
by Molly Jameson | Oct 28, 2020

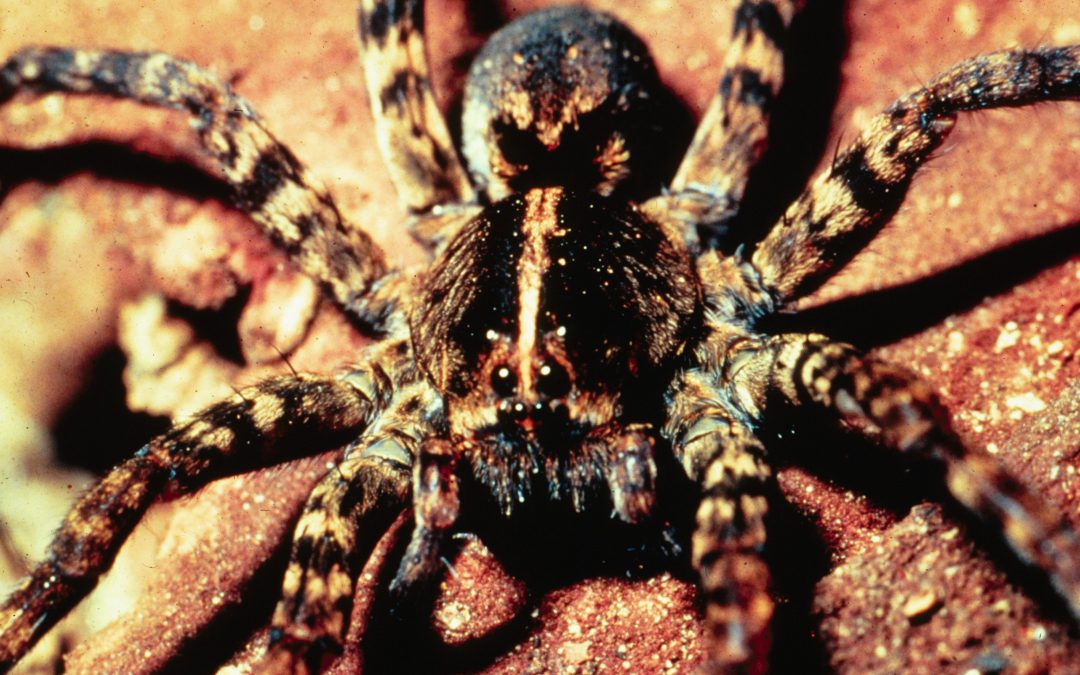
The Carolina wolf spider (Hogna Corolinensis) is the largest wolf spider, measuring up to 22-35 mm. It is the state spider of South Carolina, the only state that recognizes a spider as a state symbol. Photo by Eugene E. Nelson, Bugwood.org.
Halloween coincides with a full moon this year, so you may want to be on the lookout for hungry werewolves. In your garden, you may also be on the lookout for a much smaller, yet just as frightful, type of wolf. Well – wolf spider, that is!
But have no fear, just as the little werewolves of the neighborhood will be sated by a handful of sweets, a wolf spider will be satisfied once it finds its meal of choice. Wolf spiders are predators, feeding primarily on insects and other spiders. Much like a werewolf, wolf spiders prefer to stalk their prey at night. This is good news for gardeners – as it means you’ll have an insect hunter working for you while you sleep.
Wolf spiders are in the family Lycosidae, and there are over 2,000 species within this family. Lycos means “wolf” in Greek, inspired by the way wolves stalk their prey. Although, unlike wolves who hunt in packs, wolf spiders are very much solitary. These spiders do not spin webs; instead, they keep to the ground, where they can blend in with leaf litter on the soil floor. Some wolf spiders even dig tunnels, or use tunnels dug by other animals, to hide and hunt.

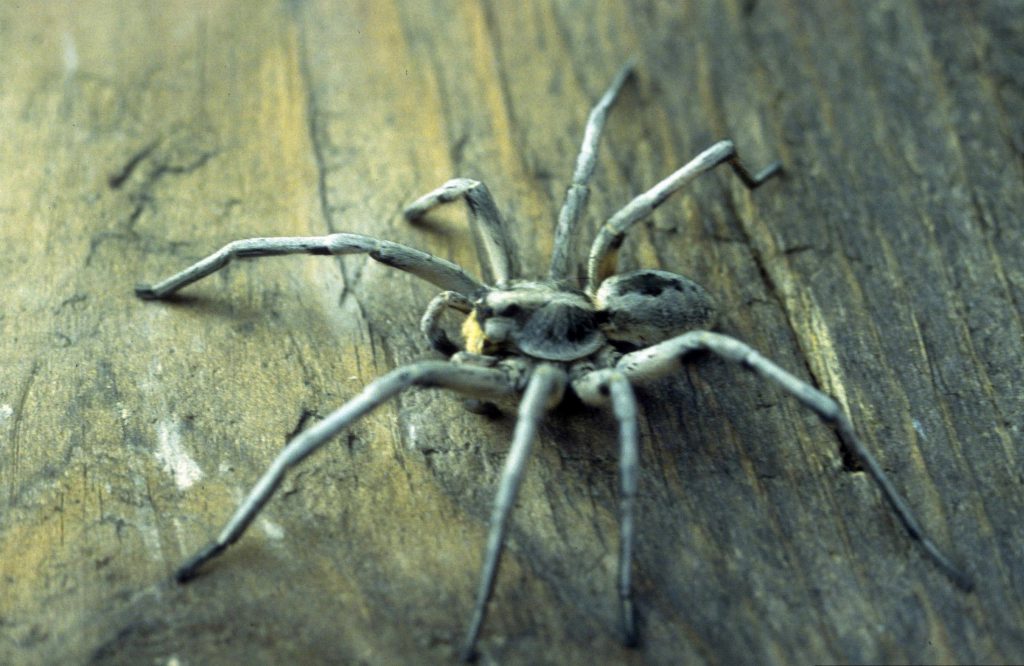
Although most spiders have poor eyesight, wolf spiders have excellent vision, which they use to spot prey. Photo by James O. Howell, University of Georgia, Bugwood.org.
Wolf spiders have eight eyes that are arranged in three rows. This includes four small eyes in the lowest row, two very large eyes in the middle, and two medium-sized eyes off to either side on top. Some of their eyes even have reflective lenses that seem to sparkle in the moonlight. Using their excellent eyesight and sensitivity to vibrations, they stealthily stalk prey such as ants, grasshoppers, crickets, and other spider species. Female wolf spiders, which are bigger than males, may even take down the occasional lizard or frog.
No matter the meal, many wolf spiders pounce on their prey, hold it between their eight legs, and roll with it onto their backs, creating a trap. They then sink their powerful fangs, which are normally retracted inside the jaw, into the victim. The fangs have a small hole and hollow duct, which allows venom from a specialized gland to pass through during the bite. This venom quickly kills the prey, allowing the wolf spider to eat in peace.
Although wolf spiders could bite a person if threatened, they prefer to run away, and their venom is not very toxic to humans. If you do get bitten, you may have some swelling and redness, but no life-threatening symptoms have been reported. Werewolves on the other hand? For these, you’re on your own!
by Pat Williams | Oct 21, 2020
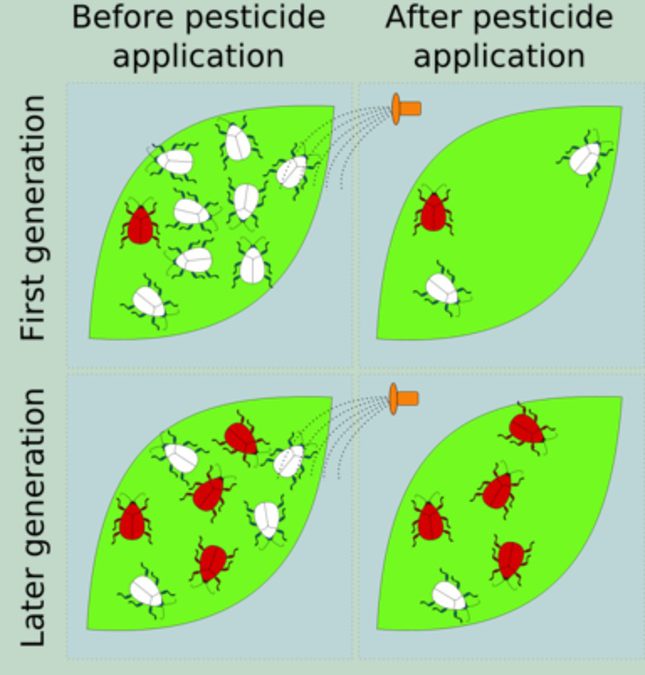
Normally, you will have one of four answers: “yes”, “no”, “I don’t know” or “what are super bugs?” The answer to the last one is an insect or other pest that has become resistant to chemical treatments through either natural selection (genetics) or an adaptive behavioral trait.
The next question is do you treat insect or pest problems at home with a purchased EPA registered chemical (one purchased from the nursery or other retailer)? If you answered yes, then the next question is how many times in a row do you apply the same chemical? If you only use one chemical until the product is used up, then you might be creating super bugs. Do you ever alternate chemicals and if you answer yes, do you understand chemical Modes of Action (how the pesticide kills the pest)? If you do not, then chances are the rotating chemicals might act in the same way. Thus, you are creating super bugs because in essence you are applying the same chemical with different labels.
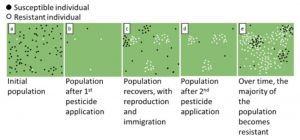
Click on image for a larger view. Taken from https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in714.
One of the first ways to reduce creating super bugs is to practice Integrated Pest Management (IPM). The very last step of an IPM philosophy is chemical control. You should choose the least toxic (chemical strength is categorized by signal words on the label: caution, warning, and danger) and most selective product. A chemical label advertising it kills many pests is an example of a non-selective chemical. You want to choose a chemical that kills your pest or only a few others. In Extension education, you will always hear the phrase “The label is the law.” To correctly purchase a chemical, you must first correctly identify the pest and secondly the plant you want to treat. If you need help from Extension for either of these, please contact us. Before purchasing the chemical, always read the whole label. You can find the label information online in larger print versus reading the small print on the container.

IRAC phone app.
You now have the correct chemical to treat your pest. Wear the recommended personal protective equipment (PPE) and apply according to directions. If your situation is normal, the problem is not completely solved after one treatment. You might apply a second or third time and yet you still have a pest problem. The diagram explains why you still have pests or more accurately super bugs.
Now the last question is how do we really solve the problem given that chemicals are still the only treatment option? A bit more work will greatly help the situation. You need to download the Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) guide and find the active ingredient on your chemical label (http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi121 or https://irac-online.org/modes-of-action/ and select the pdf). If you are like me, you can just download the IRAC MoA smartphone app and type in the active ingredient; otherwise, Appendix 5 in the pdf has a quick reference guide. Either way, you will know the Group and/or Subgroup. A lot of commonly purchased residential chemicals fall within 1A, 1B or 3. The successful treatment option is to select chemicals from different group numbers and use them in rotation. If you start practicing this simple strategy, your treatment should be more successful. Then when someone asks if you are creating super bugs, your answer will be no.
If you have any questions about rotating your chemical Modes of Action, please contact me or your local county Extension agent. For more resources on this topic, please read Managing Insecticide and Miticide Resistance in Florida Landscapes by Dr. Nicole Benda and Dr. Adam Dale (https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in714).

by Daniel J. Leonard | Oct 14, 2020
Article by Jessica Griesheimer & Dr. Xavier Martini, UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center, Quincy
Dioscorea bulbifera, commonly known as the air potato is an invasive species plaguing the southeastern United States. The air potato is a vine plant that grows upward by clinging to other native plants and trees. It propagates with underground tubers and aerial bulbils which fall to the ground and grow a new plant. The aerial bulbils can be spread by moving the plant, causing the bulbils to drop to the ground and tubers can be spread by moving soil where an air potato plant grew prior. The air potato is commonly confused with and mistaken as being Dioscorea alata, the winged yam which is also highly invasive. The plants look very similar at first glance but have subtle differences. Both plants exhibit a “heart”-shaped leaf connected to vines. The vines of the winged yam have easily felt ridges, while the air potato vines are smooth. They also differ in their aerial bulbil shapes, the winged yam has a long, cylinder-shaped bulbil while the air potato aerial bulbil has a rounded, “potato” shape (Fig. 1).

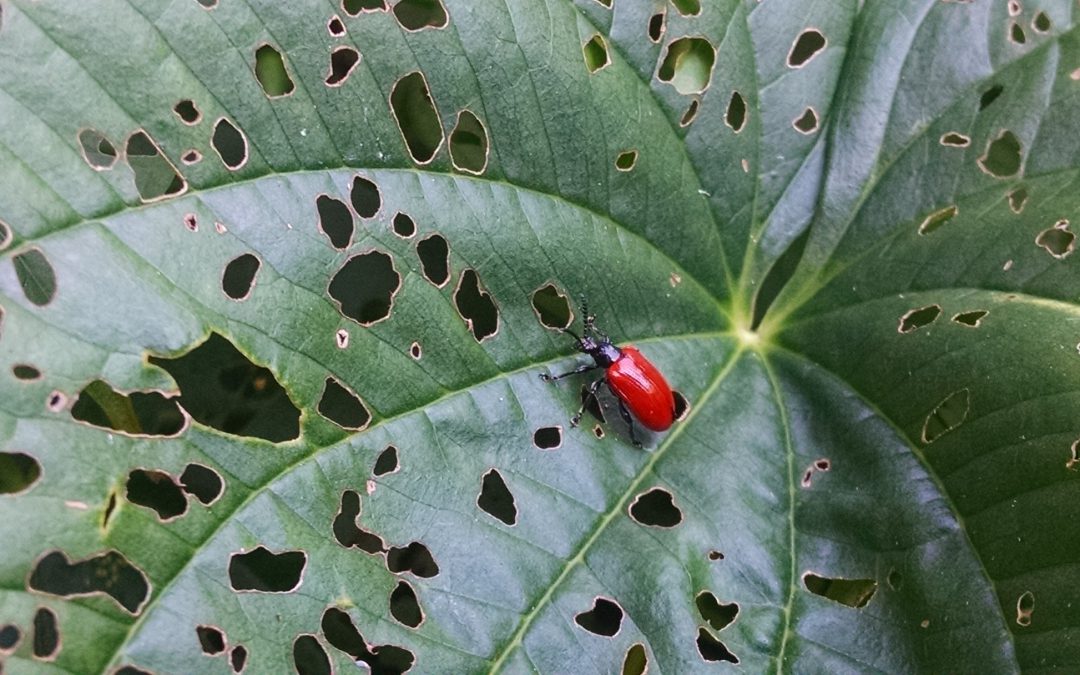
In its native range of Asia and Africa, the air potato has a local biocontrol agent, Lilioceris cheni commonly known as the Chinese air potato beetle (Fig. 2). As an adult, this beetle feeds on older leaves and deposits eggs on younger leaves for the larvae to later feed on. Once the larvae have grown and fed, they drop the ground where they pupate to later emerge as adults, continuing the cycle. The Chinese air potato beetle will not feed on the winged yam, as it is not its host plant.Current methods of air potato plant, bulbil, and tuber removal can be expensive and hard to maintain. The plant is typically sprayed with herbicide or is pulled from the ground, the aerial bulbils are picked from the plant before they drop, and the underground tubers are dug up. The herbicides can disrupt native vegetation, allowing for the air potato to spread further should it survive. If the underground tuber or aerial bulbils are not completely removed, the plant will grow back.
The Chinese air potato beetle is currently being evaluated as a potential integrated pest management (IPM) organism to help mitigate the invasive air potato. The beetle feeds and reproduces solely on the air potato plant, making it a great IPM organism choice. During 2019, we studied the Chinese air potato beetle and its ability to find the air potato plant. It was found the beetles may be using olfactory cues to find the host plant. Further research is conducted at the NFREC to increase natural aggregation of the beetles on air potato to improve biological control of the weed.

Chinese Air Potato Leaf Beetle.
If you have the air potato plant, or suspect you have the air potato plant, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension Agents for help!
by Evan Anderson | Oct 14, 2020

A newly hatched armyworm –photo by Lyle Buss
With a population that never seems to quite disappear in North Florida, the armyworm is a caterpillar pest of many plants. There are four types found in our area: fall, southern, yellow-striped, and beet armyworms. The caterpillars pupate into moths, which breed roughly from April to December, but warmer weather may lead to them being sighted even in the middle of winter. Adult moths, which are relatively nondescript and gray-brown in appearance, lay masses of 100-200 eggs on plants. Young armyworms are tiny and very difficult to detect, often hiding during the brightest parts of the day.

A fall armyworm. –photo by J L Castner
The armyworm grows to a length of about 1 ¼ inches, taking about two weeks to reach its full size. The caterpillar builds a cocoon in the soil and pupates into a moth, living another one to three weeks. With its ability to eat a broad range of plants, this can lead to large populations of these insects in a relatively short time.
Armyworms seem to prefer eating grasses (especially Bermudagrass in lawns), but will chew on almost anything in their path. They have been observed eating citrus trees, tobacco, cotton, strawberries, and even weeds like pigweed and nutsedge. A hungry armyworm might even turn on its fellow caterpillars, eating them as well if they are too close. When large numbers of these pests are present, the damage they do to surrounding foliage can be stark. Young caterpillars may skeletonize leaves, while older larvae will make holes in leaves or defoliate plants fully.
Years with an abundance of wet or humid weather seem to help armyworms reproduce. Armyworms seem to be attracted to newly established turf, and heavy fertilization of turfgrass in late summer can also cause populations to build. Scout for them

A beet armyworm. –photo by Serena Robison
during cooler hours of the day, or when it is overcast or rainy. Mixing a tablespoon of dishwashing soap in a gallon of water and pouring it over a four-square foot area will cause insects to crawl to the surface – do this if damage is present and armyworms are suspected. For lawns, treatment at the first sight of damage may help, though a lawn may very well survive an attack by armyworms. If chemical control is necessary, there are numerous options. Products containing the active ingredients Bacillus thuringiensis, acephate, bifenthrin, carbaryl, permethrin, spinosad, and others have all been labeled for use on armyworms.
For more information, see our EDIS publication on fall armyworm at https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in255 or contact your local Extension office.

by Larry Williams | Oct 1, 2020

Adult cicada on tree branch, Photo credit: Lyle Buss, UF Entomologist
“What is that noise,” asked the visitors to Middle Georgia when I was a teenager. They were visiting during the summer from El Paso, Texas. I asked, “What noise?” The reply, “That loud noise in the trees.” I responded, “Oh, those are cicadas.’ There are sounds that are so common that sometimes you quit hearing them.
Before the visitors left for El Paso, I made sure to show them the brown, dry shells (exoskeletons) of cicadas that are not difficult to find attached to the trunk of a Georgia pine tree during summer. Cicadas leave their nymph exoskeletons on the trunks of trees and sometimes shrubs when they shed them to become mature flying adults.
You may not have ever seen a cicada but you’ve undoubtedly heard one if you live in Florida. These insects make a loud buzzing noise during the day in the spring and summer. Male cicadas produce their distinctive calls with drum-like structures called timbals, located on the sides of their abdomens. The sound is mainly a calling song to attract females for mating.
Cicadas spend most of their life underground as nymphs (immature insects) feeding on the sap of roots, including trees, grasses as well as other woody plants. They can live 10 or more years underground as nymphs. In some parts of the United States, there will be news reports of when periodical cicadas are expected to emerge from the ground. Periodical cicada species mature into adults in the same year, usually on 13- or 17-year life cycles. Their numbers can be enormous as they emerge, gaining much local attention. However, cicada species in Florida emerge every year from late spring through fall and in much smaller numbers as compared to the periodical cicadas.

Cicada emerging from exoskeleton, Photo credit: Lyle Buss, UF Entomologist
There are at least nineteen species of cicadas in Florida, ranging from less than a ¼ inch to over 2 inches in length. Some people might be frightened by their size and sounds but thankfully cicadas don’t sting or bite. They are a food source for wildlife, including some bird species and mammals.
Very rarely, I’ll have someone ask about small twigs from trees found on the ground as a result of the female cicada’s egg-laying process. But because this is usually such a minor issue with practically no permanent damage to any tree, cicadas really aren’t considered to be a pest of any significance in Florida.
For more information on cicadas, contact the University of Florida Extension Office in your County. Or visit the following UF/IFAS web page. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in602

by Daniel J. Leonard | Sep 28, 2020
2020 has not been the most pleasant year in many ways. However, one positive experience I’ve had in my raised bed vegetable garden has been the use of a cover crop, Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum)! Use of cover crops, a catch-all term for many species of plants used to “cover” field soil during fallow periods, became popular in agriculture over the last century as a method to protect and build soil in response to the massive wind erosion and cropland degradation event of the 1930s, the Dust Bowl. While wind erosion isn’t a big issue in raised bed gardens, cover crops, like Buckwheat, offer many other services to gardeners:

Buckwheat in flower behind summer squash. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard.
- Covers, like Buckwheat, provide valuable weed control by shading out the competition. Even after termination (the cutting down or otherwise killing of the cover crop plants and letting them decompose back into the soil as a mulch), Buckwheat continues to keep weeds away, like pinestraw in your landscape.
- Cover crops also build soil. This summer, I noticed that my raised beds didn’t “sink” as much as normal. In fact, I actually gained a little nutrient-rich organic matter! By having the Buckwheat shade the soil and then compost back into it, I mostly avoided the phenomena that causes soils high in organic matter, particularly ones exposed to the sun, to disappear over time due to breakdown by microorganisms.
- Many cover crops are awesome attractors of pollinators and beneficial insects. At any given time while my Buckwheat cover was flowering, I could spot several wasp species, various bees, flies, moths, true bugs, and even a butterfly or two hovering around the tiny white flowers sipping nectar.
- Covers are a lot prettier than bare soil and weeds! Where I would normally just have either exposed black compost or a healthy weed population to gaze upon, Buckwheat provided a quick bright green color blast that then became covered with non-stop white flowers. I’ll take that over bare soil any day.

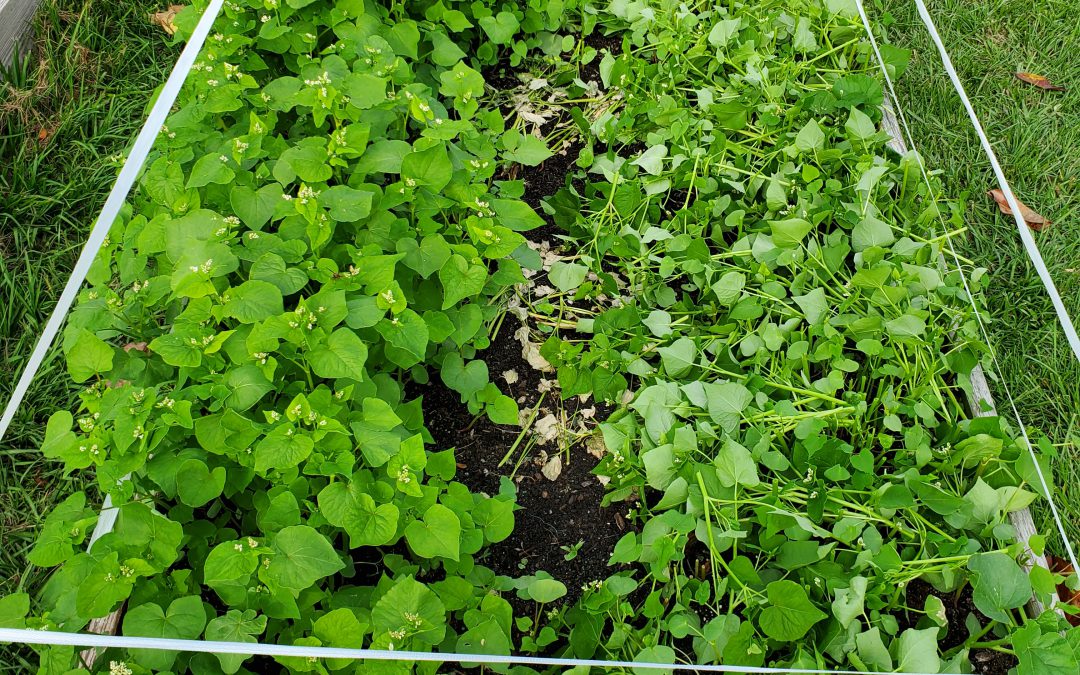
Buckwheat cover before termination (left) and after (right) interplanted with Eggplant. Photo courtesy Daniel Leonard, UF/IFAS Calhoun County Extension.
Now that I’ve convinced you of Buckwheat’s raised bed cover crop merits, let’s talk technical and learn how and when to grow it. Buckwheat seed is easily found and can be bought in nearly any quantity. I bought a one-pound bag online from Johnny’s Selected Seeds for my raised beds, but you can also purchase larger sizes up to 50 lb bags if you have a large area to cover. Buckwheat seed germinates quickly as soon as nights are warmer than 50 degrees F and can be cropped continuously until frost strikes in the fall. A general seeding rate of 2 or 3 lbs/1000 square feet (enough to cover about thirty 4’x8’ raised beds, it goes a long way!) will generate a thick cover. Simply extrapolate this out to 50-80 lbs/acre for larger garden sites. I scattered seeds over the top of my beds at the above rate and covered lightly with garden soil and obtained good results. Unlike other cover crops (I’m looking at you Crimson Clover) Buckwheat is very tolerant of imperfect planting depths. If you plant a little deep, it will generally still come up. A bonus, no additional fertilizer is required to grow a Buckwheat cover in the garden, the leftover nutrients from the previous vegetable crop will normally be sufficient!

Buckwheat “mulch” after termination. Photo courtesy of Daniel Leonard, UF/IFAS Calhoun County Extension.
Past the usual cover crop benefits, the thing that makes Buckwheat stand out among its peers as a garden cover is its extremely rapid growth and short life span. From seed sowing to termination, a Buckwheat cover is only in the garden for 4-8 weeks, depending on what you want to use it for. After four weeks, you’ll have a quick, thick cover and subsequent mulch once terminated. After eight weeks or so, you’ll realize the plant’s full flowering and beneficial/pollinator insect attracting potential. This lends great flexibility as to when it can be planted. Have your winter greens quit on you but you’re not quite ready to set out tomatoes? Plant a quick Buckwheat cover! Yellow squash wilting in the heat of summer but it’s not quite time yet for the fall garden? Plant a Buckwheat cover and tend it the rest of the summer! Followed spacing guidelines and only planted three Eggplant transplants in a 4’x8’ raised bed and have lots of open space for weeds to grow until the Eggplant fills in? Plant a Buckwheat cover and terminate before it begins to compete with the Eggplant!
If a soil building, weed suppressing, beneficial insect attracting, gorgeous cover crop for those fallow garden spots sounds like something you might like, plant a little Buckwheat! For more information on Buckwheat, cover crops, or any other gardening topic, contact your local UF/IFAS County Extension Office. Happy Gardening!



















