
by Carrie Stevenson | Nov 19, 2021

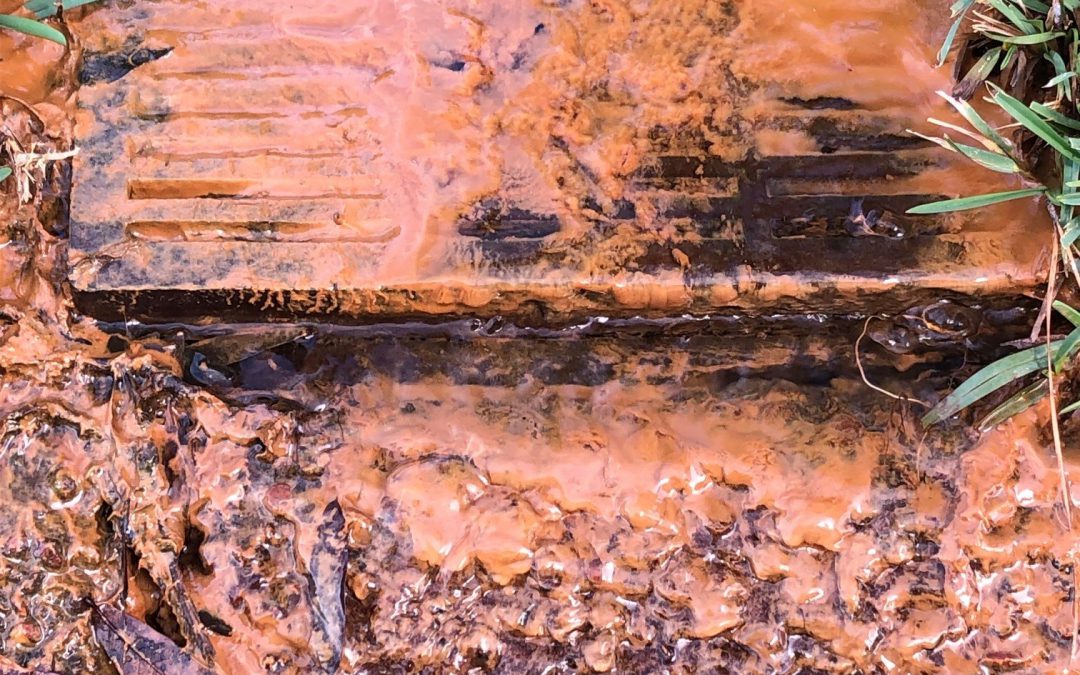
Iron-oxidizing bacteria produces an orange color and oily sheen in the floodplains of Congaree National Park, South Carolina. Used with permission from Karen Jackson, ©2020, Clemson University
“Someone dumped oil in the creek behind my house!” I had dozens of people call with that exclamation when I was a field inspector for the Florida Department of Environmental Protection’s (FDEP) wetlands compliance program. A significant portion of the job entailed responding to concerns and complaints from citizens regarding damage to wetland areas. In the field, I would come across an oily film along creeks in rural, near-pristine conditions in northern Holmes County and in heavily populated neighborhoods in the tourist hot spots of Destin and Panama City. The first time I saw it, I was taken aback. A shiny, rainbow sheen is something you might expect in an oil-soaked parking lot, not a relatively untouched body of water.

The reaction between iron, native bacteria, and oxygen can produce this orange sheen and filamentous material in streams and groundwater (as it exits the soil). Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
Thankfully, an experienced colleague explained the workings of iron-oxidizing bacteria to me, and I was able to allay the fears of all those frantic homeowners. All the places I’ve ever seen evidence of iron bacteria on the water were adjacent to wetlands with some level of iron in the soil. The bacteria essentially “eat” ferrous iron, which is common and able to react with other elements in oxygen-free (anaerobic) environments. Wetlands are classic examples of anaerobic soils, and the mucky conditions of a stream floodplain are ideal for iron bacteria. These are naturally occurring, harmless bacteria that gain energy by breaking down iron available in the soil. In addition to the oily film, side effects of iron-oxidizing bacteria can include a swampy odor, a reddish filament, or red chunks of iron. In large amounts, these byproducts can clog wells if present in pipes. This can be problematic and prevent water flow, but the iron and bacteria are not threats to human health
 A colleague with Escambia County recently responded to a homeowner call about bright orange water flowing out of their front yard. While not the typical creek location, environmental conditions were absolutely suited for this phenomenon. Their neighborhood is situated adjacent to a large wetland area, and several of the homes have French drains in the backyards that drain out to the street. During heavier rainfalls, excess groundwater enters those pipes, picks up iron bacteria in the soil, and exits to the surface along the road. The red-stained curbs are evidence that iron is common in the local soil.
A colleague with Escambia County recently responded to a homeowner call about bright orange water flowing out of their front yard. While not the typical creek location, environmental conditions were absolutely suited for this phenomenon. Their neighborhood is situated adjacent to a large wetland area, and several of the homes have French drains in the backyards that drain out to the street. During heavier rainfalls, excess groundwater enters those pipes, picks up iron bacteria in the soil, and exits to the surface along the road. The red-stained curbs are evidence that iron is common in the local soil.

When touched, the sheen produced by iron bacteria will fracture. This is an easy way to differentiate it from actual oil. Photo credit: City of Kirkland, Washington
While it’s possible someone could dump oil in a backwoods area (and if you do ever see that, report it to FDEP), it is much more likely that you are seeing the natural aftereffects of iron-oxidizing bacteria. To determine the difference between iron bacteria and actual oil, one simple test is to touch the water and its oily film with a stick. If the sheen fractures into small pieces, it’s iron bacteria. If it oozes back to an intact slick (and smells like petroleum), it could very well be oil.

by Molly Jameson | Aug 12, 2021

Article by Rachel Mathes, Horticulture Program Assistant with UF/IFAS Extension Leon County.
By Rachel Mathes
My only brother and his family live in Appleton, Wisconsin. Though I’m only able to see my niece and nephews one or two times a year, we have a deep connection through our love of the outdoors.

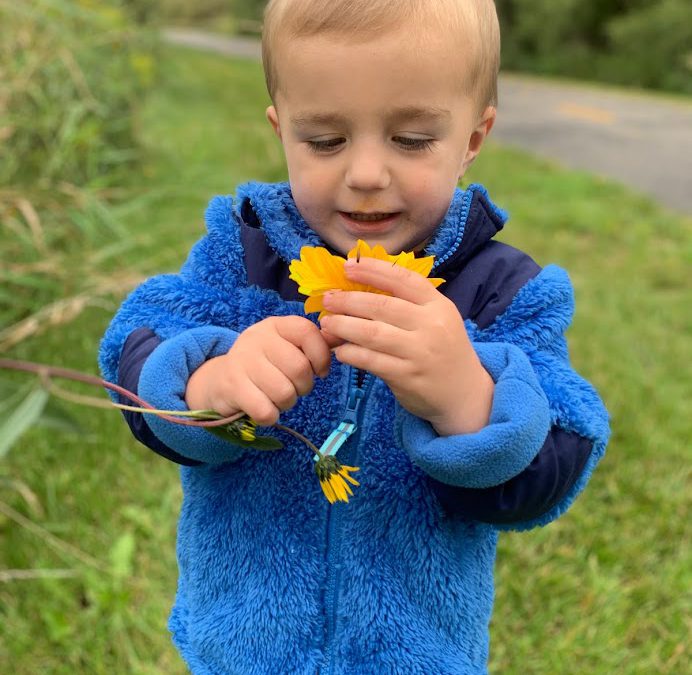
Zach discovering the joy of nature. Photo by Rachel Mathes.
Their middle son, Zachary, is a budding naturalist at just four years old. When I visit them, Zach, his brother Connor, sister Cecilia, and I, load up the wagon and go for walks on the edge of the prairie in their neighborhood. We start our walks looking for scat and signs of wildlife. Because the kids are so close to the ground, they often spot wildlife trails before I do. We talk about what animals may be there, what they eat, and how we can help them.
After each walk, we wind down at home with an iNaturalist session. Zach and his siblings help me choose what animal or plant we think we saw with the help of the app’s nearby suggestions tool. A favorite game we play after all our photos are entered into the app is a game we’ve coined, “where’s that animal?” We use the iNaturalist explore feature to find sightings of exciting creatures like wolves and beavers near their home. The kids have learned that even scientists often don’t see the animals they study, just signs of them.
At age three, Zach learned to identify milkweed with impressive accuracy. I pointed out the plant on a previous trip more than six months earlier and he remembered how to find them. Common milkweed, Asclepias syriaca, is a large leafed species that prefers winters a bit colder than we get here in the Florida Panhandle, but is native in northern states across the Eastern US, including Wisconsin. Zach is often stopping the wagon to scout for monarch caterpillars, finding even the smallest instars and eggs.

Zach learned to identify common milkweed, Asclepias syriaca, at the age of three. Photo by Rachel Mathes.
When I video call the kids from Florida, Zach is often asking to see my fruit trees, vines, and bushes. He knows that we have very different seasons than Wisconsin when I am eating blueberries in May and he’s still knocking frost off his snow boots. In July, he tells me about the raspberries they find in the woods with their dad. We both get a bit of seasonal berry jealousy. On my last trip we planted thornless blackberries in their garden together. It remains to be seen whether the birds will let the kids have a harvest, but the kids will be excited either way.
Though we may live a thousand miles apart, I know my relationship with my niece and nephews will continue to thrive as they explore the natural world around them. One day, I hope to introduce them to the awe of Florida manatees and alligators. Until then, I will relish the time we get to spend together outdoors in nature and on the phone together. I know that Zachary and his siblings will grow up having respect for the natural world and I hope he always exclaims, “Monarch! Look auntie Rachel, a monarch caterpillar!” on our walks together.
Author: Rachel Mathes, Horticulture Program Assistant with UF/IFAS Extension Leon County.

by Carrie Stevenson | Jul 29, 2021

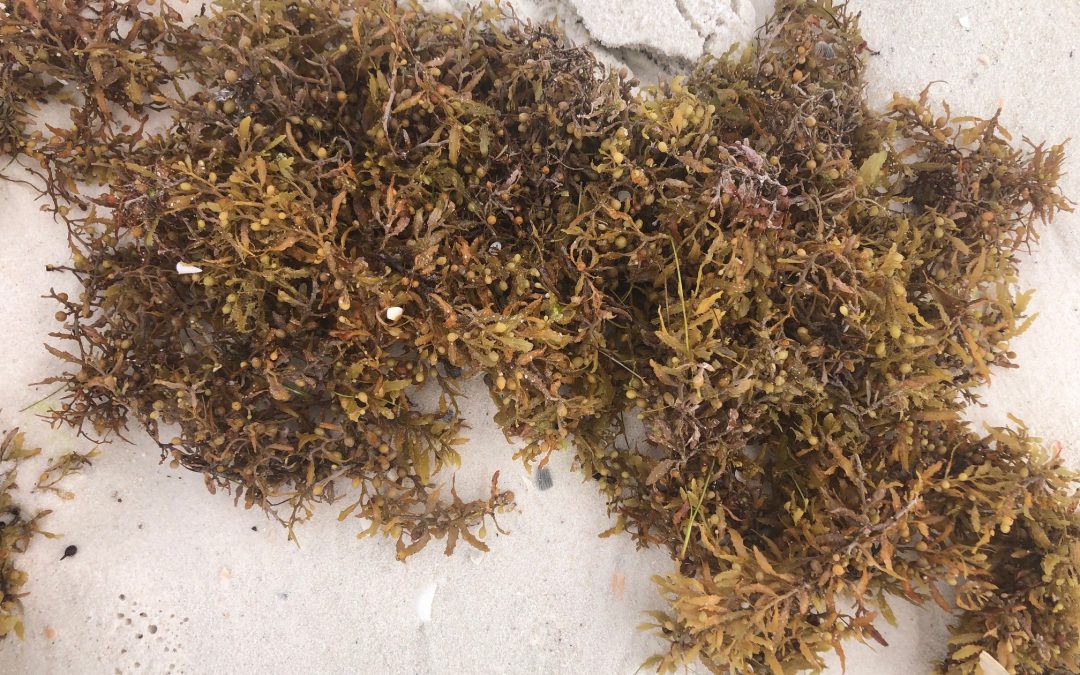
Sargassum washed ashore after a storm on Pensacola Beach. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
I am sure it drives the tourists a little crazy. After daydreaming all year of a week relaxing at the beach, they arrive and find the shores covered in leggy brown seaweed for long stretches. It floats in the shallow water, tickling legs and causing a mild panic—was that a fish? A jellyfish? A shark? Then, of course, high tide washes the seaweed up and strands it at the wrack line, shattering the vision of dreamy white sand beaches.
But for those visitors—and locals—willing to take a closer look, the brown algae known as sargassum is one of the most fascinating organisms in the sea. The next time you are at the beach, pick some up and turn it over in your hands. Sargassum is characterized by its bushy, highly branched stems with numerous leafy blades and berry-like, gas-filled structures. The tiny air sacs serve as flotation devices to keep the algae from sinking. This unique adaptation allows it to fulfill a niche at the top of the water column, instead of growing at the bottom or on another organism.

The sargassum fish blends incredibly well into its home within sargassum mats. It uses handlike pectoral fins to move around. Photo credit: Reef Builders
Sargassum tends to accumulate into large mats that drift through the water in response to wind and currents. These drifting mats create a pelagic habitat that attracts up to 70 species of marine animals. Several of these organisms are adapted specifically to life within the sargassum, reaching full growth at miniature sizes and camouflaged in shape, pattern, and color to blend in. These very specialized fauna include the sargassum crab, the sargassum shrimp, sargassum flatworm, sargassum nudibranch, sargassum anemone, and the sargassum fish! The sargassum fish (Histrio histrio) is in the toadfish family, a group of slow-moving reef fish that pick their way through coral and algae by using their pectoral fins like hands. Sea turtle hatchlings will spend their early years feeding and resting within the relative safety of large mid-ocean sargassum mats.

The small air-filled sacs of sargassum allow it to float on the surface, becoming the basis of a teeming ecosystem. Photo credit: Carrie Stevenson, UF IFAS Extension
Over time the air sacs lose buoyancy and the sargassum sinks, providing an important source of food for bottom-dwelling creatures. If washed ashore, many of the animals abandon the sargassum or risk drying out and dying.
In general, most of the larger, familiar seaweeds like sargassum are brown algae. Brown algae (including kelp and rockweed) have colors ranging from brown to brownish yellow-green. These darker colors result from the brown pigment fucoxanthin, which masks the green color of chlorophyll. Extractions from brown algae are commonly used in lotions and even heartburn medication!

by Sheila Dunning | Jul 9, 2021

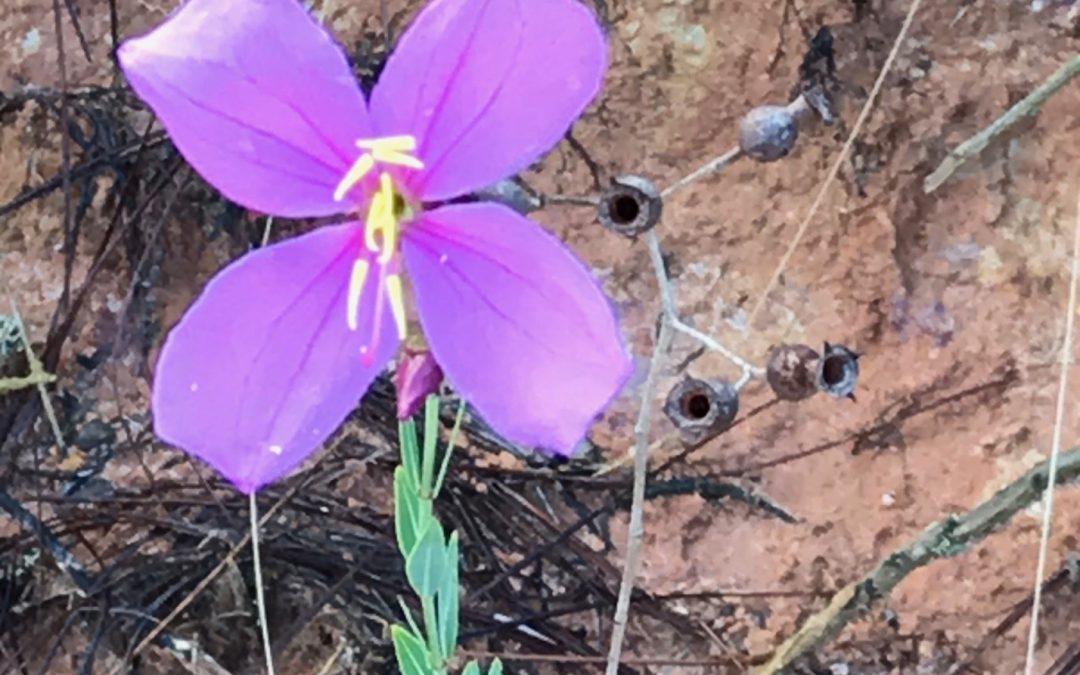
Photo by: Sheila Dunning
Have you noticed the beautiful pink flowers in the meadows near the woods? That’s what many early explorers of Florida may have said, which lead to the common name of Rhexia spp. Meadow beauty (Rhexia spp.) is a Florida native found in mainly moist habitats, including flatwoods, wet meadows, marshes and savannas. Rhexia species are herbaceous perennials that flowers from late spring to fall, going dormant in winter. The simple leaves are simple and oppositely arranged. The flower has four petals, four sepals and eight long, bright orange-yellow stamen with curving anthers on the end. The light pink flowers face outward on a 1-2 feet tall stack, each one measuring about an inch across. The unique shape of the stamen and anthers suggests that the Rhexia species are buzz pollinated.

By Bob Peterson from North Palm Beach, Florida, Planet Earth! – Buzz Pollination (Sonication), CC BY-SA 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38199019
Buzz pollination or sonication is a technique used by some bees to release pollen which is firmly held by the anthers. The anthers of buzz-pollinated plant species are typically tubular, with an opening at only one end, and the pollen inside is smooth-grained and firmly attached. In order to release the pollen, the bees grab onto the flower and move their flight muscles rapidly, causing the flower and anthers to vibrate, dislodging pollen. Honeybees cannot perform buzz pollination. Only about 9% of the flowers in the world are primarily pollinated using buzz pollination. So, meadow beauty is not just pretty, it has a unique connection with native bees.

Photo by: Sheila Dunning
Meadow beauty grows in full sun or partial shade. The plant can reproduce by seeds and underground rhizomes. Rhexia spp. are also a tasty treat for deer as they graze in the meadow. The flowers don’t last long and can’t handle being touched. In Greek, Rhexia means “breaks”. So, enjoy them as you walk through the woods, but leave them for the bees rather than picking them.

by Rick O'Connor | Jul 9, 2021
This is one strange, primitive, dinosaur-looking fish. They have large scutes embedded in their skin that give them an armored look. They are big – reaching 14 feet in length and 800 pounds (though the Gulf sturgeon does not reach the large size of their cousin the Atlantic sturgeon). They resemble sharks with their heterocercal caudal fin and possess long whiskers (barbels) suggesting a benthic mode of feeding.

Sturgeon are large fish. The barbels (whiskers) are for finding prey buried in the sediment. Notice the raised ganoid scales of this ancient creature.
Photo: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
Panhandle residents know them from their impressive leaps as they head upriver for spawning in the spring. The loud splash from one of these leaps can be heard for a long distance and is a concern for boaters who may be zipping up and down one of the local rivers on a jet sky, or even a bass boat. When in college, we asked one of the professors – “why do mullet jump?”. He paused for a second and responded – “for the same reason manta rays jump”. There was another longer pause. Understanding what was going on we took the bait and asked – “okay… why do manta rays jump?” – “we don’t know”. However, that was in 1980 and a lot has been learned since. We know that not only do mullet and mantas leap, but baleen whales and sturgeon do as well. It is believed that baleen whales leap to communicate during the breeding season. Since sturgeon breed in panhandle rivers, it is believed that this is the reason they may do so. Scientists have also found it helps adjust their swim bladders with internal gas making them more buoyant in the water.
Like salmon, sturgeon swim up rivers to breed and spawn in the spring. Fertilization is external and the gray-black eggs are laid on the substrate at the bottom. The newborn and adults spend the remaining spring in the rivers, and the adults do not feed at this time. In summer all head for the estuaries where the adults begin feeding with a vengeance. They feed on a variety of benthic invertebrates and prefer sections of the bay that are well oxygenated. Sturgeon spend the summer and much of the fall in the bays until the temperatures begins to drop at which time they head into the open Gulf of Mexico. The spring, they find their breeding rivers and the reproductive cycle begins again. This is a long-lived fish, reaching up to 50 years in age.
As far as the biogeography of this species, it is an interesting one. They have been around for about 200 million years. This was about the time the whole “Pangea” movement was going on – Florida did not look like Florida then. There was an opening between what is now the southeastern United States and the Florida peninsula. The water moving through this was called the Georgia Seaway or the Suwannee Channel. This allowed marine species to easily move from the Atlantic to the Gulf of Mexico. It was believed the current in this seaway was significant enough to keep silt and clays from reaching what would be become peninsula Florida, which was probably a submerged region of islands at the time.
During those times the Atlantic sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus) inhabited this region, using southeast rivers for breeding. About 25 million years ago global land mass changes began a period of ice formation that encouraged sea level to drop and the peninsula portion of Florida was exposed – the Florida people know today. However, this new peninsula isolated populations of sturgeon (and other fish at that time) from reaching each other. As time moved on, different genetic changes occurred in both populations to produce offspring that varied from each other. These external morphological changes were enough to let you know they were different, but genetically they are close enough to still breed. In these situations, they have deemed “subspecies” of each other. The Atlantic sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus) and the Gulf sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi). It is the Gulf sturgeon we find along the panhandle. This process of producing new subspecies and species due to population isolation over time is called speciation.
Another interesting trend is the original range of the Gulf sturgeon was from the Texas/Louisiana border to about Tampa Bay. This suggest that the fish took advantage of numerous rivers for breeding but there was a barrier as you reach the tropics. Whether that barrier was climatic (temperature) biological (food source) or something else I am not sure. With the high concentration of sturgeon in the panhandle you might think they require the alluvial rivers of this region. But sturgeon are as common in tannic rivers, such as the Suwannee and Yellow Rivers, as they are in those alluvial ones, such as the Escambia and Apalachicola.
Today, their range is even smaller. They are now found only in the rivers between Louisiana/Mississippi border to the Suwannee River. This range reduction is probably due to habitat alteration (much of it human induced – such as dams) and overharvesting (the eggs of the sturgeon are used for caviar). Today all species and subspecies of sturgeon are protected by the endangered species act.
Because this is an ancient fish, the biogeographic story of the sturgeon is an interesting one and shows how speciation occurs over time with all life. They are really cool fish and, if you have not seen one leap yet, I hope you get to. It is pretty amazing.
References
Florida’s Geologic History, University of Florida IFAS, https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/UW208.
NOAA Species Directory, Gulf Sturgeon, https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/gulf-sturgeon.
NOAA Species Directory, Atlantic Sturgeon, https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/atlantic-sturgeon.
Sturgeon, Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, https://myfwc.com/conservation/you-conserve/wildlife/sturgeon/#:~:text=When%20the%20ambient%20pressure%20changes,to%20communicate%20with%20other%20sturgeon..

by Laura Tiu | Mar 26, 2021
I am a curious person by nature. When I first moved to the Emerald Coast, I had many questions about the area. For example, why do they call this the Emerald Coast? To help answer my questions, I turned to the Destin History and Fishing Museum in Destin, FL. If you haven’t yet visited the museum, I highly recommend it for locals and visitors alike.
It was easy to see why they call this the Emerald Coast once one lays eyes on the beautiful emerald color water. Other questions weren’t so easily explained. For example, I wanted to know why the pass out of Destin Harbor is called the East Pass, when it is clearly on the west side of Choctawhatchee Bay? In fact, in the early 1900’s, the only outlet from the Bay to the Gulf was about 1.5 miles east of where the current pass resides and was called Old Pass Channel. In 1929, a storm sealed off Old Pass Channel and a heavy dose of spring rain raised Choctawhatchee Bay five feet. The threat of flooding inspired four local fishermen to take matters into their own hands and they dug a small trench across Santa Rosa Island to let the water out of the Bay. By the next morning, the trench had significantly widened into the East Pass we have today, connecting Choctawhatchee Bay to the Gulf of Mexico.
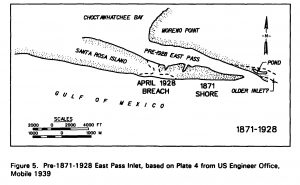
However, that still didn’t explain the East Pass moniker. To explain, we need to look west. Choctawhatchee Bay is connected to Pensacola Bay by the Santa Rosa Sound. This narrow passageway is the space between the Santa Rosa Island, a barrier island, and the mainland. In the early 1900’s, many of the goods and services traded between inhabitants in Okaloosa and Walton counties traveled on ships from Choctawhatchee Bay, through the Santa Rosa Sound, and over to Pensacola Bay, instead of going out into the Gulf. The opening between the Sound and Pensacola Bay is the West Pass, and hence the opening between the Sound and Choctawhatchee Bay is the East Pass. Another mystery solved.
If you are interested in knowing more about the history of this area, the Destin History and Fishing Museum is the place to go.
Citation: Morang, A. . A study of geological and hydraulic processes at East Pass, Destin, FL. Accessed: https://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a253890.pdf
“Foundation for a Gator Nation”



 A colleague with Escambia County recently responded to a homeowner call about bright orange water flowing out of their front yard. While not the typical creek location, environmental conditions were absolutely suited for this phenomenon. Their neighborhood is situated adjacent to a large wetland area, and several of the homes have French drains in the backyards that drain out to the street. During heavier rainfalls, excess groundwater enters those pipes, picks up iron bacteria in the soil, and exits to the surface along the road. The red-stained curbs are evidence that iron is common in the local soil.
A colleague with Escambia County recently responded to a homeowner call about bright orange water flowing out of their front yard. While not the typical creek location, environmental conditions were absolutely suited for this phenomenon. Their neighborhood is situated adjacent to a large wetland area, and several of the homes have French drains in the backyards that drain out to the street. During heavier rainfalls, excess groundwater enters those pipes, picks up iron bacteria in the soil, and exits to the surface along the road. The red-stained curbs are evidence that iron is common in the local soil.

















