by Ray Bodrey | Jun 29, 2022

A watering tin and gardening gloves at a home garden.
Spending time gardening in the summer months can be difficult, especially in the Florida Panhandle. The brutally high temperatures and sometimes intensive humidity can make gardening seem unbearable. However, for those brave outdoor enthusiasts, there are always things to do around the homestead when it comes to vegetable gardening, landscape shrubs and lawn care.
Warm season vegetable gardening at this point becomes an uphill battle for some crops, with this being peak time for both insect and disease problems to occur. However, if you planted early enough, much of your harvest is probably in the safe zone. Scouting is key to prevent any major pest damage. Be sure to scout several times a week during these hot, summer days.
Shifting gears, the warm season is a good time to take extra special care of plants such as, azaleas and camellias, while they are establishing flower buds for the next bloom. A lack of water, fertilizer and pest detection and prevention can all certainly play a role in the following season’s flower production. Summer annuals always provide quick and easy color. Remember to feed established annuals with a complete fertilizer and remove faded blooms along the way. Water annuals well during hot, dry periods and control major annual pests to insure good production.
Finally, lawn maintenance is a need for many homeowners during this time of year. Almost all highly successful herbicides are no longer recommended at this point, as many will burn the turfgrass at temperatures above 80 degrees Fahrenheit. Depending on the weed pest and type of turfgrass, most likely the best way to control weeds in your lawn is to wait until cooler fall temperature to treat. Keeping good cultural practices this time of year will help in maintaining a healthy lawn and reduce pest pressure. Be sure to water lawns thoroughly when needed by applying one to three quarters of an inch of water weekly, depending on rainfall. Be sure to keep in mind mower height/frequency, as this is critical in keeping your lawn healthy. As stated in the “Mowing Your Florida Lawn” UF/IFAS EDIS publication, mow often enough so that no more than 1/3 of the blade height is removed per mowing. For example, if your St. Augustinegrass lawn is mowed at a height of 4 inches, it should be mowed before it grows to a height above 6 inches. It is important to always leave as much leaf surface as possible so that photosynthesis can occur, particularly in a grass that is subject to environmental or site stresses.
Unfortunately, it is chinch bug time again. Chinch bugs are prone to feed on St. Augustine lawns during hot, dry weather and may cause serious damage if not controlled. Damage usually occurs as a patch with a brown, dead center and yellowish margin. It seems chinch bugs get the blame, and often unjustly, for everything. Consult with your local county extension office to be sure the damage is not due to other reasons.
For more information, please contact your local county extension office.
Supporting information for this article can be found in the UF/IFAS EDIS publications/websites below:
Florida Vegetable Gardening Guide: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/VH021
North Florida Gardening Calendar: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/ep451#SECTION_7
Lawn Maintenance: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/entity/topic/lawn_care
Mowing Your Florida Lawn: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/LH028
UF/IFAS Extension is an Equal Opportunity Institution.

by Donna Arnold | Jun 9, 2022

Photo credit Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS
The unwanted guest- Flea beetle
Having trouble with flea beetles? Tired of them showing up unannounced? Do not be alarmed here are a few tips to get rid of the unwanted guest in your garden.
Description: Flea beetles vary in appearance, where colors range from black to tan, with other, brighter colors mixed. They may also have a solid, striped, or spotted pattern depending on the species. Beetles are tiny with large hind legs which allow them to jump like fleas when disturbed.
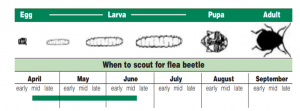
Lifecycle: These unwanted guests will overwinter as adults in the soil or beneath plant debris and become active in early spring when temperatures reach 50°F, and begin feeding on weeds or early-planted crops. Eggs are laid by adult flea beetles normally around May in the soil or at the base of host plants. After 7-14 days eggs will hatch and larvae will feed and develop on various plant parts. They pupate in the soil for 11-13 days before emerging as adults.
Host plants: Some species attack a wide range of plants, while others target only certain plant families. (Table 1). In the garden, several vegetable crops are eaten by these pests, particularly those in the Brassica family.
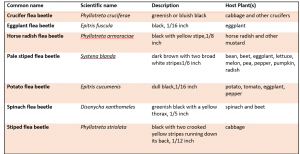
Table 1: Common flea beetles and host plants.
Scouting: Adult flea beetles are particularly active on warm, sunny days. To identify damages, scout every 1-2 days in newly planted fields, since it is easier to identify the damages than to see the beetles themselves. Flea beetle populations can be monitored with yellow sticky traps.
Damage: Adult beetles feed on foliage, producing shot holes in the leaves, especially new leaves which will have a lacy appearance. Additionally, in leafy crops like lettuce or spinach, the holes can reduce the quality of the leaves.

Photo Credits: Jeffery Hahn University of Minnesota

Photo Credit : Jeffery Hahn University of Minnesota.
Management / Control strategies:
- In the spring delay transplanting or planting by a couple weeks if possible.
- In the fall, till the garden to uncover any hiding flea beetles.
- Plant “push” or repellant crops such as catnip, sage, mint, hyssop, nasturtium, and basil.
- Use a “trap crop” such as radishes, taking the pest’ focus off more valuable plants.
- Dusting leaves with plain talcum powder repels flea beetles on tomatoes, potatoes, peppers, and other plants.
- Insecticides may be used early in the season.
- Water deters adult flea beetles. Any watering should be done in mid-day.
- Planting after adults have emerged or crop rotation can help minimize flea beetle damage.
- Apply commercially available nematodes that feed on flea beetle eggs, larvae, and pupae.
Supporting information for this article can be found in the UF/IFAS EDIS publications EENY-721/IN1238: Flea Beetles of the Genus Altica: Altica spp. (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelid) (ufl.edu); https://entnemdept.ufl.edu/creatures/ORN/BEETLES/flea_beetle.html and https://extension.uga.edu/content/dam/extension/programs-and-services/integrated-pest-management/documents/insect-pdfs/fleabeetles.pdf

by Larry Williams | Jun 9, 2022

Deer fly trap. Photo credit: Russ Mizell
Recently, I’ve been asked about a deer fly trapping method that I wrote about a number of years ago. So, here it is. This aggravating insect is active now.
Deer flies, which are in the horsefly family, are annoying as they repeatedly and persistently dive for their victims until they inflict a painful bite.
Dr. Russ Mizell, now retired UF/IFAS Extension entomologist, experimented with a method to trap this insect. Mizell wanted to identify the optimum shape, size, color and speed to attract deer flies. If successful, he could temporarily remove a deer fly population long enough to enjoy an outdoor gathering without being bothered by deer flies.
Mizell said he started the research as a high school science project with his son but “it got so interesting, I just kept doing it.”
Deer flies wait for prey to walk before attacking. So, they are highly attracted to movement.
With this in mind, Mizell and his son decided the best way to snare deer flies was to “troll” for them from a slow-moving vehicle. Working in spring and summer when deer flies are most prominent, they set out to discover what kind of trap worked best.
They built a test platform on the hood of their vehicle that could troll seven different shapes at once. They ambled along in deer fly-infested countryside for set periods of one to five minutes, testing pyramids, squares, balloons, plant containers and other shapes, all coated with Tanglefoot (commercially available sticky spray for insects), then counting immobilized prey. They tried black, tan, blue and shapes of other colors suspended from various heights.
The trap that enticed the most deer flies proved to be a 6-inch flowerpot painted bright blue and coated with Tanglefoot. This trap captured as many as 30 deer flies in a one-minute test. It worked best when suspended three to six feet above the ground and trolled no faster than 10 feet per second or about 7 miles per hour.
The traps are remarkably effective, Mizell said. “Many times, after running the traps through an area, we found there were no deer flies left,” he said. “You trap them out for a short period until they repopulate the area.”
The traps also work when attached to a baseball cap and trolled by the hat’s wearer. But instead of attaching a flowerpot to your cap, you could attach a blue drink cup painted with Tanglefoot.
Despite its effectiveness, its aesthetic appeal leaves something to be desired.
For more information including instructions and pictures of how to make a deer fly trap visit the below site. http://entomology.ifas.ufl.edu/pestalert/deerfly.htm

by Danielle S. Williams | May 12, 2022
Mosquitoes are a pesky nuisance we’re all too familiar with, especially as we move into the summer months. Their presence can certainly make being outdoors undesirable. Not only are they a blood-sucking nuisance but they also carry and can transmit many diseases to humans. Mosquito-borne diseases of public health concern in Florida include St. Louis encephalitis, eastern equine encephalitis, West Nile virus encephalitis, dengue, and Zika. While it can be difficult to eliminate mosquito populations completely, there are steps we can all take to protect ourselves and to prevent our landscape from becoming a major breeding ground for mosquitos.

Asian Tiger Mosquito. Photo Credit: James Newman. UF/IFAS Photo.
Source Reduction
One way to keep mosquito populations down is to prevent the landscape from being a breeding ground for them. Many species of mosquitoes require standing water to lay their eggs; therefore, eliminating standing water can help keep populations low. Mosquitoes can develop in a variety of water-holding containers such as flowerpots, birdbaths, pet dishes, tree holes, bamboo trunks, and many others. It is important to:
- Drain water from garbage cans, gutters, buckets, coolers, or any other containers where water is collected
- Discard any old tires, bottles, broken appliances, or items not being used that could potentially hold water
- Change water in birdbaths and/or outdoor pet dishes once or twice a week

Mosquito larvae. UF/IFAS File Photo
For areas such as ornamental ponds or water gardens, aeration or stocking them with mosquitofish (Gambusia species) can also help to keep mosquito populations down. The small fish will feed on the mosquito larvae and add movement to the water. They are most effective in small ponds with no other fish present.
For other areas with standing water that cannot be drained, such as rain barrels or ornamental ponds, products containing Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti) are effective in controlling mosquito larvae. Products containing Bti come in the form of granules or “dunks”, which look like miniature donuts. These Bti products are considered a form of biological control as it is a naturally occurring bacteria that is specific to mosquito, blackfly, and fungus gnat larvae. Therefore, Bti products are not harmful to fish, waterfowl, pets or humans when used according to label directions.
Protective Clothing and Repellents
The most effective way to protect yourself from mosquito bites is to avoid infested areas, wear protective clothing, and wear insect repellent when outdoors. There are several repellents that are currently available such as DEET, picaridin, and IR3535, or plant derived chemicals such as citronella and oil of lemon eucalyptus.
It is important to read the label before applying mosquito repellent and to remember that there are different recommendations for frequency of application for different products. Below is a table comparison of products based upon University of Florida research.
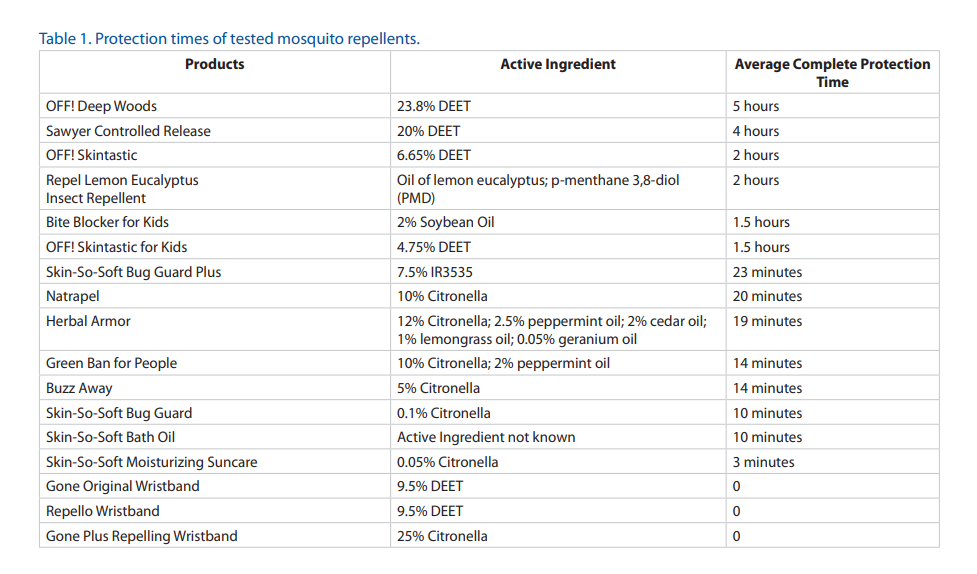
Table from UF/IFAS Publication: Mosquito Repellents
For more in-depth information on selecting mosquito repellents, please visit the UF/IFAS Publication: Mosquito Repellents.
For more information about mosquitos, please visit:

by Joshua Criss | Apr 20, 2022
Getting your landscape set up in the spring is an in-depth process. Trees are pruned, soil amended, and the plantings have been accomplished. Now you have exactly the look you want. It would be easy to sit back, open a beverage of your choice, and watch it all come together. Don’t get comfortable just yet, there is a group of pests eyeing your plants. Insects come in many forms, looking to make a meal from your hard work. Do not fear though, there is a straightforward way to protect yourself from these creatures. Integrated pest management is a system of four control approaches designed to mitigate pest damage while minimizing impact on the environment.
Identification is Key
Before any of these steps may begin pests must be identified. This starts with scouting your landscape via visual inspection. Insects leave signs of their presence wherever they visit. Be sure to inspect every part of your plants including the underside of leaves. Here is where you will find insect eggs or frass (excrement) which are tell-tale signs of activity. Once discovered, you need to identify your specific pest. Insects are identified by their mouth parts when assessing plant damage. Chewing insects remove leaf material (think caterpillars and grasshoppers). Speckled leaves of brown and yellow is a symptom of piercing/sucking insects such as aphids. Other times you may only find damage after the fact where black leaves turn out to be covered in sooty mold. The sooty mold grows on the excreted honeydew of aphids, whiteflies. Once identified, it is up to you to decide if the level of damage is worth it and how you would like to approach limiting the damage.

Sooty mold on Ixora Photo Credits: UF/IFAS Kim Gabel
The First Three
The first strategy is cultural control wherein you optimize the environment in which your plant grows. Improved drainage and removal of plants susceptible to insect attack are excellent examples. You should also look into the lifecycle of insect pests to remove anything that will provide habitat. The next control is mechanical. This methodology is the most work intensive but comes with the least environmental impact as insects will be removed by hand. Biological control is like mechanical control except that removal of the pest is left to natural predators. There are many, but birds and lady beetles are best known. Creating habitat for these will help keep insect populations to an acceptable level with the bonus of falling into Florida friendly landscaping philosophies.
Chemicals are Not the Bad Guy
Chemical control is the final approach. Some may be surprised to find this here, but it is effective. With the above in place, you may find there are still insect issues. Chemicals will be your next step but do not feel put off by this approach. Research the best products for your situation and follow the instructions on the label to the letter. The label is designed to reduce risk to you and the environment while providing effective pest control.
Insect pests have plagued gardeners since the first person intentionally planted anything. Controlling these pests using a multipronged approach is the optimal way to reduce damage to your plants while minimizing environmental impact. Following the methodology in this post will bring a pest free landscape that you and your family will enjoy. For more information on integrated pest management, see these Ask IFAS documents, or contact your local extension agent for additional information on this and any topic regarding your gardens and more.