
by Carrie Stevenson | Sep 17, 2021

Bald eagles and other large birds of prey have made a comeback in Florida.
Florida has all the elements of a wild animal’s paradise. The state has abundant rain and water sources, lush vegetation, plenty of food, and tons of nesting and hiding places. In our state and national parks, conservation easements, open waters, and acres of ranch land, large populations of animals can thrive. Particularly in areas with fewer people, healthy populations of even large animals like black bears, alligators, and panthers can maintain substantial territories. However, human migration into and throughout Florida is increasing at as steady a rate as ever. Retirees have long fled their cold northern winters to move part or full time to Florida. Now, the ability for many working people to telecommute from anywhere has made it attractive for younger families from all over the country to join us.

A black bear helps himself to a drink from the swimming pool of a Florida home. Photo provided by Patty Underwood/FWC
With more people comes the need for more housing. Some are content with high rise condos that leave a smaller footprint, but these are often located right on the water and can displace coastal wildlife and vegetation. For the thousands of families moving in weekly, more subdivisions, roads, stores, and schools are necessary. Inevitably, these lead to human-wildlife interactions that may or may not be positive experiences. In fast-growing south Santa Rosa County, I see almost daily reports of large black bears in backyards and trash cans. For smaller mammals, the threat of being hit by a car is unfortunately very common. For nearly every call we get about an exciting manatee sighting, we get word of a nerve-wracking interaction with a snake. As civilization moves closer to forested, once-wild areas, wildlife can be squeezed out, left without the protection of natural cover and drawn to human food and habitat.

A lush backyard landscape surrounds a recognition sign from the National Wildlife Federation. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
There are plenty of ways we can co-exist, though. A Florida-friendly yard is a wildlife-friendly yard, and those who go the extra mile can even be recognized by the National Wildlife Federation for their efforts. There are several steps one needs to take to become wildlife-friendly. The most important include providing food, water, and cover, so the animals’ basic needs are met. Actions like removing invasive species, keeping pets supervised when outdoors, and adding layers of vegetation are also excellent ways to attract and protect native creatures.
While small and medium sized animals can find shelter in a single yard, it takes neighborhood cooperation to be a haven for something larger, like deer, bears, birds of prey, or large tortoises. Some neighborhoods are designated from the beginning to include conservation easements that serve as amenities to the neighborhood. They include trails, shady waterfront areas, and plenty of space for wildlife. It is important when moving into one of these neighborhoods that each homebuyer understands and respects the purpose behind conservation areas. Residents of older, existing neighborhoods can also work together to designate common areas and stretches of adjoining yards as wildlife-friendly corridors, allowing more animals to use the space safely.

A gopher tortoise burrow is noted by a sign in a local city park. The tortoise is co-existing peacefully with its neighbors! Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
In my own neighborhood in the city limits, a gopher tortoise has moved in and become a neighborhood mascot of sorts! When alerted to the presence of its burrow, the city brought in a sign explaining the animal’s protected status and crucial role in the environment. Floridians share their citizenship with thousands of other species. These breathtaking birds, fish, mammals, reptiles, and insects are integral to the health of our land and water. By taking steps to look out for their well-being, we are also providing for our own.

by Pat Williams | Sep 9, 2021
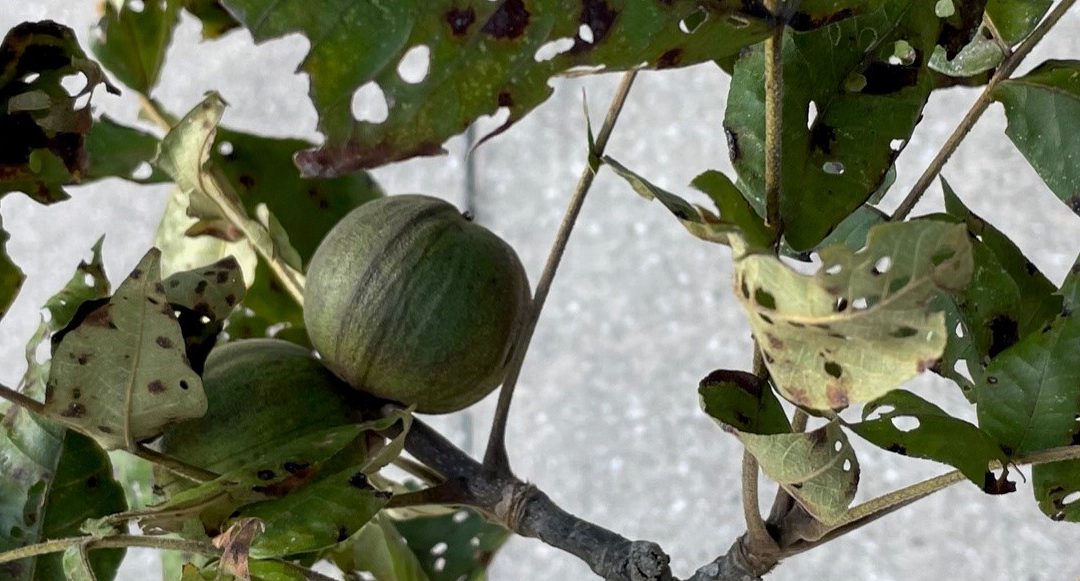
As homeowners, we do value our trees and no one wants to lose a shade tree especially on the house’s south side in Florida. On a recent site visit, a hickory tree had multiple concerns. Upon closer inspection, the tree had a bacterial infection about 30” off the ground with a smelly, black-brown ooze seeping forth. The leaf canopy was riddled with beetle holes and leaf margins were chewed by caterpillars. When leaves were viewed under the microscope, thrips (insects) and spider mites were found running around. The biggest homeowner cosmetic concern arose from hickory anthracnose (fungus) and upon closer inspection found the leaves to have hickory midge fly galls. The obvious question is should the tree come down? I’ll have you read the whole article before giving you the answer.
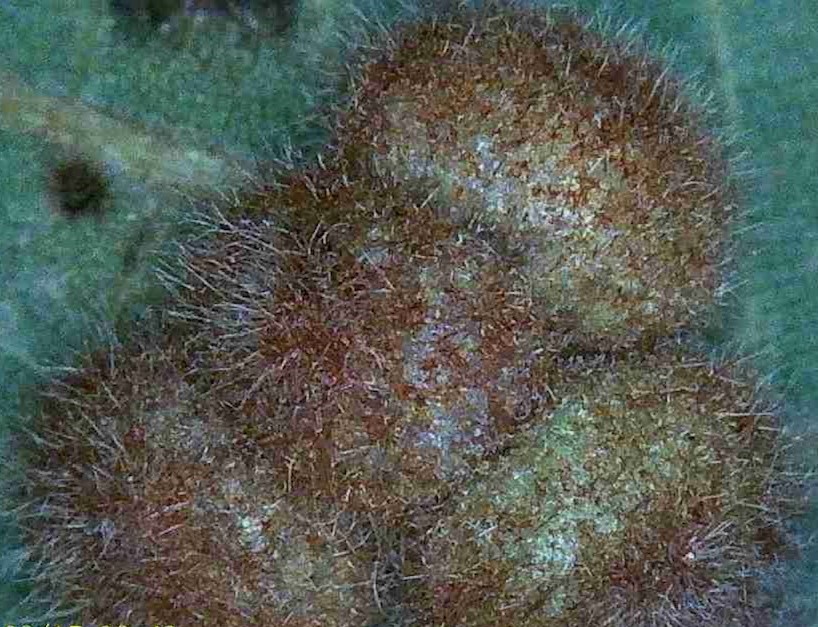

Each hickory gall is approximately 3/16″ wide.
Hickory anthracnose or leaf spot as seen in the banner photo is caused by a fungal infection during the wet summer months in Florida. The homeowner can usually recognize the disease by the large reddish brown spots on the upper leaf surface (sending a sample to the NFREC Plant Pathology Lab will confirm the diagnosis) and brownish spots with no formal shape on the bottom. Be sure to rake and remove all leaves to prevent your disease from overwintering close to the tree thus reducing infection next year.
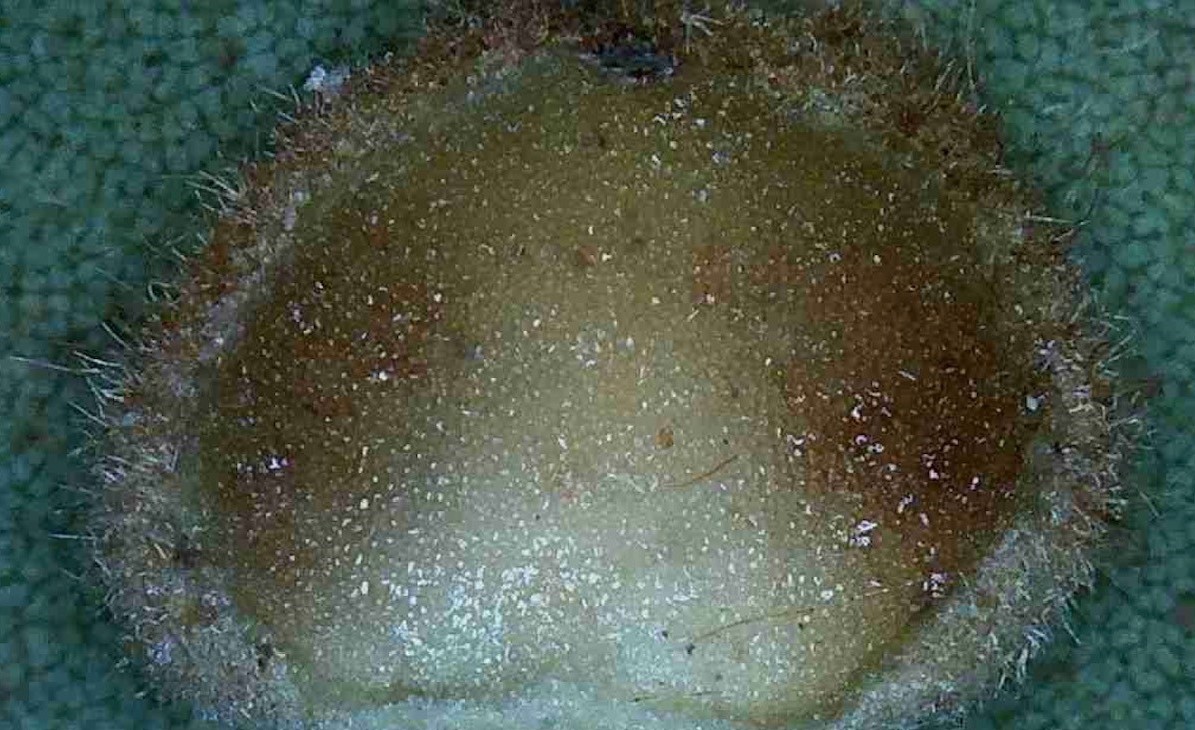
A hickory gall has been cut in half to show the leaf tissue.
The fungus can be lessened by good cultural practices and appropriate fungicidal applications. Please remember it is best left to professionals when spraying a large tree. This alone is not cause to remove your tree.
Hickory gall is caused by the hickory midge fly, an insect that lays eggs in the leaf tissue. The plant responds by building up tissue around each egg almost like the oyster when forming a pearl.
As the gall tissue grows, eggs hatch and larva start to feed on this tissue. The larva will continue to
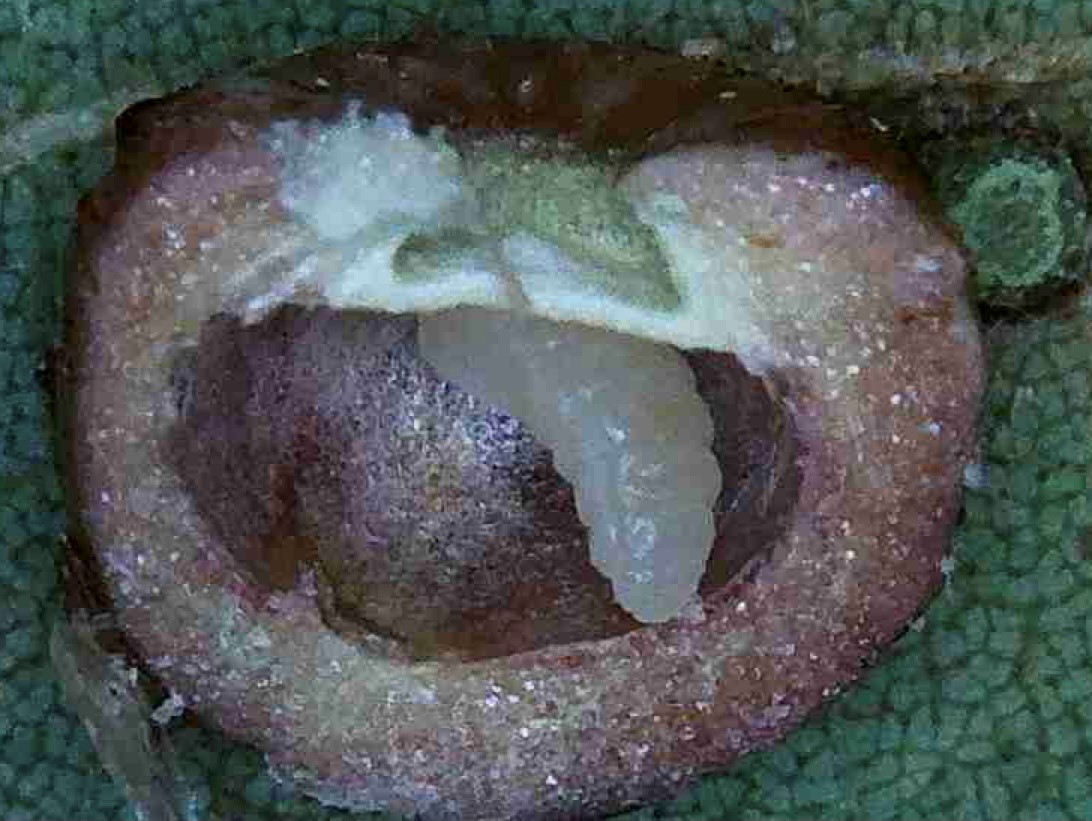
The larva has eaten all soft material inside the gall and is ready to pupate.
feed until it is ready to pupate within the gall. After forming a pupa, the midge fly will eventually emerge as an adult and females will continue to lay eggs on other leaves. The galls are more of a cosmetic damage and because your hickory leaves will fall from the tree as winter comes, the galls will normally not cause enough damage to worry about each year. Once again good cultural practices and disposal of each year’s leaves will reduce the gall numbers next year.
In a large tree with many leaves, foliar feeding by beetles and caterpillars do cause damage though the leaves will still produce enough food (photosynthesis) to keep the tree alive. Most of us never climb our trees to look at leaves to see the small insects/mites and there are more than enough leaves to maintain tree health.
The biggest concern during my site visit was their tree’s bacterial infection. A knife blade was pushed into the wound area and went in less than 1/4″. The homeowner was instructed to look at bactericide applications. In the end, this hickory tree with so many problems is still shading the home and helping cool the house. It is still giving refuge to wildlife and beneficial insects. When in doubt give our trees the benefit and keep them in place. Remember your local Extension agent is set up to make site visits and saving a tree is time well spent.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Sep 9, 2021
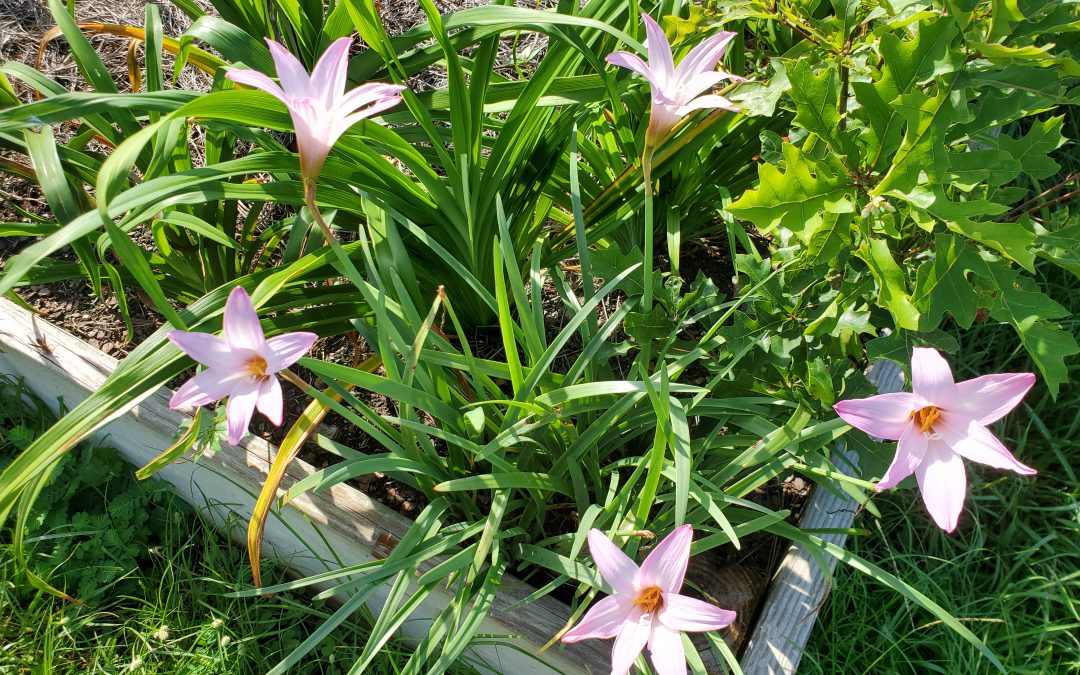
Bulbs are my favorite class of ornamental plants. They generally are low maintenance, come back reliably year after year, and sport the showiest flowers around. While many bulbs like Daylily, Crinum and Amaryllis are very common in Panhandle landscapes, there is a lesser-known genus of bulbs that is well worth your time and garden space, the Rainlily (Zephyranthes spp.).
Rainlily, aptly named for its habit of blooming shortly after summer rainfall events and a member of the Amaryllis family of bulbs, is a perfect little plant for Panhandle yards for several reasons. The plant’s genus name, Zephyranthes – which translates to English as “flowers of the western winds”, hints at the beauty awaiting those who plant this lovely little bulb. From late spring until the frosts of fall, Rainlily rewards gardeners with flushes of trumpet-shaped flowers in shades of white, pink, and yellow, with some hybrids offering even more exotic colors. While these individual flowers typically only persist for a day or two, they are produced in “flushes” that last several days, extending the show. Though Rainlily flowers are the main event for the genus, beneath the blooms, plants also offer attractive, grass-like, evergreen foliage. These aesthetic attributes lend themselves to Rainlily being used in a variety of ways in landscapes, from massing for summer color ala Daylilies, to use around the edges of beds as a showy border like Liriope or other “border” type grassy plants.

Unknown Rainlily species blooming in a raised bed. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
Continuing along the list of Rainlily attributes, the genus doesn’t require much in the way of care from gardeners either. Most species of Rainlily, including the Florida native Z. atamasca, have no serious pests and are right at home in full sun to part shade. Once established, plants are exceedingly low-maintenance and won’t require any supplemental irrigation or fertilizer! Some Rainlily species like Z. candida even make excellent water or ditch garden plants, preferring to have their feet wet most of the year – putting them right at home in the Panhandle this year. And finally, all Zephyranthes spp. do very well in containers and raised beds also, adding versatility to their use in your landscape!
The one drawback of Rainlily is that they can be somewhat difficult to find for sale. As these bulbs are an uncommon sight in most garden centers, to source a specific Zephyranthes species or cultivar, one is probably going to need to purchase from a specialty internet or mail-order nursery. As with other passalong-type bulbs though, the absolute best and most rewarding way to obtain Rainlily is to get a dormant season bulb division from a friend or fellow gardener who grows them. There are many excellent unnamed or forgotten Zephyranthes cultivars and seedlings flourishing in gardens across the South, waiting to be passed around to the next generation of folks who will appreciate them!
Even if you must go to some lengths to get a Rainlily in your garden, I highly recommend doing so! You’ll be rewarded with years of low-maintenance summer color after the dreariest of rainy days and will be able to pass these “flowers of the western wind” on to the next gardening generation. For more information on growing, sourcing, or propagating Rainlilies, check out this EDIS publication by Dr. Gary Knox of the UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center (NFREC) or contact your local UF/IFAS Extension office! Happy Gardening!

by Sheila Dunning | Aug 26, 2021

Photos by Sheila Dunning
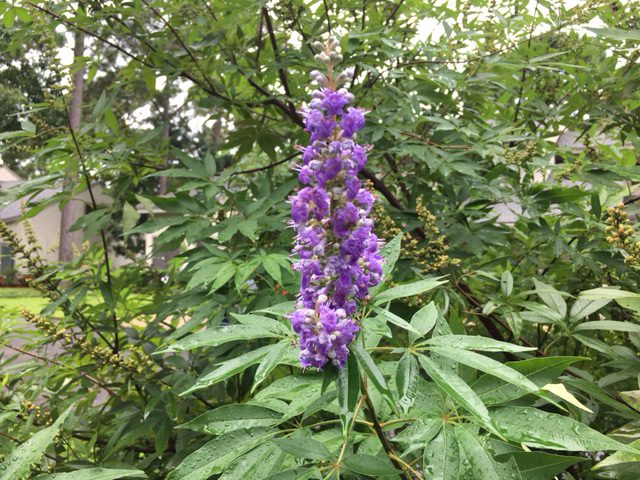
The showy chaste tree makes an attractive specimen as the centerpiece of your landscape bed or in a large container on the deck. Much more of them are being seen since the Florida Department of Transportation has recognized the tree as a desirable median planting. Easy-to-grow, drought resistant, and attractive to butterflies and bees, Vitex agnus-castus is a multi-stemmed small tree with fragrant, upwardly-pointing lavender blooms and gray-green foliage. The chaste tree’s palmately divided leaves resemble those of the marijuana (Cannabis sativa) plant; its flowers can be mistaken for butterfly bush (Buddleia sp.); and the dry, darkened drupes can be used for seasoning, similar to black pepper, making it a conversation piece for those unfamiliar with the tree.
Vitex , with its sage-scented leaves that were once believed to have a sedative effect, has the common name “Chastetree” since Athenian women used the leaves in their beds to keep themselves chaste during the feasts of Ceres, a Roman festival held on April 12. In modern times, the tree is more often planted where beekeepers visit in order to promote excellent honey production or simply included in the landscape for the enjoyment of its showy, summer display of violet panicles.
Chaste tree is native to woodlands and dry areas of southern Europe and western Asia. It will thrive in almost any soil that has good drainage, prefers full sun or light shade, and can even tolerate moderate salt air. Vitex is a sprawling plant that grows 10-20 feet high and wide, that looks best unpruned. If pruning is desired to control the size, it should be done in the winter, since it is a deciduous tree and the blooms form on new wood. The chaste tree can take care of itself, but can be pushed to faster growth with light applications of fertilizer in spring and early summer and by mulching around the plant. There are no pests of major concern associated with this species, but, root rot can cause decline in soils that are kept too moist.

by Mary Salinas | Aug 20, 2021
On August 12, 2021, our panel answered questions on a wide variety of landscape topics. Maybe you are asking the same questions, so read on!
Ideas on choosing plants
What are some perennials that can be planted this late in the summer but will still bloom through the cooler months into fall?
Duranta erecta ‘Sapphire Showers’ or ‘Gold Mound’, firespike, Senna bicapsularis, shrimp plant, lion’s ear
Where can native plants be obtained?

Dune sunflower, Helianthus debilis. Photo credit: Mary Salinas UF/IFAS Extension.
Gardening Solutions: Florida Native Plants – see link to FANN: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/ornamentals/native-plants.html
What are some evergreen groundcover options for our area?
Mondo grass, Japanese plum yew, shore juniper, ajuga, ferns such as autumn fern.
What are some ideas for partial morning sun butterfly attracting tall flowers to plant now?
Milkweed, salt and pepper plant, swamp sunflower, dune sunflower, ironweed, porterweed, and salt bush.
I’m interested in moving away from a monoculture lawn. What are some suggestions for alternatives?
Perennial peanut, powderpuff mimosa, and frogfruit.
We are new to Florida and have questions about everything in our landscape.
Florida-Friendly-Landscaping TM Program and FFL Web Apps: https://ffl.ifas.ufl.edu/
https://ffl.ifas.ufl.edu/resources/apps/
UF IFAS Gardening Solutions: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/
What are some of the top trends in landscaping today?
Houseplants, edible gardens, native plants, food forests, attracting wildlife, container gardening, and zoysiagrass lawns
Edibles

Artwork broccoli is a variety that produces small heads. Photo credit: Mary Salinas UF/IFAS Extension.
What vegetables are suitable for fall/winter gardening?
Cool Season Vegetables: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/edibles/vegetables/cool-season-vegetables.html
North Florida Gardening Calendar: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/EP451%20%20%20
Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/vh021
How can I add herbs to my landscape?
Herbs in the Florida Garden: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/edibles/vegetables/herbs.html
My figs are green and hard. When do they ripen?
Why Won’t My Figs Ripen: https://www.lsuagcenter.com/profiles/rbogren/articles/page1597952870939
What is best soil for raised bed vegetable gardens?
Gardening in Raised Beds: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/EP472
And there are always questions about weeds
How can I eradicate cogongrass?

Chamber bitter is a troublesome warm season weed in our region. Photo credit: Brantlee Spakes Richter, University of Florida, Bugwood.org
Cogongrass: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/WG202
Is it okay to use cardboard for weed control?
The Cardboard Controversy: https://gardenprofessors.com/the-cardboard-controversy/
What is the best way to control weeds in grass and landscape beds?
Weed Management Guide for Florida Lawns: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/EP141
Improving Weed Control in Landscape Planting Beds: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdf/EP/EP52300.pdf
Landscape practices
Can ground water be brackish and stunt plants?
Reclaimed Water Use in the Landscape: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/ss545
How can I prevent erosion from rainwater runoff?
Stormwater Runoff Control – NRCS: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/national/water/?cid=nrcs144p2_027171
Rain Gardens: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/design/types-of-gardens/rain-gardens.html
And https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/pdf/articles/rain-garden-manual-hillsborough.pdf
What is the best time of the year to propagate flowering trees in zone 8B?
Landscape Plant Propagation Information Page – UF/IFAS Env. Hort: https://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/database/lppi/
Which type of mulch works best on slopes greater than 3 percent?
Landscape Mulches: How Quickly do they Settle?: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/FR052
When should bulbs be fertilized?
Bulbs and More – UI Extension: https://web.extension.illinois.edu/bulbs/planting.cfm
Should I cut the spent blooms of agapanthus?
Agapanthus, extending the bloom time: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/ornamentals/agapanthus.html
http://blogs.ifas.ufl.edu/wakullaco/2020/10/07/extending-bloom-time/
Plant questions

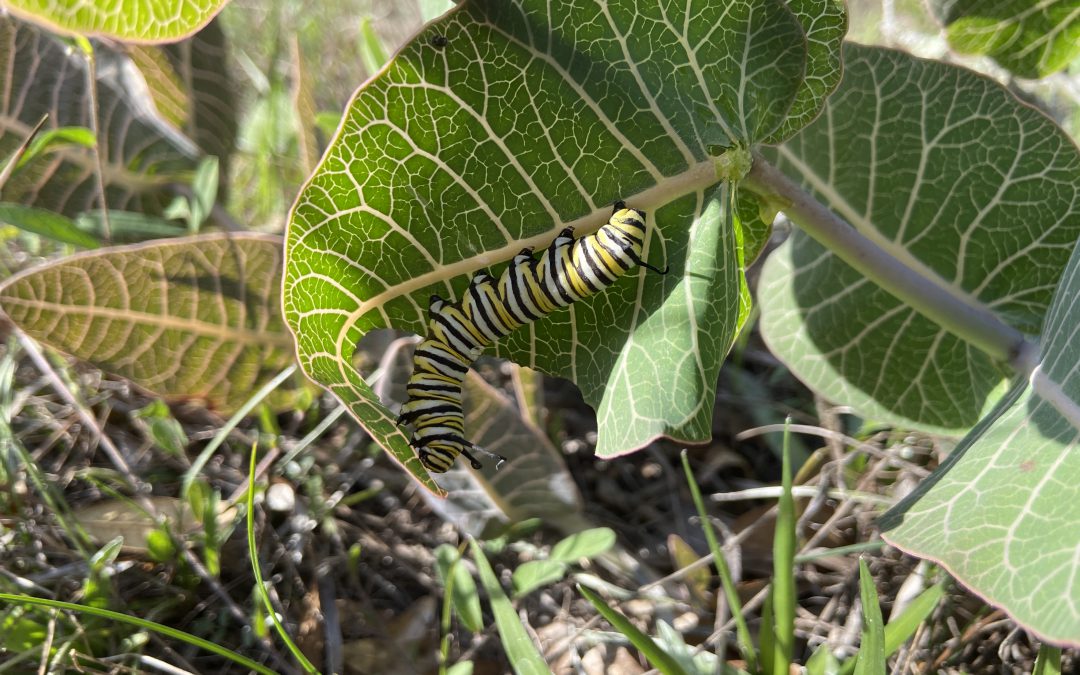
Monarch caterpillar munching on our native sandhill milkweed, Asclepias humistrata. Photo credit: Mary Salinas, UF IFAS Extension.
I planted native milkweed and have many monarch caterpillars. Should I protect them or leave them in nature?
It’s best to leave them in place. Featured Creatures: Monarch Butterfly: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdf/IN/IN780/IN780-Dxyup8sjiv.pdf
How does Vinca (periwinkle) do in direct sun? Will it make it through one of our panhandle summers? Can I plant in late August?
Periwinkles and No more fail with Cora series: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/ornamentals/periwinkles.html#:~:text=Plant%20your%20periwinkles%20where%20they,rot%20if%20irrigated%20too%20frequently.
Insect and disease pests
What to do if you get termites in your raised bed?
The Facts About Termites and Mulch: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/IN651
How to combat fungus?
Guidelines for ID and Management of Plant Disease Problems: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/mg442
Are there preventative measures to prevent diseases when the humidity is very high and it is hot?
Fungi in Your Landscape by Maxine Hunter: http://blogs.ifas.ufl.edu/marionco/2020/01/16/fungi-in-your-landscape/
If you missed an episode, check out our playlist on YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bp0HfdEkIQw&list=PLhgoAzWbtRXImdFE8Jdt0jsAOd-XldNCd

by Mary Salinas | Aug 18, 2021
For those of you who tuned into the July 29 edition of Gardening in the Panhandle LIVE, beneficial insects was the topic of the day. Here are links to the publications our panelists talked about.

Mantid. Photo credit: David Cappaert, Bugwood.org.
How do I identify the kind of insect I have?
Recognizing beneficial bugs: Natural Enemies Gallery from UC Davis http://ipm.ucanr.edu/natural-enemies/
How to distinguish the predatory stink bug from the ones that harm our crops: https://entomology.ces.ncsu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/FL-pred.jpg
How to tell difference in stink bugs and leaf footed insects. Are both harmful? UF/IFAS Featured Creatures: leaffooted bug – Leptoglossus phyllopus (Linnaeus) (ufl.edu)
How can I tell bad beetles from good ones? Helpful, Harmful, Harmless Identification Guide is one resource available: http://ifasbooks.ifas.ufl.edu/p-153-helpful-harmful-harmless.aspx
How can we encourage beneficial insects?
How can we encourage the beneficial insect species?
- Plant more flowers attract pollinators that also feed on insects.
- Diversity of plants in the landscape.
- Use softer or more selective pesticides to minimize damage to beneficials.
Is it helpful to order beneficial insects such as lady bugs? Encouraging Beneficial Insects in Your Garden OSU: https://catalog.extension.oregonstate.edu/sites/catalog/files/project/pdf/pnw550.pdf
How effective is buying predatory insects to release in your greenhouse? Natural Enemies and Biological Control: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/IN120
Can I buy beneficial insects to start breeding in my garden? Natural Enemy Releases for Biological Control of Crop Pests: https://www2.ipm.ucanr.edu/agriculture/natural-enemy-releases-for-biological-control-of-crop-pests/
What benefit would result by planting city right-of-ways with native wild flowers? https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/in1316; https://adamgdale.files.wordpress.com/2020/03/gcm_feb2020.pdf
Can an individual gardener sustain an ecosystem for beneficial insects? Penn State Article on beneficial insects that mentions some flowering plants that help support predators and parasitoids: https://extension.psu.edu/attracting-beneficial-insects
Specific Insects
How do I get rid of mole crickets? UF/IFAS Mole Crickets: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/entity/topic/mole_crickets
Are wasps really beneficial? Beneficial Insects: Predators!: https://sfyl.ifas.ufl.edu/sarasota/gardening-and-landscaping/horticulture-commercial/integrated-pest-management/beneficial-insects/
Is a dish soap solution effective against wasps? Soaps, Detergents, and Pest Management: https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/care/pests-and-diseases/pests/management/soaps-detergents-and-pest-management.html
How to control leaf footed bugs? Handpick them, attract beneficials, create diverse plantings in landscape, accept some damage, and control them when in the juvenile stage.
Can you tell me about praying mantids? Praying Mantids: https://entomology.ca.uky.edu/files/efpdf2/ef418.pdf
Are there any beneficial insects that keep mosquito populations down? Dragonfly larvae in water, mosquitofish
What are the little insects that hop out of centipede grass? Are they beneficial?
Spittlebugs and your lawn: https://nwdistrict.ifas.ufl.edu/hort/2020/05/27/spittlebugs-and-your-lawn/
How to stop Eastern Black Swallowtail Butterflies laying eggs on parsley – the hatched caterpillars eat it all. Plant extra or put a screen over plant.
Extra fun video!
Take a look at this video of parasitic wasp attacking aphids: Parasitic Wasps | National Geographic – YouTube





















