
by Larry Williams | Jan 14, 2019

Ice on Satsuma fruit from January 2014 ice storm in Crestview, FL. Photo credit: Larry Williams
Northwest Florida winters can be a rollercoaster ride of temperatures. One week it dips to freezing for a short time and the next week it rises to spring-like temperatures. We need to hold on for this ride of up and down temperatures but not over react too soon.
Following the sudden ride down to the lower temperatures, we may think winter is over. But we don’t see the next drop in temperatures that’s coming, as we are experiencing the ride upwards in temperatures.
On average, it’s not until we reach mid-March that we expect our last killing frost. A killing frost is heavy enough to kill tender plant growth. And, we can have light frosts well into the latter part of March and into early April. This is particularly true in the more northern portions of our Panhandle Counties.
The main point is to not get spring fever too early and encourage new plant growth by pruning or fertilizing too soon.
When landscape plants freeze, the first impulse may be to get out the pruning shears and cut away dead and dying leaves and branches. But this isn’t a good idea. Pruning can force new tender growth that is more likely to be injured by the next freeze. And, you can’t tell how much damage has been done until plants start new growth in spring. If you prune immediately after a freeze, you may cut away live wood that doesn’t have to be lost. Also, leaves and branches, which have been killed, can help protect the rest of a plant

Cold injury to lawn that happened March 31 in Crestview, FL. Photo credit: Larry Williams
against further cold injury.
Some people want to “jump start” their lawns before our weather will allow our grasses to grow. Waiting allows for more efficient use of the lawn fertilizer. You will not injury your lawn by
waiting but you can certainly injure your lawn by fertilizing too early.
So, have patience, allow your lawn to green up on its own and then fertilize, even if it’s not until April or May.
Finally, be a little philosophical. If you do lose one or two of your tender ornamentals, so what? Worse things could happen. And now you have a chance to add something new, perhaps some species native to our area that are not as subject to cold damage.
Even with this winter/spring rollercoaster ride, with thousands of plants to choose from and a generally mild climate, who can complain?

by Julie McConnell | Sep 25, 2018
Finding professional landscape services for your home or business can be difficult. Unlike many skilled trades in Florida, landscapers/groundskeepers are mostly unregulated. No state exams exist to determine mastery of the basic skills required to perform lawn or landscape maintenance. Ultimately, consumers are left on their own to determine who to hire.
As UF/IFAS Extension Agents, we cannot endorse or provide referrals to companies; however, we can offer some guidance to help you with your search for qualified professionals.
- Be an informed consumer. You don’t have to be an expert in landscapes. Instead you should have an idea of what you envision for your landscape. Familiarize yourself with the type of turf grass and plants you want and learn what the basic maintenance is for their upkeep.
The Florida Friendly Landscaping™ program is a great place to start. Most Extension offices have free books on how to care for Florida landscapes. Or you can find online resources at www.deactivated_site
- Fertilizer and pesticide applications DO require state certifications.

Commercial landscape fertilizer applicators must obtain state certification.
- Fertilizer applicators for hire must maintain the Limited Urban Fertilizer Applicator Certification (Chapter 482.1562, Florida Statutes). Each applicator must have an individual certification. No one can “work under” another applicator’s certificate.
- Pesticide applicators (any substance applied with the intent to kill or inhibit growth of weeds, insects, nematodes, fungi, bacteria, etc.) have two options depending on application site and qualifications.
- Residential or commercial building turf pesticide applicators must hold the Commercial Lawn & Ornamental Pest Control License or be a current Employee Cardholder of the Certified Pest Control Operator
- Residential or commercial ornamental beds (trees, shrubs, flowers) pesticide applicators can hold either Commercial Lawn & Ornamental, as above, or Limited Commercial Landscape Maintenance Certification
- You can check to see if the applicator has a current certification by visiting http://aessearch.freshfromflorida.com/PersonSearch.asp You must enter the applicator’s legal name (name listed on his driver’s license, no nicknames) or their certification number (this will start with two letters)
- Ask about affiliations with professional organizations. Although landscapers are not required to obtain state certifications (excluding fertilizer and pesticide applicators), many take the extra steps to increase knowledge and keep up with industry standards and trends. Voluntary participation in organizations such as Florida Pest Management Association (FPMA), Florida Nursery, Growers and Landscape Association (FNGLA), Florida Turfgrass Association (FTGA), Tree Care Industry Association (TCIA), International Association of Arboriculture (ISA), etc. Some of these groups offer certification programs for professionals to help them increase knowledge.
- Word of mouth/observation. If you see a landscape that looks good, ask who they use and if they are pleased with their service. Talk to friends and colleagues for recommendations.
- Check references. Always ask for references and contact them. Yes, they may only give you the names of happy clients, but you can still ask questions to get a feel for the type of service offered and assess the longevity of the company.
Landscape professionals looking for certification classes should visit Green Industries in the Panhandle Upcoming Events page. 
by Matt Lollar | Feb 14, 2018
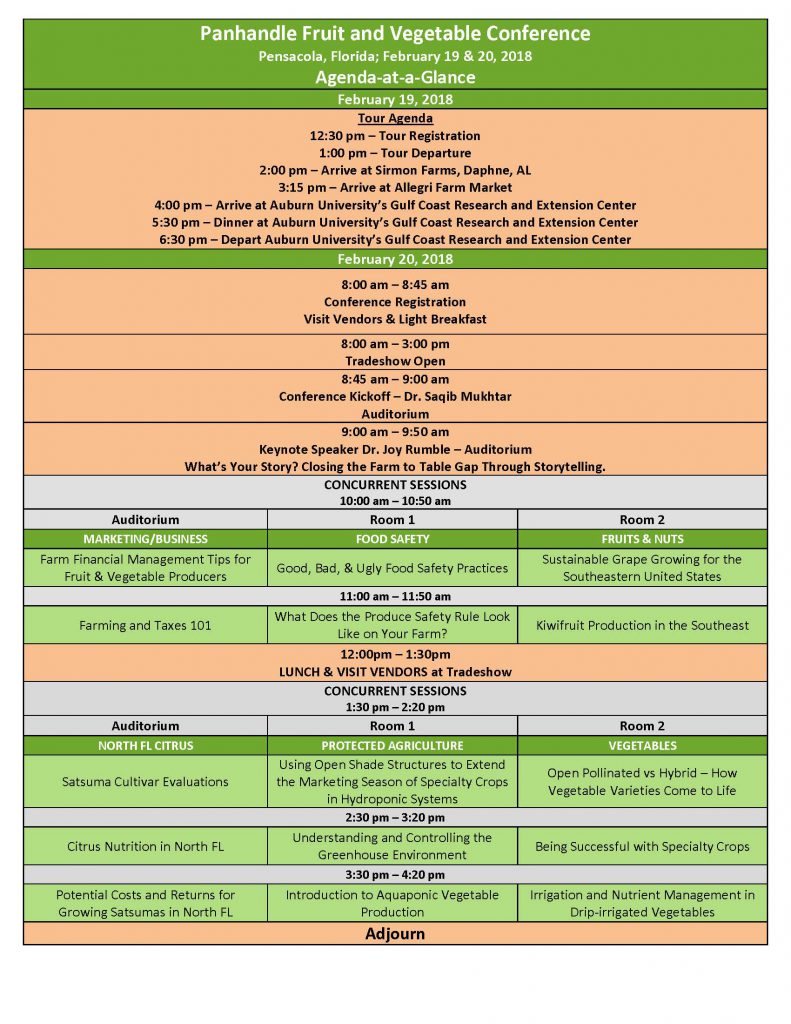
Register today for the 2018 Panhandle Fruit & Vegetable Conference! The Panhandle Fruit & Vegetable Conference is scheduled for February 19th & 20th. On the 19th we will go on an afternoon farm tour in Baldwin County, AL that will end with dinner (included) at Auburn University’s Gulf Coast Research and Extension Center in Fairhope. Educational sessions with guest speakers from University of Florida, Auburn University, and Texas A&M University will be held on February 20th where topics will include Citrus Production, Vegetable Production, Protected Ag Production, Marketing/Business, Food Safety, and Fruit & Nut Production. A full list of topics can be found here. Fifty dollars (plus $4.84 processing fee) covers the tour and dinner on the 19th and educational sessions, breakfast, and lunch on the 20th! The complete agenda is now available. Use your mouse or finger to “click” on the image below for full screen viewing.
Make sure to register by Wednesday, February 14th! – Registration Link

by Mary Salinas | Aug 25, 2017
After you have chosen the right fertilizer, fungicide, herbicide or insecticide to apply to your landscape, the question becomes: how much do I buy? Labels on these products will tell you how many square feet it will cover – so that leads to the next question: how many square feet of lawn do I have?
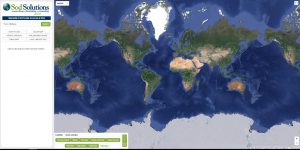
Here’s an easy way to determine your square footage. This online tool from Sod Solutions uses GIS mapping to figure it out from the comfort of your lounge chair.
On this front page, search for your address.
A bird’s eye view of your property comes up. Zoom in by using the + sign in the lower right corner of the screen.
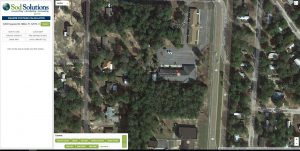
Plot points on the area you want to measure. This makes it so easy to measure those curved and odd-shaped areas!

The calculation of the area in square feet, yards, and acres is displayed on the left side. The perimeter is also calculated; that might be handy for determining the length of a fence line.
For more information:
Your Florida Lawn website
The Florida Fertilizer Label
Interpreting Pesticide Label Wording

by Sheila Dunning | Jul 21, 2017

(UF/IFAS photo Thomas Wright)
Northwest Florida’s weather patterns can present challenges to maintaining a health lawn. Heavy rains promote fast growth and relentless sunshine causes lawns to fade. In the last 200 days we have received at least 68 days of rain. While the rest of Florida was experiencing record drought, the Panhandle was experiencing torrential downpours. With every drop of rain your spring fertilizer is being metabolized by the lawn, reducing how many nutrients remain in the soil. Even the best slow-release fertilizer will only last 3-4 months. The message is: “It’s time for more fertilizer.”
A healthy lawn is an important component of the urban landscape. Not only do lawns increase the value of a property, they also reduce soil erosion, filter stormwater runoff, cool the air, and reduce glare and noise. A healthy lawn effectively filters and traps sediment and pollutants that could otherwise contaminate surface waters and groundwater. Lawns require nutrients throughout the growing season to stay healthy. In Northwest Florida the growing season is typically April to October.
Proper fertilization consists of selecting the right type of fertilizer and applying it at the right time and in the right amount for maximum plant uptake. The type of fertilizer should be based on a soil test, available through UF/IFAS Extension. The timing of application and amount of fertilizer is dependent on the research-based recommendations for the grass species and the fertilizer analysis of the product being used.
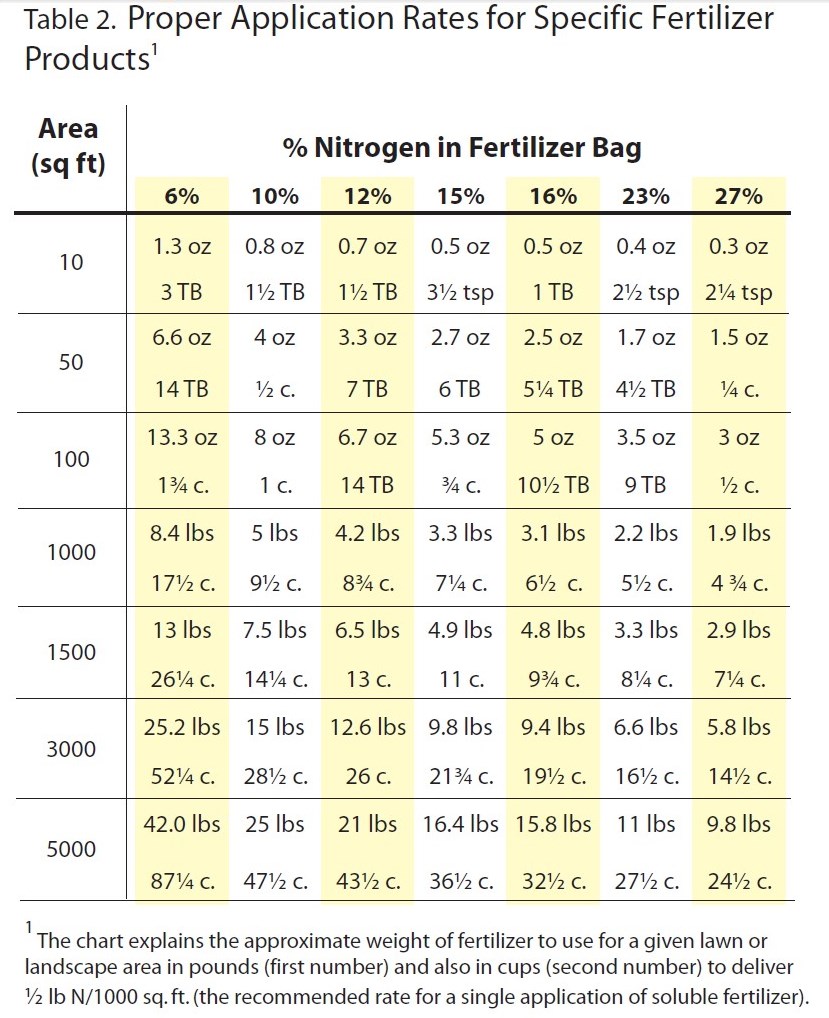
Chart excerpted from Florida Friendly Landscaping publication
Select only a fertilizer that states that the product is for use on residential turf. Do not use a fertilizer meant for flower or vegetable gardens on lawns. By Florida Administrative Code, Rule 5E-1.003, the Urban Turf Rule requires that the fertilizers being applied to residential lawns are labeled for the site and the application rates be followed. Typically, these products will contain both slow-release nitrogen and low or no phosphorus. Slow-release nitrogen will provide a longer-lasting response from the grass and reduces the potential for burning. For more information on the Urban Turf Rule go to: http://www.edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/EP/EP35300.pdf.
With frequent rain the soil is also losing iron. Keep in mind that the green fading to yellow appearance in your lawn may be an iron deficiency. Before applying your summer fertilizer put out a liquid chelated iron. It will improve the health of the lawn while you are trying to find a dry day to fertilize. While it is necessary to water in fertilizer with ¼” of water to reduce burn potential and volatilization, never apply fertilizer when heavy rain is expected. The rainfall over ¼” can encourage runoff and/or leaching of that fertilizer, which can be costly and environmentally harmful.
by Beth Bolles | Jun 10, 2017
It is common in Northwest Florida for palms to show signs of nutrient deficiencies. In general our sandy soil is often nutrient poor and available nutrients can easily move out of soils with frequent rainfall. In landscapes where fertilization is occurring, often the wrong types of fertilizer are applied. Fertilizer miss-application actually increases nutrient problems for the palm.
Palms can be deficient in many nutrients but the most common deficiencies we see in landscapes are from inadequate amounts potassium and magnesium. The simple solution would be to purchase a fertilizer labeled for palms to correct the problem. The difficulty is that most easily available fertilizers for palms do not have the correct form of nutrients that are required for the problems. With the exception of nitrogen, all other nutrients are in a quick release form so while the slow release nitrogen lasts for 2-3 months, all other nutrients have been used up. In response, the palm is encouraged to grow by the nitrogen but does not have enough of the other critical nutrients to carry out vital plant functions. What we see is often older leaves that are yellowing, browning, and die off before they should because the plant is pulling any available potassium and magnesium from old fronds to support new growth. Without the application of proper nutrients to the soil, the deficiency can continue until even new fronds are affected or the palm dies.

The fertilizer used for lawns does not have all the slow release and correct forms of nutrients for the palms. Older leaves turn yellow and brown indicating potassium deficiency. Photo by Beth Bolles, UF IFAS Extension Escambia County.
There is a solution that will help keep your palms healthy and attractive. Make sure you choose a specially designed fertilizer that has all nutrients in slow release form. Look for an analysis such as 8-2-12-4 (Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium-Magnesium). Also read further on the label for Polymer Coated Sulfate of Potash, Magnesium Sulfate (Kieserite), and Chelate (Iron EDTA). These are the forms of nutrients that will be beneficial to your palms.

Look in the area ‘Derived From’ (outlined in blue) on your fertilizer label to find the forms of nutrients. Photo by Dr. Monica Elliott, US/IFAS Extension.
If you have a mixed landscape where the palms are planted in the lawn, be sure to keep all lawn fertilizers out of the root zone of the palms. Lawn fertilizers do not have the correct forms of nutrients for palms. Remember also that palms roots extend many feet beyond the palm canopy so your ‘no lawn fertilizer zone’ may be past the mulch ring.
The recommendation from the University of Florida is 1.5 pounds of fertilizer over a 100 square foot area. Broadcast this on top of the ground and lightly water after application. In North Florida, you will likely apply the correct palm fertilizer about at least two times in May and end of August or 1st of September. If you are not able to use a palm fertilizer with the correct form of slow release nutrients, it is best not to fertilize palms at all.
















