
by Molly Jameson | Jul 23, 2020

Join us via Zoom on Saturday, August 8, for our Leon County Seed Library Virtual Workshop. Graphic by Molly Jameson.
Leon County’s Seed Library Program Continues On
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed many aspects of our lives. In Extension, we have learned new ways to be innovative in our programs, and we have made adaptations to continue to reach the community through technology. While these technologies have allowed us the opportunity to connect with clientele and continue to allow important discussions related to the life sciences, there is no substitute for hands-on learning.
For this reason, I am thankful that the Leroy Collins Leon County Public Library System is proceeding with the Leon County Seed Library Program this fall. Since the spring of 2015, the Leon County Public Library has provided Leon County community members with sample vegetable seed packets to take home and plant in their gardens. While many aspects of the Seed Library Program will be altered this season, seeds will still be available to be “checked-out” from all Leon County library branches.

While face coverings and other safety precautions will be required, Leon County residents can still “check-out” seeds starting August 8. Photo by the Leon County Public Library.
As we continue to strive to keep ourselves and our community safe, many of us have used gardening as a way to relax and find some peace during these turbulent times. Planting vegetable seeds is a great way to learn about agriculture and our natural environment and gives us an opportunity to spend some time outdoors.
As an Extension Agent in Leon County, I have had the pleasure of partnering with the Leon County Library to help pick out the Seed Library Program seed selections, plan kickoff events, and provide hands-on workshops at various library branches. While “checking-out” seeds at the library this season will be a socially distanced activity, we still want to provide an opportunity for the community to engage with UF/IFAS Extension and learn about planting seeds, growing vegetables, and how to incorporate vegetables into snacks and meals to stay healthy.
Whether you are located in Leon County or not, everyone is welcome to join us Saturday, August 8, from 10:00 a.m. to 12:00 p.m., our Leon County Seed Library Virtual Workshop. Via Zoom, agents with UF/IFAS Extension Leon County will discuss vegetable gardening techniques and the importance of eating healthfully. We will also be doing a live virtual cooking demonstration featuring vegetables available in the Fall 2020 Seed Library Program.
For more information about the Leon County Seed Library Virtual Workshop, please visit our Eventbrite page: https://seedlibraryworkshop2020.eventbrite.com. There is no cost to attend the workshop, but registration is required.
If you are a resident of Leon County, all you need is your Leon County library card to check-out the vegetable seeds. Don’t have a library card? No problem! Leon County residents can apply online at the LeRoy Collins Leon County Public Library online card application page here: https://lcpl.ent.sirsi.net/custom/web/registration/.
Here is the list of the vegetable seeds that will be available starting August 8: Calabrese Broccoli, Cosmic Purple Carrots, Georgia Green Collards, Lacinato Kale, Buttercrunch Bibb Lettuce, Giant of Italy Parsley, Easter Egg Radishes, and Silverbeet Swiss Chard.

by Sheila Dunning | Jul 16, 2020
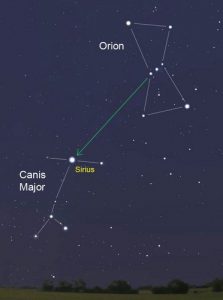
Dog Star nights Astro Bob
The “Dog Days” are the hottest, muggiest days of summer. In the northern hemisphere, they usually fall between early July and early September. The actual dates vary greatly from region to region, depending on latitude and climate. Life is so uncertain right now. But, fall is coming.
In ancient times, when the night sky was not obscured by artificial lights, the Romans used the stars to keep track of the seasons. The brightest constellation, Canis Major (Large Dog), includes the “dog star”, Sirius. In the summer, Sirius used to rise and set with the sun, leading the ancient Romans to believe that it added heat to the sun. Although the period between July 3 and August 11 is typically the warmest period of the summer, the heat is not due to the added radiation from a far-away star, regardless of its brightness. The heat of summer is a direct result of the earth’s tilt.
Spending time outdoors this time of year is uncomfortable, potentially dangerous, due to the intense heat. However, the chinch bugs are very active in St. Augustine grass (for more information: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/lh036), and the summer flowers need water. So, take care of those tasks early in the day and then retreat to the air conditioning to plan your fall planting.
Plant tomato plants in August for fruit in October. Varieties such as Phoenix, Florida 91, Solar Set and Heat Wave II are good selections for setting fruit in high temperatures, should summer temperatures continue. Otherwise, try some of the newer UF/IFAS recommended varieties for fall planting in North Florida such as Bella Rosa, Tribute or Finishline. For more information on tomato selection refer to: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in756. For information on other vegetables for fall gardening refer to the Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vh021.
Many bedding plants flower quickly and can add color to the fall landscape. These include pentas, African marigolds, torenia, zinnias, melampodium and scaevola. Other can be planted in October for blooms all

Hummingbird at Firespike flower
winter-long. Plan spaces and color themes for calendulas, pansies, snapdragons and violas. Add in ornamental cabbage or kale and some dusty miller to accent the garden. They too will perform through the cold. For more information on Annuals for the Florida Garden refer to: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/mg319.
Dependable fall blooming perennials include lion’s ear (Leonotis leonurus), pineapple sage (Salvia elegans), firebush (Hamelia patens), cigar plant (Cuphea micropetala), yellowbells (Tecoma stans) and firespike
(Odontonema strictum). Also, garden mums (Chrysanthemum sp.) and many different Irises will add color again in the spring. To gain information on perennials for Florida refer to: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/mg035.
Webster’s second definition of “dog days” is a period of stagnation or inactivity. But, even when the heat forces you to slow down on the labor-intensive work, there is plenty of gardening “activity” to do. Stay in the air conditioning and plan that spectacular fall and winter yard.

by Ray Bodrey | Jul 1, 2020
Sunflowers, Helianthus spp., are a great choice for gardeners who are looking for some cheerful color in their landscape. Here in Florida, we have the main ingredient for success, lots of sunshine!

‘Skyscraper’ Sunflower bloom. Photo courtesy of Ray Bodrey.
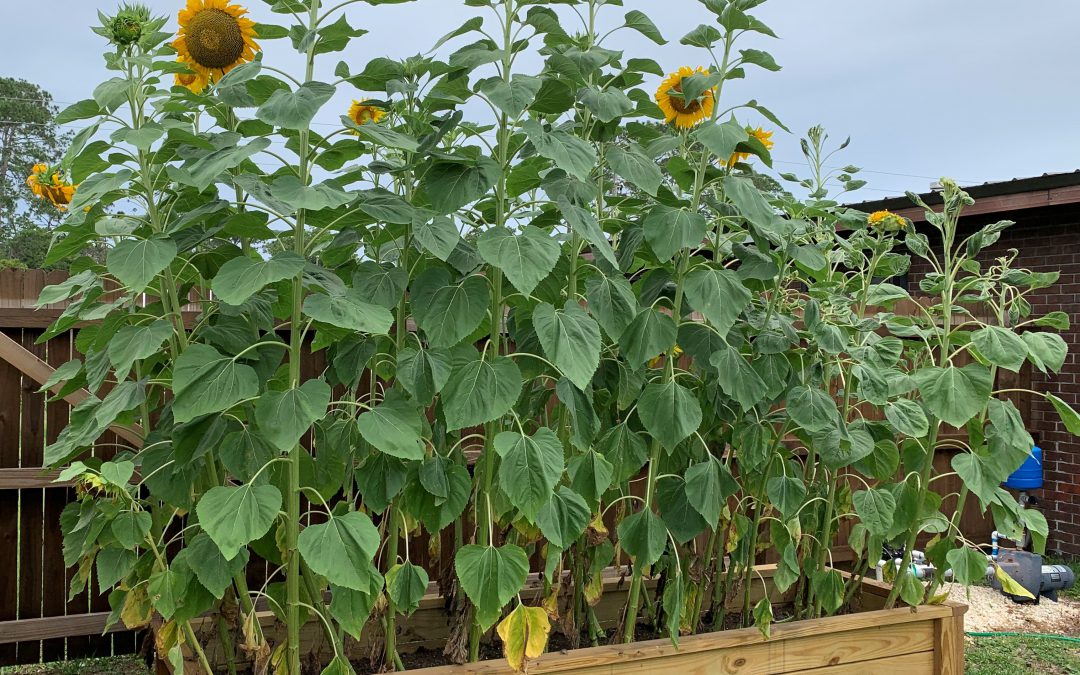
Sunflowers are short-lived annuals. The average time between planting and bloom is roughly 65 days. You can typically plant sunflowers in Florida beginning in late winter until early fall. Only the coldest months cause problems, and for most years that’s only November – January. Sunflowers can be planted almost anywhere there is full sun. The major selling point with sunflowers is, of course, the impressive blooms (figure 1). These yellow to sometimes orange or red-petaled flowers develop a central seed disc, with most variety’s flowers having approximately an 8” diameter.
When planting, you may choose to plant in narrow rows with close seed spacing in order to cull weaker plants later. A final row and seed spacing of 2’-3’ is recommended for full height and development of most varieties. However, you may also choose to plant in a bed, using a close pattern as seen in the photo below. In any event, sunflowers are easy to propagate by seed and are very low maintenance. Occasionally, powdery mildew and spittle bugs can be a nuisance. A general garden fungicide and insecticide will help if problems occur.

‘Skyscraper’ sunflowers planted on close spacing. Photo courtesy Ray Bodrey.
Sunflowers are available in many varieties, consisting of different color blooms and plant sizes. These sizes range from dwarf (1’-3’) to tall (10’-15’) varieties. You may wish to stake taller varieties at some point, as plants will tend to lean with no wind break in place. Here’s a few garden variety common names to look for: ‘Sunbright’, ‘Sonja’, ‘Sunrich Lemon’, ‘Sunrich Orange’ and ‘Autumn beauty’. Seed companies also have mixes available in packets. For tall plants, ‘Mammoth’ or ‘Skyscraper’ varieties will do the trick.
If you are fond of the sunflower bloom and looking for a groundcover, there are a couple of native perennials that fit this category. Beach sunflower, Helianthus debilis or swamp sunflower, Helianthus angustifolius, are groundcovers/ornamentals for landscapes and thrive in dry, hot climates and in a range of soil types. They also are great pollinator attractors.
For more information on growing sunflowers, contact your local county extension office.
Supporting information for this article and links to other publications on sunflowers can be found at the UF/IFAS Gardening Solutions website: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/ornamentals/sunflowers.html
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Jan 23, 2020
Cruciferous vegetables, mostly cool-season annuals in the Brassicaceae (formerly Cruciferae) family, are part of a healthy diet, prized for their high fiber content and unique sulfur-containing compounds known as glucosinolates. This vegetable family includes things many of us love (or love to hate) like Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, collards, kale, mustard, turnips, bok choy, and Chinese cabbage. They’re also commonly grown in Panhandle gardens. However, as anyone who has grown these species knows, some are easier than others. For example, kale and radish are among the easiest of all plants to grow. But get beyond the basics and folks often run into difficulty with species like broccoli and cabbage. The high rainfall/humidity and frequent warm spells experienced here during the growing season often lead to serious pathogen problems, dooming my garden in years past. However, this winter, thanks to a couple of new cultivars, ‘Capture’ Cabbage and ‘Burgundy’ Sprouting Broccoli, I’ve enjoyed a plentiful supply of tasty crucifers!

4’x 8′ raised bed planted with ‘Capture’ on 24″ centers.
‘Capture’ Cabbage, developed by Bejo Seeds of California as a mid-season “white” fresh market cabbage for the South, has been an outstanding performer in my garden this year. Touted as highly resistant to Black Rot and Fusarium Yellows (by far the two most devastating pathogens of Cabbage), I had to try it for myself. I planted seeds 24” apart in my standard 4’ wide x 8’ long x 12” deep raised beds filled with mushroom compost and aged pine bark. Seedlings were fertilized once about three weeks after germination with a general purpose 10-10-10 fertilizer. The plants that developed have been extremely vigorous (I’m glad I paid attention to plant spacing guidelines on the seed packet!) and have not shown ANY evidence of disease, even through an unusually warm and wet winter that would have hammered older susceptible varieties. My plants have begun to develop heads and should be ready for harvest and the kitchen in just a couple more weeks! If you’ve had problems getting a cabbage from germination to head formation and harvest without serious disease pressure, give ‘Capture’ a try next fall!

‘Burgundy’ Broccoli in the author’s raised bed garden.
‘Burgundy’ Broccoli, developed by Elsom Seeds in the United Kingdom, is a unique variety sure to turn heads in your garden. True to its name, the prolific florets are a deep, purple color. Though the central “head” on ‘Burgundy’ is quite small, that’s not the primary feature anyway. Considered a “sprouting” broccoli, this cultivar puts out an abundance of side shoots that make ‘Burgundy’ sort of a cut-and-come-again broccoli, allowing for a long harvest window. Another advantage from a disease avoidance perspective is the short maturity time (the time from planting seeds to having harvestable shoots) of around 40 days! For perspective, a “regular” heading broccoli has a maturity of around 60 day, lots more time for problems to happen. In the same growing conditions described above for cabbage, ‘Burgundy’ performed amazingly well for me, growing strong, healthy stalks, large, unblemished leaves and an abundance of purple shoots with a nice flavor profile!
If you want to enjoy homegrown broccoli and cabbage but disease pressures have made your previous efforts unproductive, give ‘Capture’ Cabbage and ‘Burgundy’ Broccoli a try! These two selections have made it easier than ever to enjoy unique, homegrown, healthy cruciferous veggies. Keep these and other quality, disease-resistant cultivars in mind when planning your winter garden in 2020!

by Larry Williams | Dec 4, 2019

Fall oak tree leaves abound and can be recycled as landscape mulch. Photo credit: Larry Williams
Weed control is not top on my list as a reason to use mulch. There are weeds that can push through mulch such as nutsedge (nutgrass) or that can germinate and grow in the mulch. But done correctly, mulching plant beds and gardens can help inhibit some weeds. Tree leaves can be used as a mulch.
In addition to weed control, mulch provides other benefits. It can make landscapes look more attractive. It keeps roots evenly moist, acts to insulate roots from extreme heat and cold and can help decrease loss of soil from wind and water erosion. Mulch serves as a barrier to some soil-borne diseases, especially in the vegetable garden. And, as organic mulch breaks down, it improves the soil’s fertility, aeration, structure and drainage.
Tree leaves make good mulch. They can be placed on the soil surface beneath and around shrubs, trees, perennials, annuals and vegetables.
Fall leaves are abundant. Some people feel overwhelmed by the volume. One resident reported raking more than 100 large bags of leaves from his half-acre property. One large oak tree can contain over 250,000 leaves!
Tree leaves can be placed in landscape beds or around vegetables “as is” or chopped up with a shredder or mower into smaller pieces and then spread around vegetables, shrubs and trees. Mixing leaves from several different species of trees can make better leaf mulch. Leaves of the same size tend to mat together and produce a shingling effect that can shed water and reduce gas exchange in the soil. Shredded leaves stay seated better on the landscape than whole leaves.
A mulch layer three inches deep after settling is enough for most plants. If possible, extend the mulched areas out to the outermost leaves (called the drip line) and beyond. And be sure to pull the mulch back a few inches from the main trunk. Never pile mulch around the trunk.
Using those fallen tree leaves as mulch recycles a natural resource and saves you money, enriches your soil, fertilizes your plants and keeps them out of the local landfill.
So, instead of putting all those leaves curbside in plastic bags to be hauled off, use them to benefit your landscape, which may include less weeds.
For additional information on landscape/garden mulch, contact the UF/IFAS Extension Office in your County or access the following sites.
http://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/care/planting/mulch.html
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/topic_mulch

by Matthew Orwat | Sep 17, 2019

Fall Pruned Azalea. Image Credit Matthew Orwat
Although Northwest Florida is well known for its beautiful Azalea displays every spring, many do not understand that these shows of bloom could be sacrificed completely by pruning at the wrong time.
Pruning Azaleas in the fall will result in a loss of spring bloom the following spring, since flower buds are initialized on previous year’s growth for most azalea cultivars.This means that they flower on growth put on throughout the previous growing season. If a gardener removes the previous season’s new growth, they are removing the blooms as well.
So, when is the proper time to prune Azaleas? The ideal time to prune is directly after the spring bloom. This will give the plant enough time to generate abundant new growth, thus maximizing bloom next spring. One might think that when growing the repeat blooming Encore azaleas, pruning time doesn’t matter. Should the need arise to prune these compact, repeat blooming shrubs the optimal time is directly after spring bloom and not after the final fall bloom cycle.
For more information on pruning Azaleas or on general Azalea culture, please read the UF / IFAS publication Azaleas at a Glance or check out the Pruning Azalea page on Gardening Solutions.















