
by Sheila Dunning | Sep 7, 2019
“There are these weeds spreading all over my yard. They have little round leaves that are real close to the ground and creep in every direction. I keep trying to get rid of them by mowing my grass shorter, but they are killing my grass. What are they and how do I get rid of them?” Here at the Extension office, this is a conversation I have had nearly daily for the past month. We are here to help with identification and control of many landscape problems, including weeds.
However, my first word of advice is to change the mowing practice. Short, spreading weeds cannot be mowed out. You need to do just the opposite. Mowing as high as possible (3-4”) will help to reduce weeds by shading them out, therefore, reducing their spread.
In every instance, the weeds have been common lespedeza (Kummerowia striata (Thunb.) Schind syn. Lespedeza striata) and/or prostrate spurge (Euphorbia maculata syn. Chamaesyce maculata). Both grow close to the ground with a spreading habit. Both have small, rounded leaves and produce small, light-colored flowers. But, if you look close, there are significant differences that will help with identification.
 Common lespedeza, also known as Japanese clover, is prostrate summer annual that forms 15-18 inch patches. The stems are wiry. It has dark green trifoliate
Common lespedeza, also known as Japanese clover, is prostrate summer annual that forms 15-18 inch patches. The stems are wiry. It has dark green trifoliate  (arranged in threes) leaves with three oblong, smooth leaflets. Leaflets have parallel veins nearly at right angles to a prominent mid-vein. Its leaves have smooth edges and a short spur at the tip of each leaflet. Flowers appear in late summer with small pink to purple, single flowers found in leaf axils on most of the nodes of the main stems. As common lespedeza matures, the stems harden and become woody.
(arranged in threes) leaves with three oblong, smooth leaflets. Leaflets have parallel veins nearly at right angles to a prominent mid-vein. Its leaves have smooth edges and a short spur at the tip of each leaflet. Flowers appear in late summer with small pink to purple, single flowers found in leaf axils on most of the nodes of the main stems. As common lespedeza matures, the stems harden and become woody.
Prostrate spurge is a summer annual broadleaf weed that spreads by seed. The leaves are oval in shape, small, and opposite along the stem. As it matures, a red spot may form in the center of the leaf, earning it the common name spotted spurge. Another distinct characteristic is the stem contains a milky sap that oozes when the stem is broken. Light pink to white-colored flowers appear from early-summer through the fall.
Both are annual,broadleaf weeds, so there are several post-emergent herbicides available to kill the ones present. Don’t forget the pre-emergent herbicide application in late winter though. These weeds can drop plenty of seed. The importance of knowing which weed you have is more about the message they are trying to send you. These weeds can indicate other issues that may be part of the reason the grass is thinning and allowing the weeds to take over in the first place.
Common lespedeza is a legume. It thrives when water is plentiful and soil nutrients are low. If this is the weed “taking over” your yard, you need to get a soil test and evaluate your watering habits. Improving fertility and reducing soil moisture will naturally weaken common lespedeza.
If your thin patches of declining grass are being replaced with spurge, it may be time to submit a sample for a nematode assay. Research has shown that spurge is a weed that can thrive with high populations of nematodes. Turfgrass species are easily harmed by nematodes (microscopic roundworms that imbed into and on grass roots). If the assay indicates harmful population levels, unfortunately there are few options for reduction of the nematodes. However, several ornamental plants are tolerant. So, you may need to consider creating a landscape bed area rather than continuing to battle poor-looking grass.
Weeds can serve as indicators to soil conditions that may need to be addressed. Learning to identify weeds may teach you more than just their names.

by Matt Lollar | Sep 7, 2019
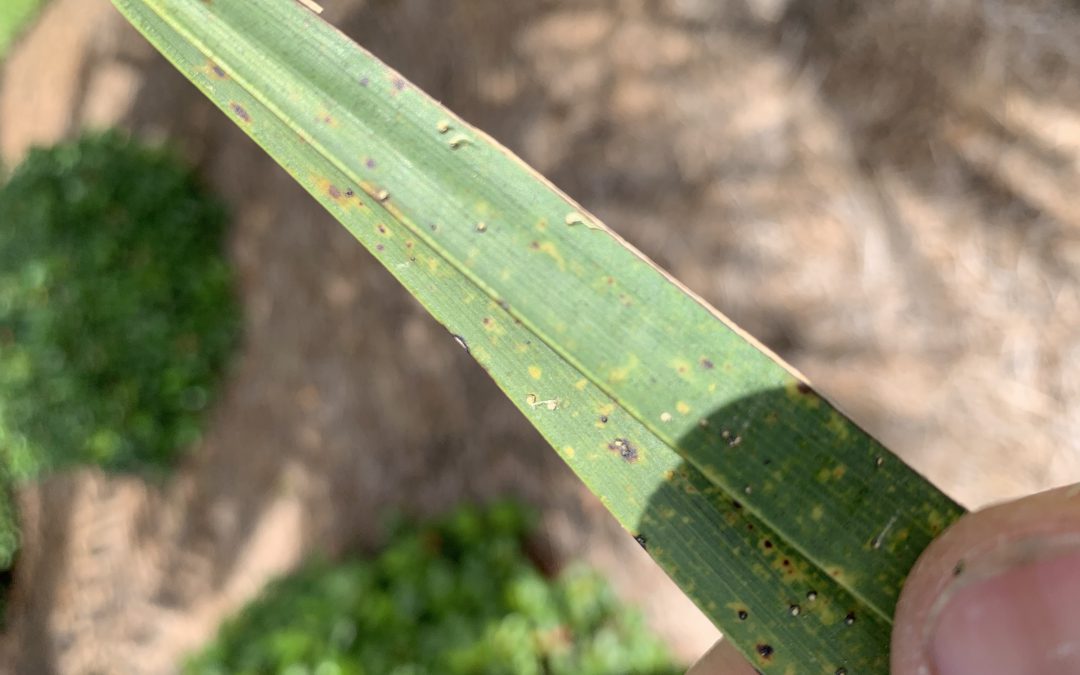
A couple weeks ago, I was on a site visit to check out some issues on Canary Island Date Palms. The account manager on the property requested a site visit because he thought the palms were infested with scale insects. He noticed the issue on a number of the properties he manages and he was concerned it was an epidemic. From a distance, lower fronds were yellowing from the outside in and the tips were necrotic. These are signs of potassium deficiency with possible magnesium deficiency mixed in.

Transitional leaf showing potassium deficiency (tip) and magnesium deficiency (base) symptoms. Photo Credit: T.K. Broschat, University of Florida/IFAS Extension
Nutrient deficiencies are slow to correct in palm trees. It’s much easier to prevent deficiencies from occurring by using a palm fertilizer that has the analysis 8N-2P2O5-12K2O+4Mg with micronutrients. Even if the palms are part of a landscape which includes turf and other plants that require additional nitrogen, it is best to use a palm fertilizer with the analysis previously listed over a radius at least 25 feet out from the palms. However, poor nutrition wasn’t the only problem with these palms.
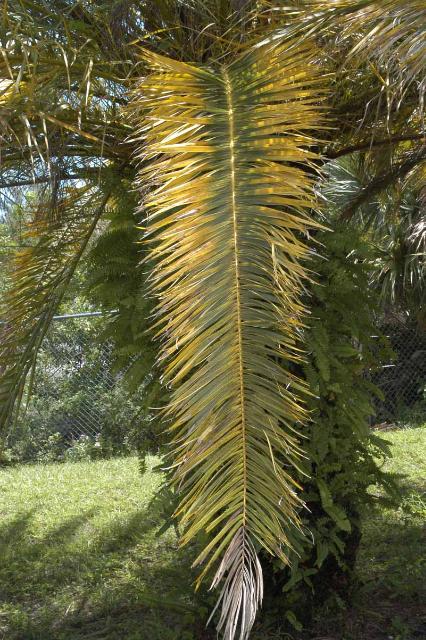
Upon closer look, the leaflets were speckled with little bumps. Each bump had a little white tail. These are the fruiting structures of graphiola leaf spot also known as false smut.
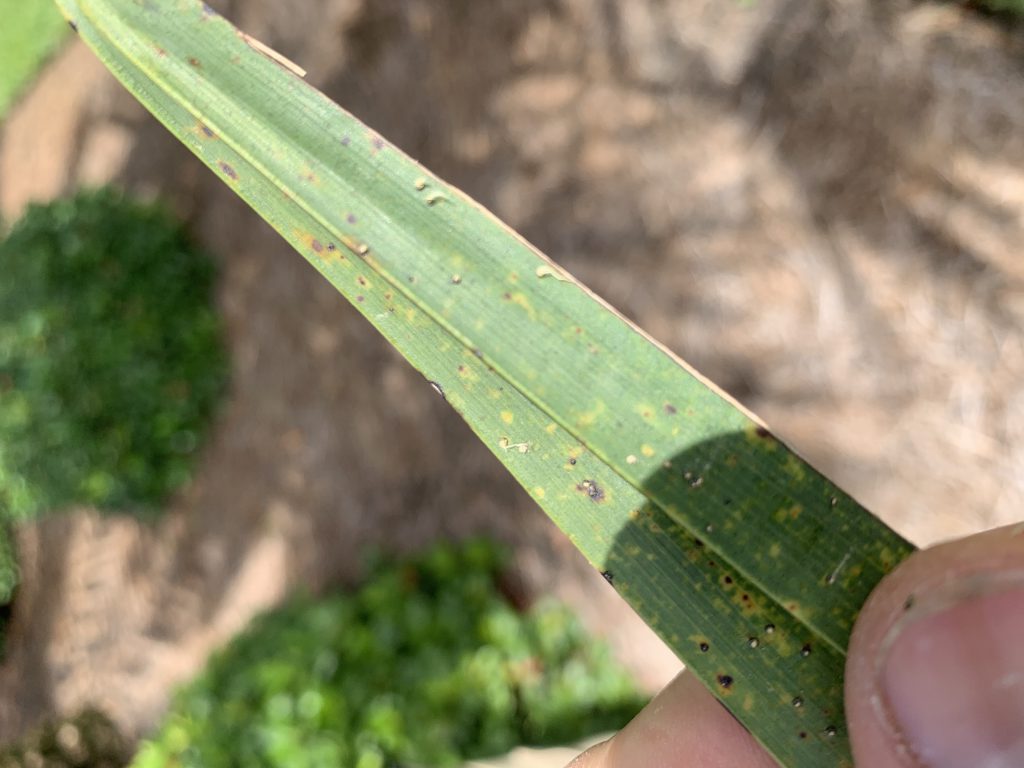

Graphiola leaf spot (false smut) on a Canary Island Date Palm. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
Graphiola leaf spot is a fungal leaf disease caused by Graphiola phoenicis. Canary Island Date Palms are especially susceptible to this disease. Graphiola leaf spot is primarily an aesthetic issue and doesn’t cause much harm to the palms infected. In fact, the nutrient deficiencies observed in these palms are much more detrimental to their health.
Graphiola leaf spot affects the lower fronds first. If the diseased, lower fronds are not showing signs of nutrient deficiencies then they can be pruned off and removed from the site. All naturally fallen fronds should be removed from the site to reduce the likelihood of fungal spores being splashed onto the healthy, living fronds. A fungicide containing copper can be applied to help prevent the spread of the disease, but it will not cure the infected fronds. Palms can be a beautiful addition to the landscape and most diseases and abiotic disorders can be managed and prevented with proper pruning, correct fertilizer rates, and precise irrigation.

by Ray Bodrey | Aug 22, 2019
Seldom do we find the answer to a problem as being easy. More often, a difficult and complicated answer is what’s needed. However, the solution to a healthy lawn rebound may be found simply by adjusting your mower height and mowing schedule.
Mowing strategy is an important variable that keeps a lawn healthy and flourishing, no matter the species or cultivar of grass. Mowing too high can lead to an undesirable look and cause unwanted thatch buildup, which can create a favorable environment for pests and diseases. Mowing too low can weaken the root system causing thinning, which allows space for weeds to invade. Another problem with mowing too low is that it affects nutritional needs. Lawn grasses generate food for themselves through a process called photosynthesis. A healthy leaf surface area is needed to effectively accomplish this. If the lawn is mowed too low, then leaf surface area is lost. The grass can literally starve itself.
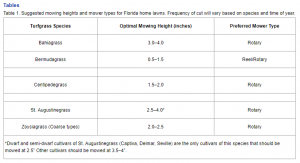
Table: Suggested mowing height for lawn grasses. Frequency of cut will vary based on species and time of year. Credit: L. E. Trenholm, J. B. Unruh & J. L. Cisar, UF/IFAS Extensio
Not all lawn grasses should be mowed at the same height, as show in the table above. Fine textured grasses like Bermuda and Zoysia matrella can be cut significantly lower than coarse textured grasses, such as Bahia or St. Augustine. Not sure of the type of lawn grass you have? Visit this site https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/topic_book_florida_lawn_handbook_3rd_ed to review the Florida Lawn Handbook or contact your local county extension office for questions.
Mowing schedule is the other side of the coin. How often to mow ultimately depends on how fast your grass grows. By nature, Bermuda will grow quickly and Zoysia is somewhat slower growing. Regardless, summer months are when warm-season lawn grasses grow more rapidly. Historically, lawn grasses begin a dormant-slow growth stage in October and continues through March. Fertilizer schedule also plays a role in grass growth rate. So how often do you need to mow? This rate is best determined by the amount of growth since the last cutting, rather than the number of days which have elapsed. You should mow often enough so that no more than 1/4 to 1/3 of the total leaf surface is removed at any given mowing. In other words, leave twice as much leaf surface as you cut off. Remember, incremental adjustments should be made to your current practices. Never drastically change the height of the grass. If the lawn has been allowed to grow too long, you should gradually lower the mowing height on successive cuttings.
What are some other helpful tips? Always use a well-adjusted mower with a sharpened blade. You may find it easier replace your blade each year or every 2 years than periodic resharpening. Dull mower blades do a tremendous amount of damage with uneven cuts. This will cause gashes and splits in the leaf where fungal and bacterial pathogens can thrive. Never mow grass when it’s wet, either. Dry grass cuts are cleaner cuts and won’t clog the mower deck. If you have built up thatch, it’s a good idea to attach a bag to your mower that will catch clippings. These clippings will be great additions to your compost pile or to use as natural mulch. If no thatch problems exist, mowing without a bag will distribute clippings throughout the lawn, and the clippings will decompose into nutrients for the root system.
With proper mowing strategies, along with fertilizing & watering, your lawn grass can bounce back. For more information contact your local county extension office.
Information for this article provided by the UF/IFAS Extension EDIS Publication, “Mowing Your Florida Lawn”, by L. E. Trenholm, J. B. Unruh & J. L. Cisar: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/LH/LH02800.pdf
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Matt Lollar | Aug 1, 2019
Large patch Rhizoctonia solani (known as brown patch in cool season grasses) is a common disease of many turfgrass species. It usually occurs during the cooler months from October through May when temperatures are below 80 degrees Fahrenheit. However, signs and symptoms of large patch and other Rhizoctonia diseases can be observed throughout the summer. Less common Rhizoctonia species that occur during the summer months are Rhizoctoni zeae and Rhizoctonia oryzae. Extended periods of turf wetness from excessive rainfall or overwatering provide ideal conditions for the disease to develop and spread.
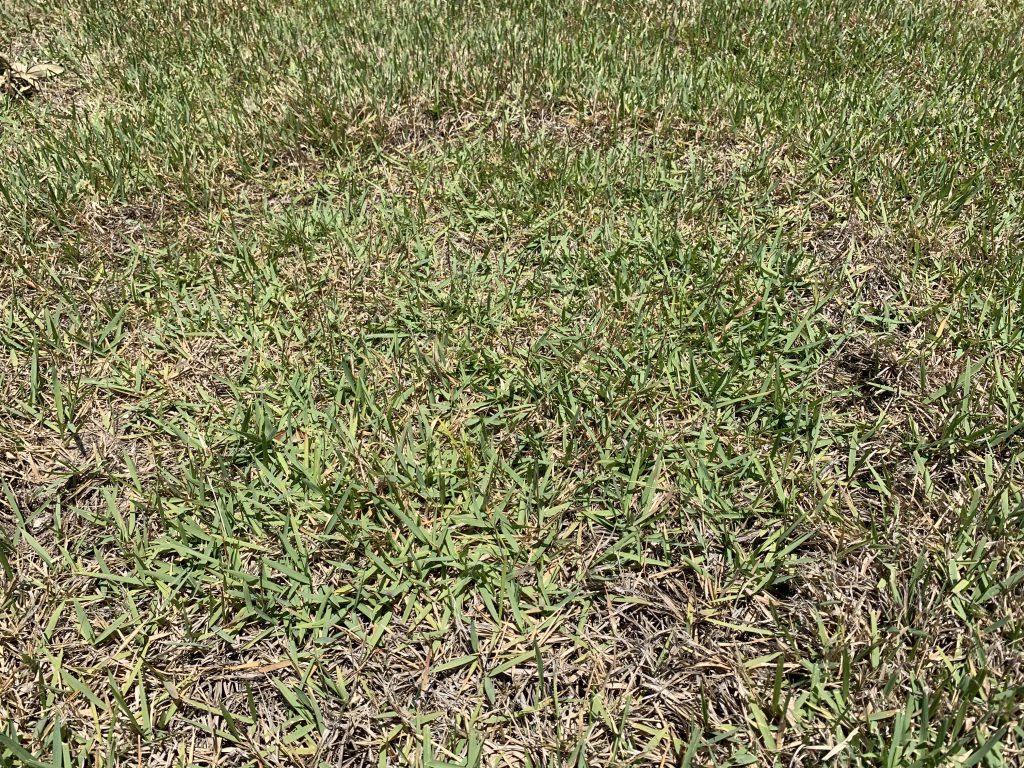

Rhizoctonia in a zoysiagrass lawn. Photo Credit: Matt Lollar, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
This summer in Santa Rosa County, Rhizoctonia has been positively diagnosed in both St. Augustinegrass and zoysiagrass lawns and suspected in a number of centipedegrass lawns. The disease usually starts as small, yellow patches (about a foot in diameter) that turn reddish brown, brown, or straw colored as the leaves start to die. Patches often expand to several feet in diameter. It is common to see rings of yellow or brown turf with otherwise healthy turf in the center. The fungus infects portions of the blades closest to the soil, eventually killing the entire leaf. Grass blades can easily be pulled off their stems, but roots are not affected by the disease.
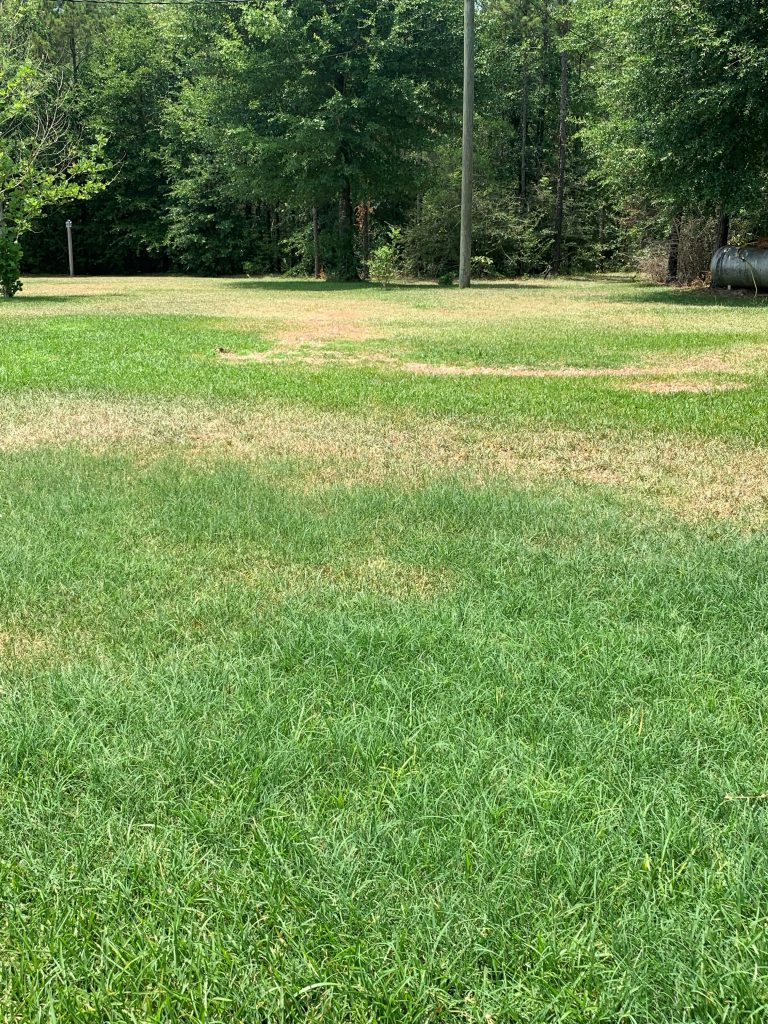

Rhizoctonia in a St. Augustinegrass lawn. Photo Credit: John Atkins, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Santa Rosa County
Overwatering and excessive fertilization can both contribute to the development of Rhizoctonia disease. Improper timing of fertilizer application can also promote disease development. In the Florida Panhandle, turfgrass is actively growing from April to October. Slow-release fertilizers are recommended to allow for a more even distribution of nutrients over the course of multiple months. Recommended fertilizer rates are based on turfgrass species, geographical location, and fertilizer analysis. Please refer to the UF/IFAS Publication: “Urban Turf Fertilizer Rule for Home Lawn Fertilization” for rate recommendations.
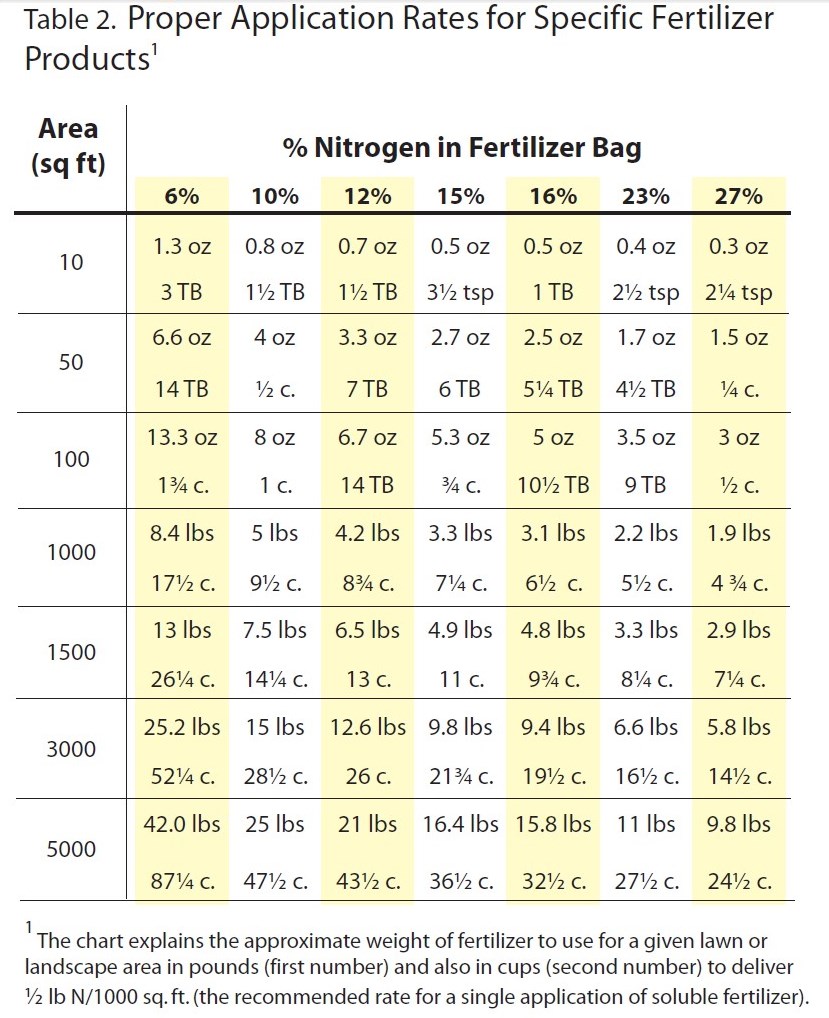
Chart excerpted from Florida-Friendly Landscaping publication.
If large patch or another Rhizoctonia disease is confirmed in your lawn, then chemical controls are necessary to keep the disease from spreading. Fungicide products containing the active ingredients azoxystrobin, chlorothalonil, fludioxonil, flutolanil, iprodione, mancozeb, metconazole, myclobutanil, polyoxin D, propiconazole, thiophanate-methyl, thiram, triadimefon, trifloxystrobin, or triticonazole are viable options for keeping the disease from spreading. For best results, follow the fungicide label for application instructions. It’s important to not only treat the affected areas, but also the healthy turf surrounding these areas in order to keep the diseased spots from growing in size.
Unfortunately, turf diseases are often not noticed until large patches of declining and dead turf are noticed. In these cases when large dead patches exist in the lawn, it is usually necessary to resod these areas. As with most problems that arise in the landscape, good cultural practices are the most proactive way to mitigate the chances with turfgrass diseases. The UF/IFAS Florida Friendly Website provides up-to-date solutions and recommendations for caring for Florida landscapes.
by Sheila Dunning | Jul 11, 2019
The Irrigation Association (IA) kicks off the official start of this year’s campaign on Tuesday, July 9, 2019. The initiative promotes the social, economic and environmental benefits of efficient irrigation technologies, products and services in landscape, turf and agricultural irrigation.
Irrigation (agricultural and turf/landscape) accounts for 65-70% of total freshwater use in the United States. According to the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) WaterSense program, the average American family household uses more than 300 gallons of water per day; roughly 30% of this occurs outdoors. Efficient landscape irrigation systems and practices dramatically reduce water being lost or wasted.
The starting point for improving the efficiency of a home landscape sprinkler system is to calibrate each zone (http://ufdc.ufl.edu/IR00003389/00001) and make adjustments and repairs. That includes the rain shut-off device.
Florida is one of the few states with a rain sensor law. The most recent version of the statute (2010) states the following: “Any person who operates an automatic landscape irrigation system shall properly install, maintain, and operate technology that inhibits or interrupts operation of the system during periods of sufficient moisture.” (Florida Statute 373.62). Regardless of the water source or age of the system, all in-ground irrigation systems must be connected to a functioning rain sensor of some kind.
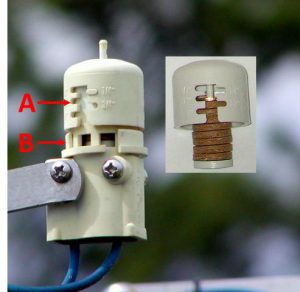
Expanding disk Rain Sensor
Expanded disk devices are the most popular rain sensor due to their low cost, ease of installation, and low maintenance. Traditionally, they are wired into the controller, but a wireless version allows for quicker installation and mounting up to 300 feet from the controller. These “mini-click” sensors contain disks made of cork that absorb rainfall and expand, triggering a pressure switch. The disk cover is rotated to adjust for the predetermined amount of rainfall required to trigger the switch. It should be set on ½ – ¾ inch, depending on soil type and rooting depth of irrigated plants. The switch continues to interrupt the scheduled controller as long as the disks are swollen. When the rain stops, the disks begin to dry out. Once they have contracted, the switch closes and the regularly scheduled irrigation cycle begins where it left off before the interruption. These small cork disks wear out in Florida’s heat and need to be replaced. By checking and repairing the sensor parts, the sprinkler system will operate much more efficiently. We have all seen irrigation systems running in pouring rain. Keep yours maintained to avoid this needless waste of water.
So, join the kids this summer. Go outside and play in the water. Turn on the sprinkler system and check it out. July is Smart Irrigation Month. Let’s see how efficient you can make your system and reduce the water waste in Florida.

by Daniel J. Leonard | Jun 25, 2019

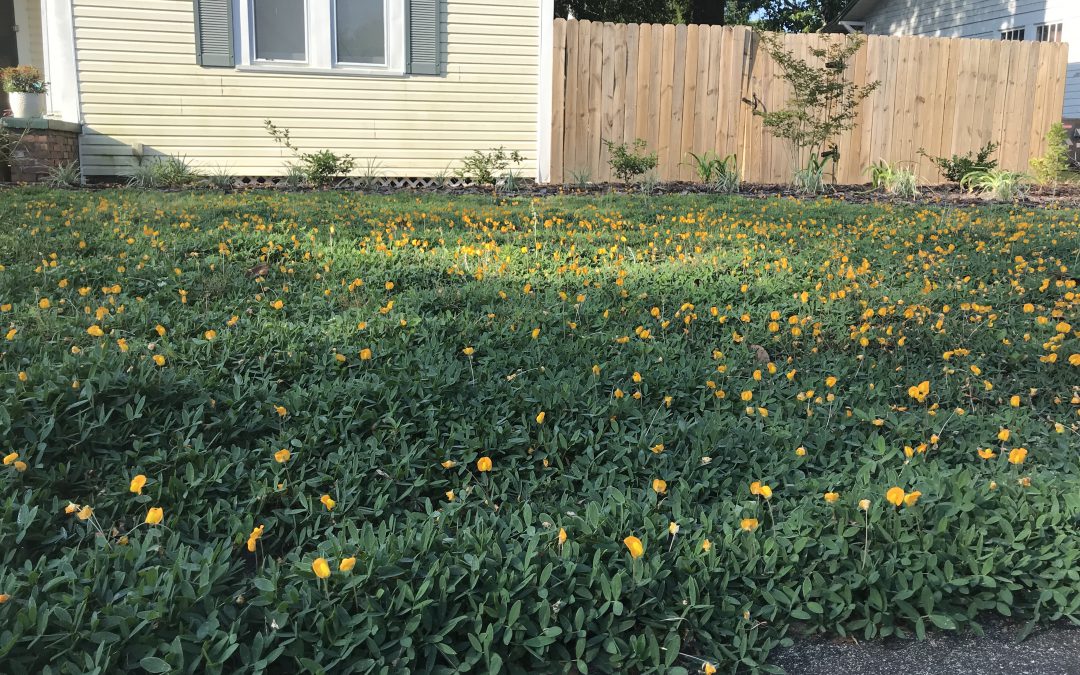
‘Needlepoint’ Perennial Peanut in the author’s lawn.
What began as my journey toward a turf-less lawn in September of 2017 is finally beginning to come together! In the fall of 2017, I installed about 120 one-gallon-sized ‘Needlepoint’ Perennial Peanut (Arachis glabrata) plants, purchased from Sunset Specialty Groundcovers in Live Oak, FL, on roughly 20” centers in my front lawn, an oddly shaped (650 ft2) patch of ground that had been previously filled with spotty centipedegrass and a healthy and diverse weed population. 18 months later, the peanut has almost completely filled in, shaded out all the weeds, and blooms nonstop!
Looking back, I definitely learned a few lessons the hard way. First, you should mulch bare ground in between plants at time of installation. Because there are few herbicides labelled for residential use on this crop and I didn’t want to experiment on my new “lawn”, I spent a lot of time on my hands and knees (much to the amusement of my neighbors and folks driving by) pulling weeds in the first two years that could have been prevented with mulch. Second, have a plan for keeping the perennial peanut in bounds once it has filled in the area it was supposed to and begins to travel into adjacent landscaped beds! The area my peanut inhabits is surrounded on two sides by inescapable concrete. It was on the other two sides, however, that I have had to improvise after they came under siege (literally under, because perennial peanut spreads by underground rhizomes). Installing some sort of edge blocker at planting and vigilance with routine mechanical edging is a must to keep it in bounds! Third, I recommend that you have a counter-argument prepared when the peanut goes dormant in the winter and your wife asks why the yard is bare dirt!

‘Needlepoint’ Perennial Peanut overhead shot showing complete ground coverage in the author’s lawn.
Overall, though there are a couple of things I would have done differently, I’m extremely pleased with my lawn of perennial peanut. It is absolutely stunning in the warm months, incredibly low maintenance, and unique! Plant some today!
As always, if you have any questions about perennial peanut or any other plant/crop, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension office.

 Common lespedeza, also known as Japanese clover, is prostrate summer annual that forms 15-18 inch patches. The stems are wiry. It has dark green trifoliate
Common lespedeza, also known as Japanese clover, is prostrate summer annual that forms 15-18 inch patches. The stems are wiry. It has dark green trifoliate  (arranged in threes) leaves with three oblong, smooth leaflets. Leaflets have parallel veins nearly at right angles to a prominent mid-vein. Its leaves have smooth edges and a short spur at the tip of each leaflet. Flowers appear in late summer with small pink to purple, single flowers found in leaf axils on most of the nodes of the main stems. As common lespedeza matures, the stems harden and become woody.
(arranged in threes) leaves with three oblong, smooth leaflets. Leaflets have parallel veins nearly at right angles to a prominent mid-vein. Its leaves have smooth edges and a short spur at the tip of each leaflet. Flowers appear in late summer with small pink to purple, single flowers found in leaf axils on most of the nodes of the main stems. As common lespedeza matures, the stems harden and become woody.














