
by Matt Lollar | Jun 9, 2022
This article was written by Kacey Aukema, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Walton County.
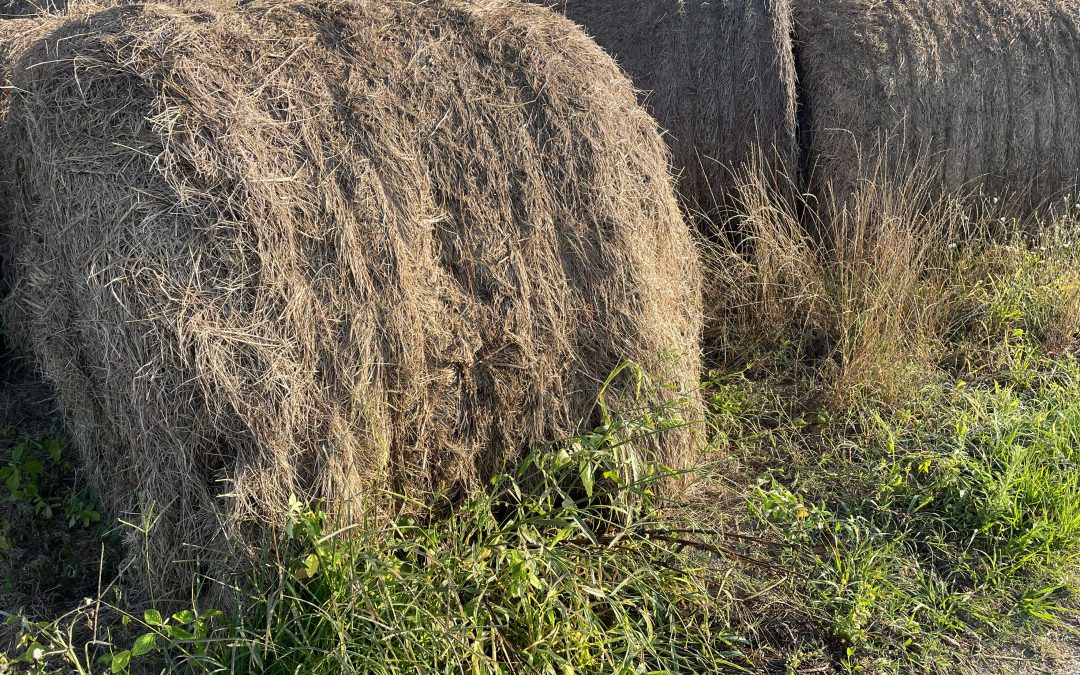
I recently met with a home gardener who brought in tomato plants showing strange symptoms on the leaves. Together we puzzled over the odd leaf-curling symptoms that were affecting their tomato beds, but not other areas of the garden. Upon further investigation it was revealed that hay, used as mulch, had recently been spread around the tomatoes, but not in other areas of the garden. It quickly became apparent that the symptoms were likely related to herbicide residual on the hay that was used. The herbicide aminopyralid was the potential culprit. In this case the residual herbicide was not enough to outright kill the growing tomato plants. However, it was interfering with their growth and development and is a cautionary tale reminding us how important careful sourcing of hay used in mulch or compost can be.
What is aminopyralid and how does residual herbicide affect non-target plants through mulch, compost, etc.?
Aminopyralid is a herbicide active ingredient found in several popular pasture products such as GrazonNext™, Milestone™, Chapparral™ and similar products. This and other similar chemicals have residual activity and can be retained in plant tissues, animal manure, and soil, which makes them a very useful for controlling certain troublesome broadleaf weeds in grass pastures for an extended period of time. Unfortunately, this residual activity increases the potential for causing trouble in vegetables or other crops when hay or animal manure from aminopyralid treated pastures is mistakenly used for mulch, compost, etc. In Florida, aminopyralid containing pasture herbicides are often used as the “go to” for control of hard to control weeds like horsenettle and tropical soda apple which are potentially toxic to livestock. Tomatoes, potatoes, and eggplant are in the same genus (Solanum) as those weeds and are therefore very susceptible to this herbicide as are many other vegetable and other broadleaf crops.

Residual aminopyralid damage on a tomato plant. Photo Credit: Kacey Aukema, University of Florida/IFAS Extension – Walton County
How can I know if hay is safe to be used for mulch or compost?
Before acquiring hay to be used as mulch or to compost for vegetable beds, be sure to ask if the hay is free of herbicides with residual activity. Find out what was sprayed on the field in the last two seasons before the hay was harvested. Given that hay destined to be used as mulch or compost is usually old and spoiled, management history of a particular hay bale is likely to be hard to pin down. Do not trust hay to be used for mulch or compost in vegetable beds if prior spray management details are unknown. Also consider that well-stored hay may retain residual herbicide better and for a longer period of time than weathered hay, as the active ingredient is less subject to weathering and biological breakdown.
Those who use broadleaf herbicide products with residual activity such as those containing aminopyralid are subject to follow herbicide label guidelines. For instance, supplemental labeling of GrazonNext HL™ (including FL, AL, and GA) indicates that hay/straw from fields sprayed in the past 18 months should not be used for compost, mulch, or mushroom spawn. When in doubt refer to the label of the particular herbicide product used on hay you purchase for any restrictions and/or reach out to your local county extension agent if you have questions about a specific herbicide product. Relevant use restrictions and considerations like in this example should be conveyed between hay producer and buyer.
Perhaps you already have some hay for mulch/compost with an unclear management history, or you would like to double-check and be sure that it is safe. How could one test it to see if it was safe to use? There is a test called a “bioassay”, conducted by growing susceptible plant seedlings like tomatoes or beans in small pots with the hay/compost/mulch in question incorporated into the potting soil. Then, the test plants can be observed to see if any herbicide symptoms develop to know whether the material is safe to use, before using the hay over a larger area or garden where there would be more risk. For more information on how to conduct a bioassay see: Herbicide Residues, in Manure, Compost, or Hay. Similar in-field bioassays are also recommended when rotating areas out of pasture and into other crops when pasture herbicides with residual activity were used. If susceptible crops like peanuts are grown in areas where such herbicides were used in the recent past they can be damaged, as in this case in an older Panhandle Agriculture Newsletter post.
When used according to label instructions, herbicides with residual activity are very useful for control of broad-leafed weeds in pasture and hay fields and may reduce the spread weeds through seed coming in on purchased hay. However, problems can emerge when hay from fields treated with these products change hands without the use restrictions and considerations being adequately explained. Therefore, caution should be taken by both producer and buyer to avoid damaging sensitive crops when hay or livestock manure are used for mulch or compost.

by Matthew Orwat | Jun 9, 2022

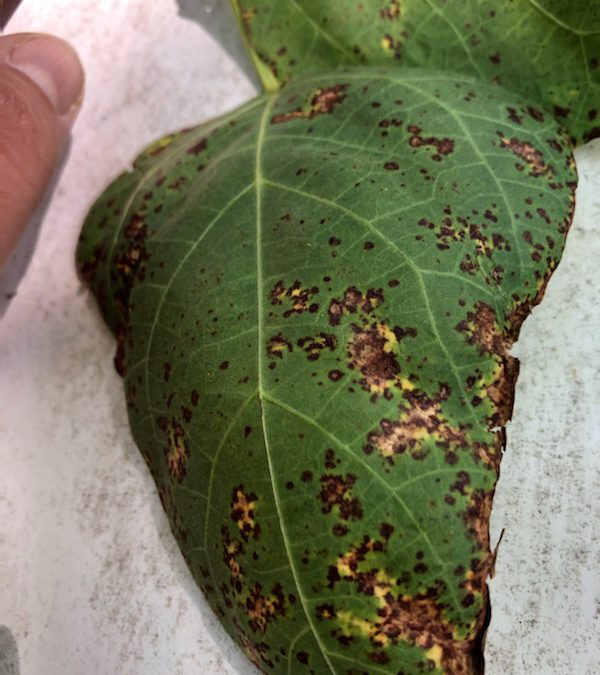
Snap Bean leaf with common bacterial spot – Image Credit Matthew Orwat, UF/IFAS Extension
As snap bean season is winding down and daytime temperatures regularly approach the lower 90s, common bacterial blight is making its presence known. In March or April, when snap bean plants are young and full of fresh growth, vegetable gardeners would never guess that their leafy plants could turn spotty and ugly during harvest time.
That is exactly what happens when daytime temperatures steadily remain in the mid-80s and low-90s, and nighttime temperatures are in the lower 70s. The perfect storm for this bacterial disease occurs when these temperatures combine with afternoon and evening showers, creating sticky, humid nights perfect for the proliferation of the causal agent, Xanthomonas campestris pv. Phaseoli.
Common bacterial blight begins showing up on older leaves first and then slowly spreads to younger growth and pods. If plants are left untreated, disease progression will continue if rainy nights and warm daytime temperatures continue. If weather conditions are consistently dry, daytime temperatures are above 90 and overhead irrigation is limited to mornings or eliminated, the blight will stop progressing to new growth. This disease may also be transmitted by insects.
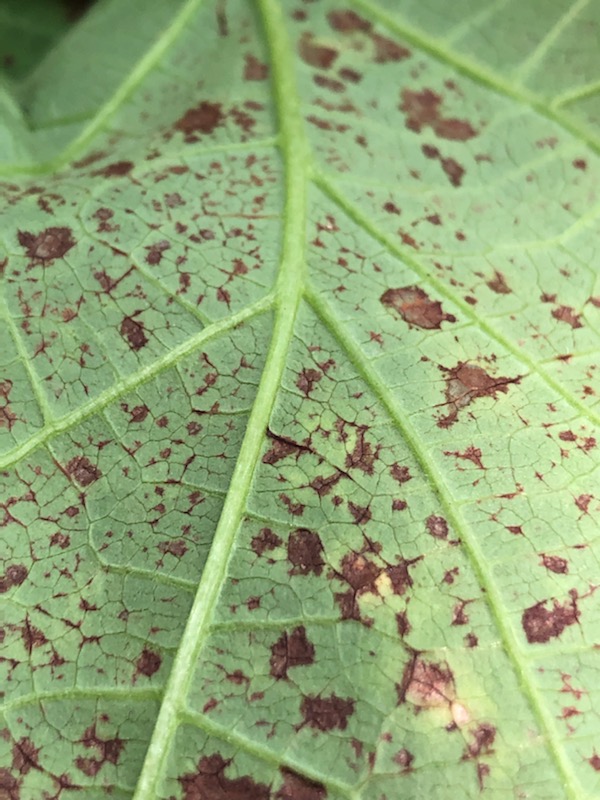

Note the brown, water-soaked spots on the underside of this leaf, typical of a bacterial infection – Image Credit Matthew Orwat, UF/IFAS Extension
If conditions favorable to common bacterial blight exist, preventative sprays of copper fungicide will work to
Snap Bean leaf with common bacterial spot – Closeup – Image Credit Matthew Orwat, UF/IFAS Extension
reduce infection and damage to crop, but there is no product to cure what has already been infected.
One of the best techniques available to manage common bacterial blight in beans is to rotate crops regularly so that legumes are not grown on the same ground year after year. This is easily accomplished in a diverse home garden with different raised beds or garden plots.
To learn more about common bacterial blight of bean follow these links to the NFREC Plant Pathology U-Scout page or read IFAS Extension PUBLICATION #PP-62

by Donna Arnold | Jun 9, 2022

Photo credit Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS
The unwanted guest- Flea beetle
Having trouble with flea beetles? Tired of them showing up unannounced? Do not be alarmed here are a few tips to get rid of the unwanted guest in your garden.
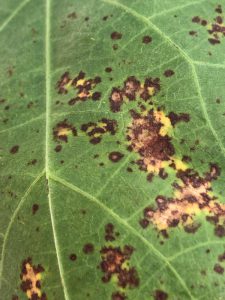
Description: Flea beetles vary in appearance, where colors range from black to tan, with other, brighter colors mixed. They may also have a solid, striped, or spotted pattern depending on the species. Beetles are tiny with large hind legs which allow them to jump like fleas when disturbed.
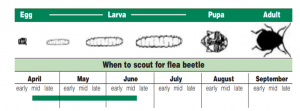
Lifecycle: These unwanted guests will overwinter as adults in the soil or beneath plant debris and become active in early spring when temperatures reach 50°F, and begin feeding on weeds or early-planted crops. Eggs are laid by adult flea beetles normally around May in the soil or at the base of host plants. After 7-14 days eggs will hatch and larvae will feed and develop on various plant parts. They pupate in the soil for 11-13 days before emerging as adults.
Host plants: Some species attack a wide range of plants, while others target only certain plant families. (Table 1). In the garden, several vegetable crops are eaten by these pests, particularly those in the Brassica family.
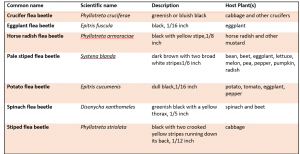
Table 1: Common flea beetles and host plants.
Scouting: Adult flea beetles are particularly active on warm, sunny days. To identify damages, scout every 1-2 days in newly planted fields, since it is easier to identify the damages than to see the beetles themselves. Flea beetle populations can be monitored with yellow sticky traps.
Damage: Adult beetles feed on foliage, producing shot holes in the leaves, especially new leaves which will have a lacy appearance. Additionally, in leafy crops like lettuce or spinach, the holes can reduce the quality of the leaves.

Photo Credits: Jeffery Hahn University of Minnesota

Photo Credit : Jeffery Hahn University of Minnesota.
Management / Control strategies:
- In the spring delay transplanting or planting by a couple weeks if possible.
- In the fall, till the garden to uncover any hiding flea beetles.
- Plant “push” or repellant crops such as catnip, sage, mint, hyssop, nasturtium, and basil.
- Use a “trap crop” such as radishes, taking the pest’ focus off more valuable plants.
- Dusting leaves with plain talcum powder repels flea beetles on tomatoes, potatoes, peppers, and other plants.
- Insecticides may be used early in the season.
- Water deters adult flea beetles. Any watering should be done in mid-day.
- Planting after adults have emerged or crop rotation can help minimize flea beetle damage.
- Apply commercially available nematodes that feed on flea beetle eggs, larvae, and pupae.
Supporting information for this article can be found in the UF/IFAS EDIS publications EENY-721/IN1238: Flea Beetles of the Genus Altica: Altica spp. (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelid) (ufl.edu); https://entnemdept.ufl.edu/creatures/ORN/BEETLES/flea_beetle.html and https://extension.uga.edu/content/dam/extension/programs-and-services/integrated-pest-management/documents/insect-pdfs/fleabeetles.pdf

by Larry Williams | Jun 9, 2022

Deer fly trap. Photo credit: Russ Mizell
Recently, I’ve been asked about a deer fly trapping method that I wrote about a number of years ago. So, here it is. This aggravating insect is active now.
Deer flies, which are in the horsefly family, are annoying as they repeatedly and persistently dive for their victims until they inflict a painful bite.
Dr. Russ Mizell, now retired UF/IFAS Extension entomologist, experimented with a method to trap this insect. Mizell wanted to identify the optimum shape, size, color and speed to attract deer flies. If successful, he could temporarily remove a deer fly population long enough to enjoy an outdoor gathering without being bothered by deer flies.
Mizell said he started the research as a high school science project with his son but “it got so interesting, I just kept doing it.”
Deer flies wait for prey to walk before attacking. So, they are highly attracted to movement.
With this in mind, Mizell and his son decided the best way to snare deer flies was to “troll” for them from a slow-moving vehicle. Working in spring and summer when deer flies are most prominent, they set out to discover what kind of trap worked best.
They built a test platform on the hood of their vehicle that could troll seven different shapes at once. They ambled along in deer fly-infested countryside for set periods of one to five minutes, testing pyramids, squares, balloons, plant containers and other shapes, all coated with Tanglefoot (commercially available sticky spray for insects), then counting immobilized prey. They tried black, tan, blue and shapes of other colors suspended from various heights.
The trap that enticed the most deer flies proved to be a 6-inch flowerpot painted bright blue and coated with Tanglefoot. This trap captured as many as 30 deer flies in a one-minute test. It worked best when suspended three to six feet above the ground and trolled no faster than 10 feet per second or about 7 miles per hour.
The traps are remarkably effective, Mizell said. “Many times, after running the traps through an area, we found there were no deer flies left,” he said. “You trap them out for a short period until they repopulate the area.”
The traps also work when attached to a baseball cap and trolled by the hat’s wearer. But instead of attaching a flowerpot to your cap, you could attach a blue drink cup painted with Tanglefoot.
Despite its effectiveness, its aesthetic appeal leaves something to be desired.
For more information including instructions and pictures of how to make a deer fly trap visit the below site. http://entomology.ifas.ufl.edu/pestalert/deerfly.htm

by Daniel J. Leonard | Jun 2, 2022
The Oracle of Omaha, Warren Buffett, once said “Someone is sitting in the shade today because someone planted a tree long ago.” While that’s all fine and good and I’m happy that the next generation gets to enjoy the things we grew, most of us would like to enjoy shade in our lifetimes too! If you too want to plant your own shade, one of the best rapidly growing shade tree choices for the Panhandle is the majestic Florida native Green Ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica).

Green ash trees have a vase shape form. Photo Credit: University of Florida/IFAS
Green Ash is a large (50-100’ tall), oval-shaped, deciduous shade tree native to the entire eastern half of North America, but best of all for those of us craving shade, it grows to its mature height in a relative hurry. While most trees that grow extremely fast tend to be inherently weak and short-lived, this is not the case with Green Ash. Capable of growing 6-10’ in a single year if irrigated and fertilized appropriately and often living well over 100 years, there aren’t many plants in the Panhandle that grow quicker or live longer.
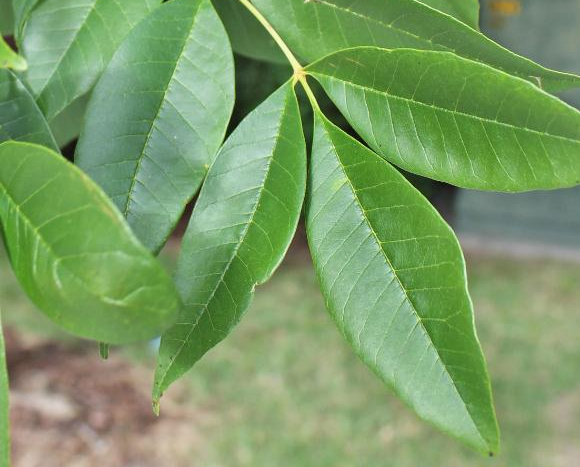
There’s much more to Green Ash than growth rate and life span, however. The tree is also one of the prettiest around. Come on, you didn’t think I’d recommend an ugly plant, did you? A look up into the canopy at different times of the year and one can see the tree’s deep, dark green foliage, good-for-Florida yellowish fall color, and slightly showy light green seed pods. Below, the straight trunk is laced with distinctive diamond-shaped bark that hints at the extremely high-quality wood underneath. Fun fact, Ash is historically the most popular wood used to make baseball bats due to its hardness at a relatively light weight – more MLB home runs have been hit with Ash than any other species!

The compound leaf of a green ash tree. Photo Credit: University of Florida/IFAS
As a Florida-Friendly plant, Green Ash is fairly low-maintenance and provides many environmental services. The species, like any other plant, requires supplemental water and fertilizer during the establishment period, generally the first year or so after planting, but doesn’t demand much else from gardeners after that. Green Ash specimens in Florida also don’t have much in the way of pest problems (the invasive Emerald Ash Borer has devastated ash populations in northern states but thankfully has not yet been found in Florida). However, as a host plant for several native pollinators, including the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail, Mourning Cloak, Orange Sulphur, and Viceroy Butterflies, you may occasionally find caterpillars munching away on the tree’s foliage. If you can handle a little leaf damage, try to leave any caterpillars alone and enjoy the stunning butterflies they later morph into!
Green Ash is a beautiful, ultra-adaptable shade tree. Though the species prefers moist areas, there aren’t many sites the tree can’t thrive in. Do you have a low-lying area near a swamp or stream that stands in water from time to time? Great! Green Ash will thrive. Do you need a street tree to survive in a harsh environment with a cramped root zone surrounded by concrete? Green Ash will be right at home there as well. Green Ash is simply a classic shade tree with many interesting attributes that improves the look of any landscape it occupies. Plant one today!
For more information about Green Ash, other shade tree species, or any other horticultural/agricultural topic, contact us at the UF/IFAS Calhoun County Extension office.

















