed on the program “Swamp People” and as the mascot of the University of Florida, most visitors to our state view this animal more on television than in the wild; but they are certainly there. In need of mates and calories from the lack of eating over the winter, alligators and other reptiles become more active this time of year. Visitors and residents alike should be a little more cautious.

Alligator basking on the Escambia River; photo: Molly O’Connor
Like most predators, alligators seek food that will provide them energy. Generally predators will target prey that will cost them very little energy to capture and kill. Obviously small alligators will feed on small prey but adult alligators feed on smaller prey than many think. Fish, turtles, snakes, small mammals and birds make up the bulk of their diet. If the opportunity presents itself, and they do not have to expend too much energy, alligators will certainly take larger mammals and birds.
For humans the bigger problem has been the loss of pets and livestock. Small dogs are certainly easier prey than a human, and with the loss of habitat encounters with humans and their pets have increased. Since 1948 FWC has estimated about 300 alligator attacks on humans directly, less than 10% of these were fatal. As more alligators are forced into suburban areas more encounters have occurred. In the last 10 years 16,000 nuisance alligator calls have been reported to the FWC. As with other wildlife, like coyotes, many of these animals are living in ditches and other watering holes where they seek fish and turtles. However if we visit such places, particularly with our pets, these animals may certainly make an attempt to grab them. If you feel an alligator is a nuisance and could be a potential problem you can call FWC at (866) FWC-GATOR; (866) 392-4286). Folks should be aware that FWC does not relocate nuisance alligators, they will be destroyed. Currently FWC issues about 7000 permits for alligator control across the state.
A couple of safety notes if you live near waterways with alligators.
- Do not swim in these locations at night; alligators are more active hunters between dusk and dawn
- Try to discard fish remains after cleaning in another location besides the water; if these locations have a few alligators they will certainly learn this habitat and hang around the boat ramp more.
- DO NOT FEED alligators; help us let visiting tourists know this and that it is illegal in our state. Alligators fed by humans will eventually lose their natural fear of us and this could bring on problems.
These are awesome animals. We should better understand their natural history so that we can exist with them. For more information on alligators in your area contact your county extension office.

by Rick O'Connor | Apr 10, 2015
These curious ancient animals have been roaming the waters of the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico for over 450 million years. Though they appear dangerous they are quite harmless and are actually more closely related to spiders and scorpions than crabs. Horseshoe crabs are not as common in Pensacola as they are in Panama City and Port St. Joe areas, but once were once found here and occasionally still are. Many coastal states have been concerned by the decline in their numbers. In the Chesapeake area where they were once very common, horseshoe crabs are harvested for their copper-based blood and also as bait for eel fishermen. The copper-based blood contains lysate which has been used to detect bacterial contamination in many drugs, as well as use for the diagnosis for some diseases.

The ancient horseshoe crab. Photo UF/IFAS Communications
Though there is a fishery for them in Florida, the issue with most locals is just the loss of a really neat animal that has been around longer than the dinosaurs,. This time of year, near the full moon, horseshoe crabs begin to gather near nesting beaches to mate and lay eggs. The Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission is asking locals and tourists who find a horseshoe crab to report it. They are interested in sightings of both adults and juveniles (less than 4” in length), the date seen, the time, the location, and type of habitat if possible. To report you can visit their website (www.MyFWC.com), email at FWRI@horseshoe@fwc.state.fl.us , or call 1-866-252-9326
If you have any questions contact your county Sea Grant Agent for more information.

by hollyober | Apr 8, 2015

Bats are extremely beneficial, but they can be unwelcome guests when they choose to roost indoors, like this evening bat. Photo credit: LeiLani Davis.
Bats typically sleep during the day in natural structures such as trees and caves. In areas with few natural roost structures, bats may instead choose to spend their days in buildings.
Bats are beneficial because each bat consumes hundreds of insects per night. Bats save farmers billions of dollars annually by substantially reducing the abundance of insect pests. However, they can be unwelcome guests when they choose to live in buildings. The safe, humane, effective way to coax a colony of bats out of a building permanently is through a process called an ‘exclusion’.
A bat exclusion is a process used to prevent bats from returning to a building once they have exited. It is accomplished by installing a temporary one-way door. This one-way door can take many forms, but the most tried-and-true is simply a sheet of heavy plastic mesh screening (with small mesh size) attached at the top and along both sides of the sheet, but open on the bottom. The one-way door should be attached over each of the suspected entry/exit points bats are using to get in and out of the building.
It is illegal to harm or kill bats in Florida, but exclusions from buildings are allowed if you follow practices recommended by the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC). According to Florida law, all bat exclusion devices must be left in place for a MINIMUM of 4 consecutive nights with temperatures above 50 o F before each entry point can be permanently sealed to prevent re-entry by bats. Also, it is unlawful in Florida to attempt to exclude bats from a building between April 15 and August 15, which is bat maternity season. This is when female bats form colonies and raise young that are unable to fly for their first few weeks of life. If bats were excluded during this time period, young bats (called pups) would die indoors.
For more information on how to conduct a bat exclusion, check out this video that features interviews with bat biologists from the University of Florida, FWC, and the Florida Bat Conservancy: How to Get Bats out of a Building.
For additional information on Florida’s bats, visit University of Florida’s bat advice or FWC’s bat website.
Remember, bat maternity season in Florida runs from April 15 to August 15. If you have a colony of bats roosting indoors that you want to exclude, you must either act quickly or else wait until the middle of August to coax them out.
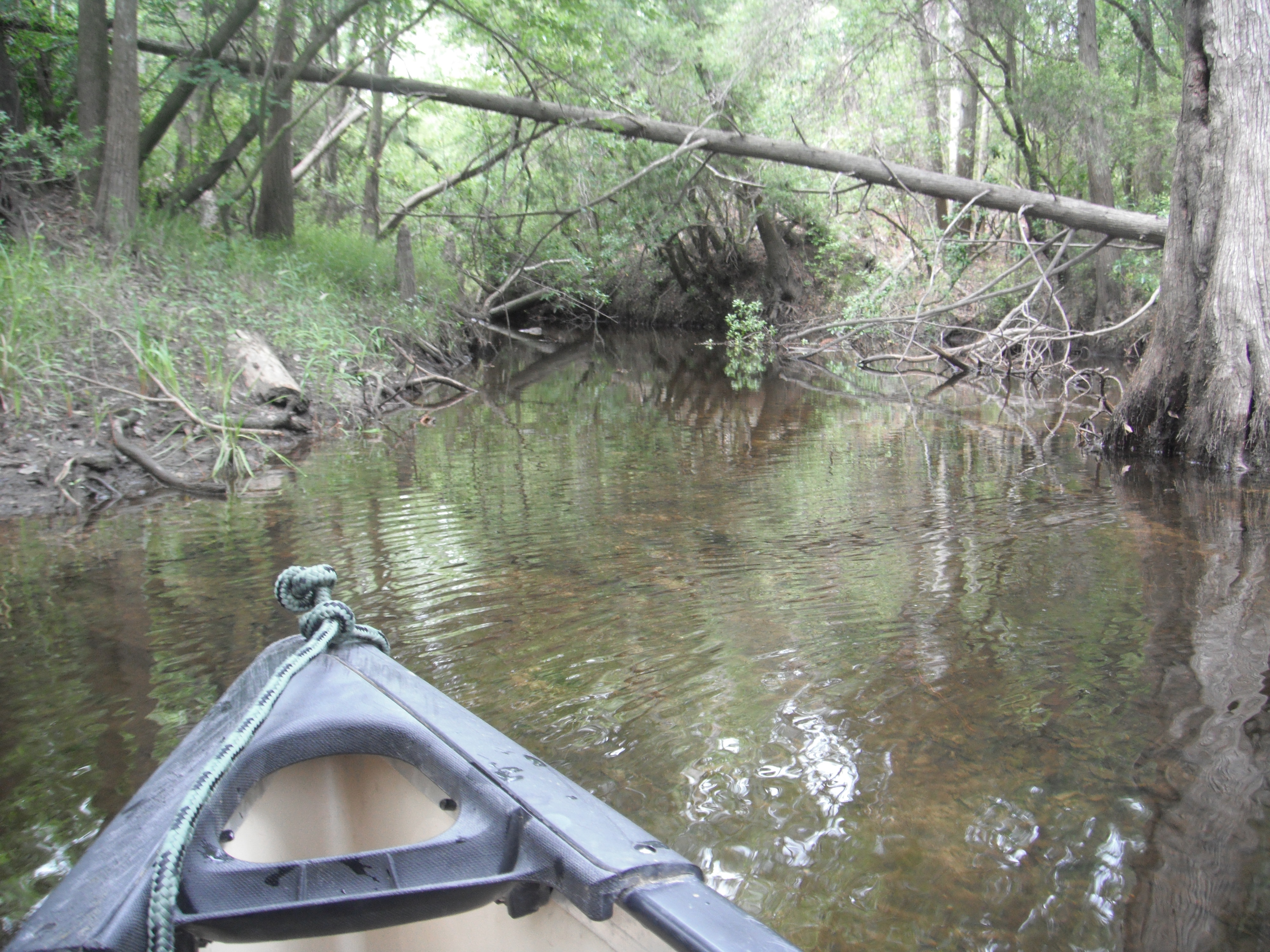

by Carrie Stevenson | Mar 27, 2015

Canoeing in Perdido River Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
This time of year, many families are looking for ways to entertain their kids during spring break. For those not planning to travel far, our area is full of fun, and often inexpensive, outdoor adventures.
As part of a series of field excursions led by Extension Agents over the past few years, we’ve been able to introduce visitors and lifelong residents of the panhandle to some tremendous natural resources that are right at our back door.
Following are three examples of family friendly trips worth marking off your “Florida bucket list.”
Perdido River: the natural border between Alabama and Florida, the Perdido stretches over 65 miles from its source near Atmore, Alabama and ends up at Perdido Key in the Gulf. Clean, clear, and sandy-bottomed, the Perdido River is a perfect spot to tube, kayak, canoe or paddleboard and several local outfitters can provide equipment. While on the river, you might experience a flyover from a bald eagle, see towering bald cypress, or explore shallow backwater springs and swamps.

Majestic bald cypress trees serve as wildlife habitat at Wakulla Springs State Park. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
Further east is Florida Caverns State Park in Marianna. This region is one of the most biodiverse in the state, with endemic tree species—like the Florida Torreya, found only in three counties in the state—along with many hardwood species found more typically in the central Appalachians. The extensive limestone cavern and spring systems in Jackson County are home to beautiful swimming/diving spots as well as the caverns. The ranger-led tours are excellent, as well as the hiking trails within the park grounds. The cave tour takes about an hour and is mildly strenuous. There are no tours on Tuesday or Wednesday, so keep this in mind when planning a visit.

The crystal clear springs of Wakulla are home to alligators and manatees. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson
At the edge of our district is Hollywood-famous Wakulla Springs. Film site for both “Tarzan” and “Creature from the Black Lagoon”, the spring teems with wildlife year-round. A guided tour via pontoon boat will bring you up close to manatees, alligators, ospreys, anhingas, and large herons. Hiking trails, a swimming hole, and the historic lodge and restaurant are open to visitors as well. The nearby Chipola River is also a beautiful spot to paddle.
Every county in the Florida panhandle has tremendous water resources, from the Gulf to inland rivers and even waterfalls. Take time to explore on your days off this spring!
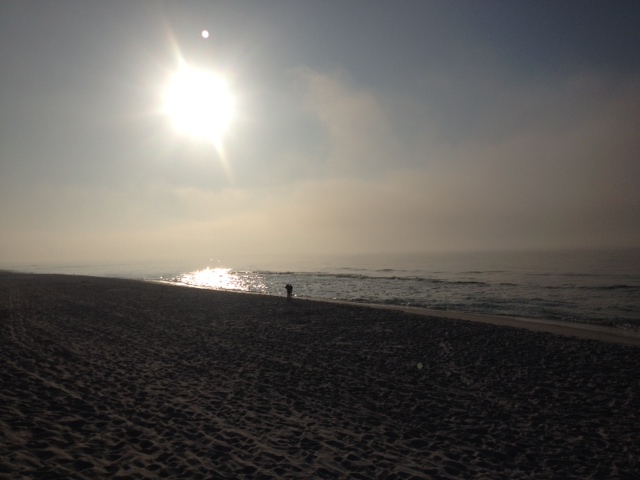

by Rick O'Connor | Mar 21, 2015
What many have been waiting for… spring is here! HAPPY EQUINOX EVERYONE!
Today’s photoperiod will be 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness – equinox. Many cultures around the world celebrate this and many ancient cultures built great structures to celebrate the event. It is also a time that many forms of plants and wildlife on our barrier islands begin to awaken and become more active.

The spring equinox sunrise over Santa Rosa Island, March 21

Fog rolling over the Gulf of Mexico in the early morning.
You might remember in our January edition of this series we showed the low angle of the sun over the Gulf on a January morning. Here we see the sunrise is slightly higher. The equinox is a special time of year for many. Moving form the cooler winter temperatures to the milder spring we typically will find water vapor condensing near the earth’s surface forming fog. This first morning of spring was no different. As the day warmed quickly the fog “burned off” producing a fabulous sunny warm day for all.

The spread toes of the opossum make identifying this track easier.

Armadillo digs are evidence of night time insect raid by this animal.
We did not see any live mammals moving across the dune fields but we did see plenty of tracks of the presence. We could identify at least 4 different types of creatures moving across the dune faces with all sorts of crossing patterns indicating these longer warner days have them moving. After lying dormant during the colder months it is time to find food, and for some, mates. Many of the mammals on the barrier islands are nocturnal in habit but may be spotted in the early mornings or late afternoons.

Tracks of an ATV moving across a dune face near the sound side of the island.

The mysterious unknown drag.
We were not sure whether this ATV track was from an official vehicle checking on something or from a local who did not want to walk all the way to the sound, but we would remind everyone that vehicles such as these are not allowed on the dunes and can cause much damage. I have been hiking this area for years and this is the first vehicle track I have seen in a long time. If you are interested in fishing the sound and can not access by boat, there are other locations on the island where the walk is much closer. Please consider walking there.
We once again we found the “mysterious drag” mark. Each month since I began this series we have found these drag marks near one of the salt marshes. Each time it appears that something has either crawled or has been dragged from the water to the top of a small sand ridge and then… abruptly stops. Not sure… have not been able to find claw marks, tail drags, etc. Just what you see in the photo above. We are going to find out though!

The bloom of a black berry.

The scarring of seagrass but a propeller.
For early spring we did not see many blooming plants. Last month the beach heather (Conradina) began to bloom, and much of it was in full bloom this month, but the only other bloom we found was that of the dewberry, called blackberry by many locals. This plant will eventually produce sweet berries which is enjoyed by many animals on the barrier islands… including hikers.
Prop scars are a common site during the summer months and the fact that we saw several today indicate that many are “itching” to get their boats out and enjoy our bay. Prop scars are problem though. Seagrasses are an important ecosystem in our local estuaries. They provide food and shelter for a great variety of marine creatures including commercial important ones. In general seagrasses have declined in our state over the last few decades. Causes include increased turbidity, decrease in salinity, increase in sedimentation (all caused by increase runoff), and damage such as prop scarring. Many of lawn grasses can grow after being mowed too low but they are, at times stressed and take time to recover. This is the case with some species of seagrass. Turtle grass, one of the more common found in our sound, can take several years to recover from severe scarring. We know that boaters want to “bring her up on the beach” for a day in the sand and sun, but avoiding seagrass beds when doing so benefits the local marine life.

The burrows of fiddler crabs.

The crown conch.
On this early spring morning we did not find a lot of wildlife moving in and near the salt marshes. Gone were the cannonball jellies we had seen in the winter and there were no dead fish from cold stress on the beach. We did find the burrows of the common fiddler crab. These small crustacean digs burrows down to the water table where they end in a chamber. These chambers are half filled with water and keep their gill chambers moist. During high tide the fiddler crab will block the entrance of the burrow with sand and wait it out down in the chamber. When low tide arrives they emerge to feed on organic material within the sand, forming round pellets that resemble coco-puffs, and socialize. Fiddler crabs are very social and form large groups which remind one of the great herds of buffalo on the plains of the 19th century. The males have one claw (cheliped) larger than another. They use this to “wave” at the females and rub their legs to generate sounds to attract her. They use their small cheliped for feeding. They are popular prey item for creatures like shorebirds, fish (if they venture into the water), raccoons, and terrapins.
The Crown Conch is a common predator of our bays and bayous. This snail prefers higher salinities of 20 – 30 parts per thousand, which keeps them in the lower parts of our estuary, but there they are quite common. This time of year they begin moving along the shallow waters of grassbeds and salt marshes searching for other mollusk to feed on, they will also scavenge dead organisms. There are separate males and females in this snail who produce a linear string of egg capsules which they attach to seagrass, roots, rocks, or some other structure. They have their own predators, such as horse conch, who lurk in the deeper waters of the sound. Their scientific name, Melongena corona, describes their “crown” they appear to have. These can reach lengths of 8″ but most are much smaller. The larger ones are known to be cannibals.

Evidence of dogs on the beach.
The last thing we found on this first day of spring was evidence of dogs running the beach. Many people are dog lovers, including me, and there are areas on the island where dogs can enjoy the sand and surf. However they are not allowed on all beaches. There are several problems with dogs on the beach. One their feces, like all feces, harbors bacteria and piles such as this can easily be washed into the water. Increase in fecal coliform bacteria in the water column can be a health concern. Dogs outside of the areas where they are allowed can kill island wildlife. This time of year many species of shorebirds begin nesting on the sands of these beaches. Dogs in the area can cause the parents to fly off the nest leaving the eggs (or hatchlings) exposed to predators and extreme temperature changes. Many of our island shorebirds are protected species and need our help to assure as many young as possible survive. Finally, there will be other families following you… who wish to set up chairs and towels and have their kids play in the water and sand… they really do not want to encounter this. So please let you pet enjoy the beach but in areas where they allow it.
We will see what April brings to the beach.



















































